Overview
Sections:
Overview:
- DHCP or the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol is a network protocol used to automatically assign IP addresses and other network configuration parameters to clients on a network
- DHCP uses TCP ports 67 and 68 to communicate between clients and servers
- Port 67: Used by the DHCP server to listen for incoming DHCP requests from clients
- Port 68: Used by DHCP clients to receive responses from DHCP servers
Use Case Scenarios:
- Automatic IP Address Assignment
- Efficient IP Address Management
- Simplified Network Configuration
- Scalability, Flexibility, and Mobility
- Reduces Manual Configuration Errors
- Centralized Management
- Security Features
- Load Balancing and High Availability
DORA DHCP Process
The D.O.R.A acronym in DHCP refers to the DHCP steps used by a client to obtain an IP address and other configuration settings from a DHCP server.
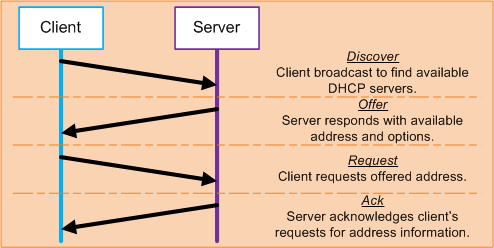
Discover
- Initial process of a client needing to obtain an IP address
- Message is sent to the network as a broadcast 255.255.255.255
- DHCP servers will listen in on incoming Discover packets
Offer
- Stage when a DHCP server receives a Discover packet
- Offer packet is sent via unicast towards the client offering an available IP address
- Offer packet contains the IP/mask, lease duration, and other configuration parameters
Request
- Stage when the client receives an Offer packet from the DHCP server
- The client will accept and choose the first offer packet received and send a Request packet towards the DHCP server via broadcast 255.255.255.255
Acknowledge
- Final stage when the DHCP server receives the Request packet from the client
- The DHCP server sends an Ack packet towards the client confirming the IP address assignment for the client and records the entry in its DHCP database
Cisco DHCP Features
A Cisco Router has the ability to function and run as a full DHCP server implementation that assigns and manages IP addresses from specified address pools to DHCP clients.
Cisco devices can support the following roles and features:
- DHCP Server
- DHCP Client
- DHCP Relay Agent
- DHCP Snooping
- DAI Dynamic ARP Inspection
DHCP Server
Routers and certain layer 3 switches can operate as a DHCP server and maintain a pool of IP addresses to assign to DHCP clients. This feature can be a cost effective option for small office or home office networks with a small amount of clients. While Cisco routers can provide basic DHCP server functionality, they may lack some advanced features offered by dedicated DHCP servers for medium to large sized networks.
DHCP Client
By using a Cisco router or layer 3 switch as a DHCP client, the device will receive its IP address and other network configuration details dynamically from another DHCP server on the network. This case is common for scenarios in which the Cisco device is at the edge of the network connecting to an ISP (Internet Service Provider) however not suited for cases in which you require services like remote access or Site to site VPNs. Static IP address assignments will be better suited for VPN services.
DHCP Relay Agent
A DHCP Relay agent is a feature in which a device forwards DHCP messages between DHCP clients and a DHCP server when they are located on different networks. The relay agent acts as an intermediary, helping DHCP clients obtain IP addresses when the server is not on same local network. Cisco routers and certain layer 3 switch devices are capable of using the relay feature.
DHCP Snooping
DHCP snooping is a security feature that is configured and implemented on Cisco and other vendor switches that helps protect a network from malicious DHCP servers. DHCP Snooping ensures that only authorized DHCP servers are allowed to assign IP addresses to clients.
DAI Dynamic ARP Inspection
DAI often paired with DHCP Snooping, is a security feature configured and implemented on Cisco and other vendor switches to protect against ARP spoofing and poison attacks. DAI ensures that only valid ARP requests and responses are allowed on the network to prevent rogue devices from impersonating authorized devices by sending spoofed ARP messages.