Speed & Duplex
Sections:
Overview:
- Speed and Duplex refer to the settings that determine how data is transmitted between two networking devices over a physical network link or cable
- These settings are essential for optimizing network performance to ensure reliable communication between devices
- In this lab example, let's demonstrate the purpose of each setting and configure devices in a lab topology
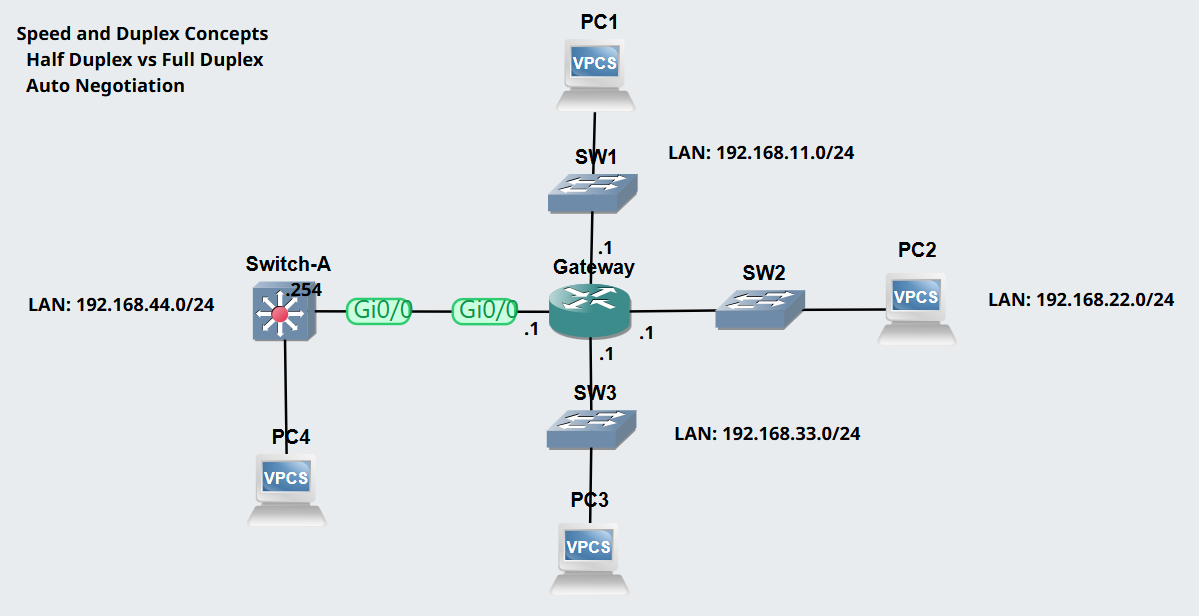
Lab Topology
Speed
Speed determines how fast data can be transmitted over a network interface typically measured in Mbps or Gbps. In IP networking, this setting can either be auto-negotiated by default or manually configured.
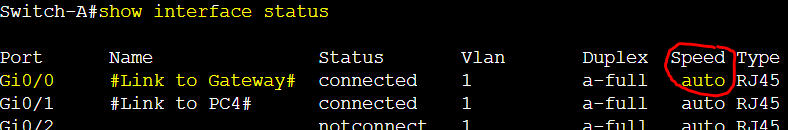
Switch-A to Gateway Speed Configuration
The following switch link is by default set to auto negotiation and results in auto speed.
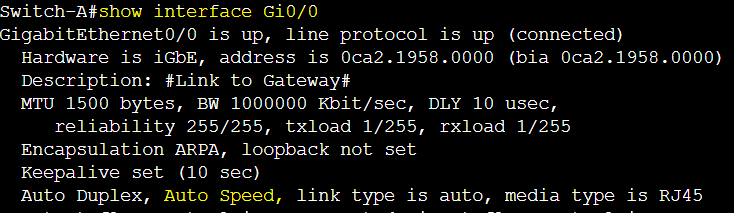
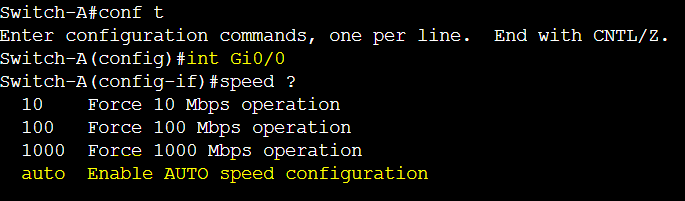
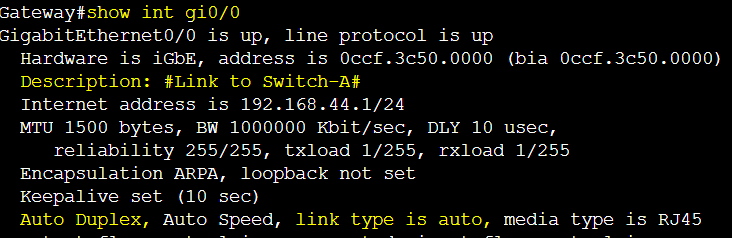
The following gateway link is by default set to auto negotiation and results in auto speed.
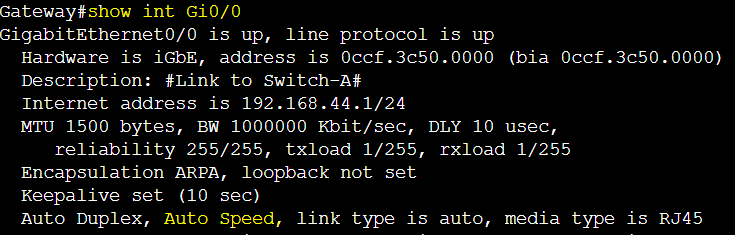
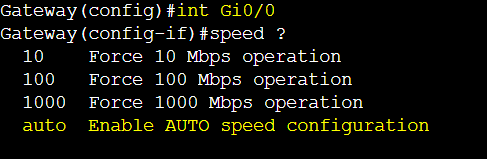
Duplex
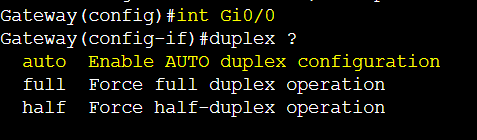
Duplex refers to the direction in which data can flow over a network link. In IP networking, this setting can either be auto-negotiated by default or manually configured to either half-duplex or full-duplex.
Half Duplex
- Not common in today's networks and is only recommended when using legacy layer 1 hub hardware
- Data transmissions flow one way at a time thus a device can either send or receive data, but not both simultaneously
- An example of this scenario involves traditional walkie-talkies as only one person can speak at a time
- Mismatching duplex settings between links can cause collisions causing network performance degregation
Full Duplex
- Data transmissions flow bi-directionally thus a device can send and receive data simultaneously
- Full duplex communications allows for higher throughput, reducing wait times and improving overall performance
Auto Negotiation
- Auto Negotiation is a feature used in networking devices to automatically determine the best possible speed and duplex mode between two devices
Switch-A to Gateway Duplex Configuration
The following switch links were by default set to auto negotiation and results in full duplex mode.
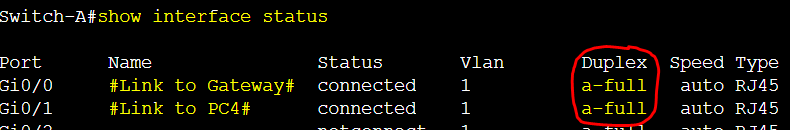
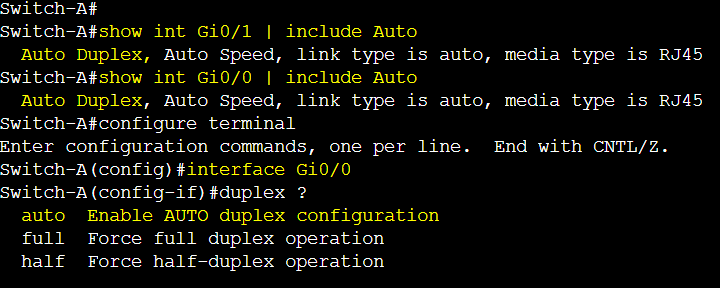
The following gateway link to switch is by default set to auto negotiation and results in full duplex mode.
Mismatched Speed and Duplex
When there is a mismatch in speed or duplex settings between two devices, several issues can arise leading to network inefficiencies. Collisions can occur if one side is manually configured to full-duplex and the other as half-duplex. Collisions cause data to be lost and require retransmissions leading to slower network performance. It is recommended to leave auto negotiation configured by default. There are certain use case scenarios to manually configure these settings, including situations where auto negotiation is experiencing issues due to incompatible hardware, using legacy equipment, or controlling bandwidth and traffic flow for certain systems.