DHCP Snooping
Sections:
- Lab Topology
- Rogue DHCP Effects
- Trusted vs Untrusted Ports
- DHCP Snooping Configuration
- Additional Snooping Features
Overview:
- DHCP Snooping is a security feature that acts as a traffic filter to protect the network from rogue DHCP servers
- By default most client devices such as PCs accept the first DHCP offer message they receive from a DHCP server. Once accepted, clients will ignore any subsequent DHCP offers that it receives which can be a concern if a rogue DHCP server sends the first DHCP offer before the legitimate DHCP server
- DHCP Snooping ensures that only trusted DHCP servers can assign IP addresses on the network
- When enabled, a switch monitors and controls DHCP messages between clients and servers and verifies the validity of DHCP servers by preventing malicious devices from offering incorrect IP addresses
- DHCP Snooping uses the concept of trusted and untrusted ports
- Trusted Port
- Ports where legitimate DHCP servers are connected
- Ports can forward DHCP offer and acknowledgement messages
- Usually configured at the Core of the network or on point to point links
- Untrusted Port
- Ports where DHCP clients are connected
- Ports can only forward DHCP discover messages
- Usually configured on access ports
- Trusted Port
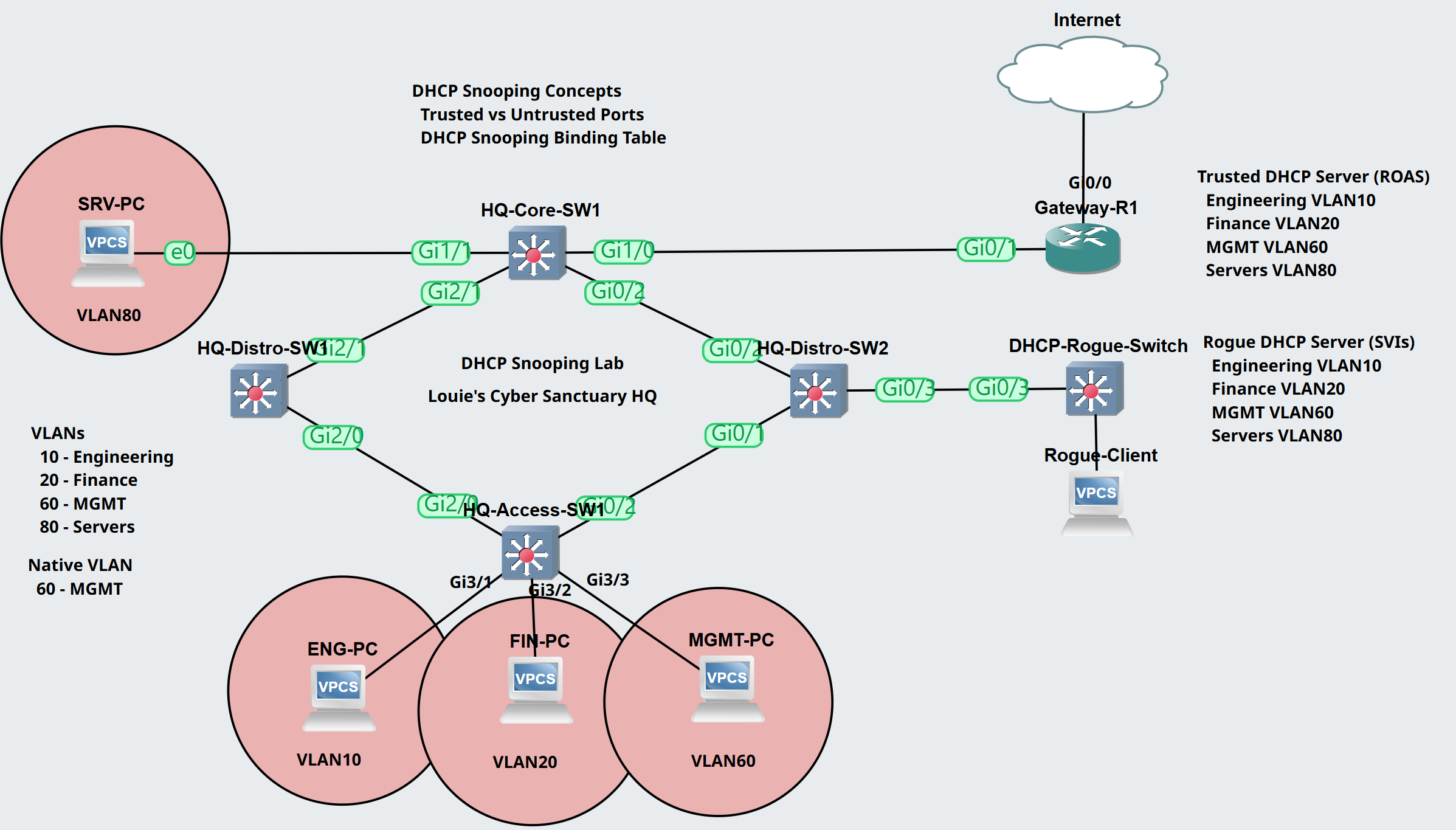
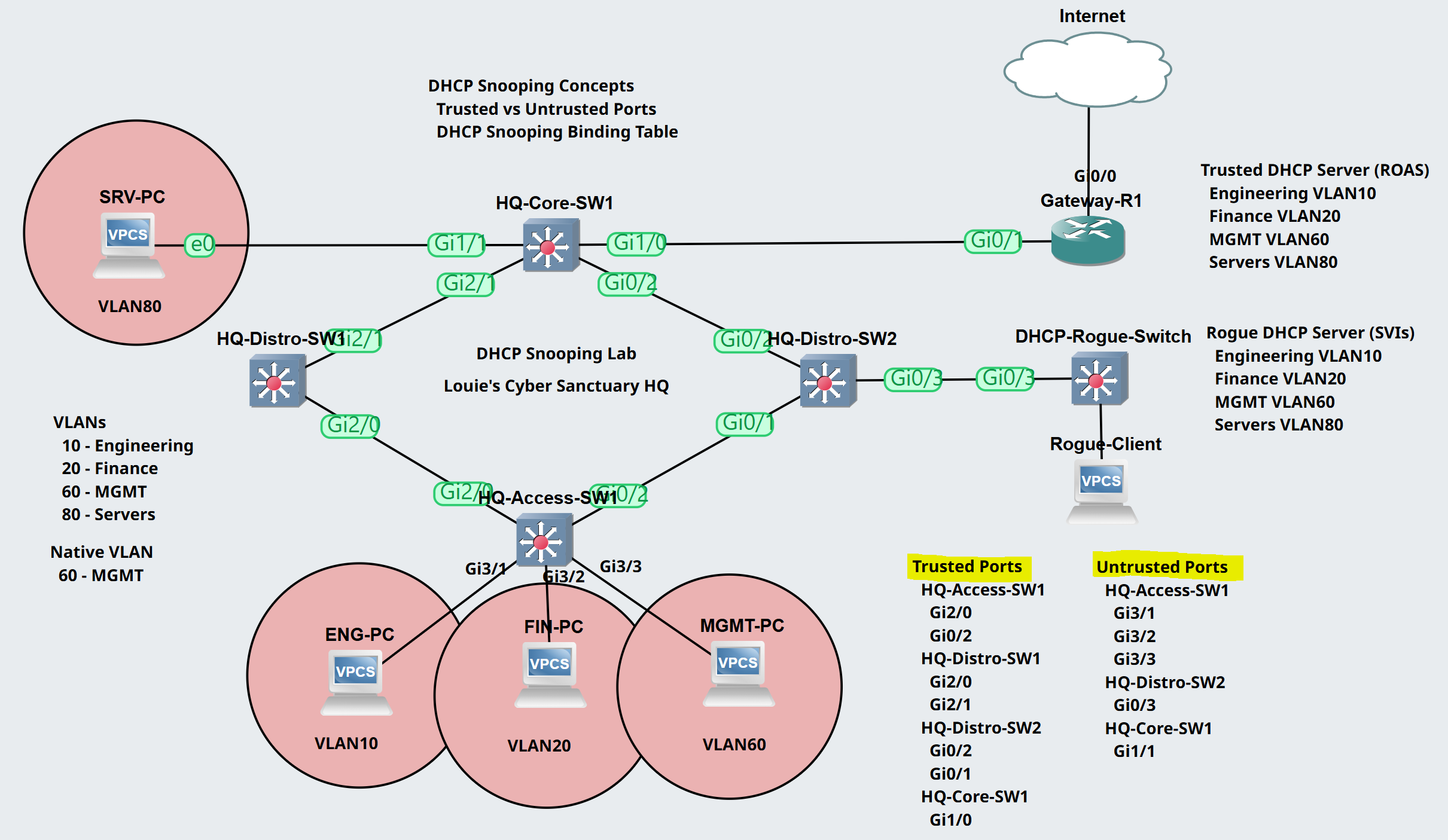
Lab Topology
Scenario:
- In this lab scenario, let's demonstrate a DHCP Snooping configuration in the GNS3 lab environment by defining trusted and untrusted ports of the Cisco switches
- Trunk links, VLAN assignments, and ROAS Inter-VLAN routing have already been configured at the HQ site topology
- In this lab example, I will implement a rogue DHCP switch off of HQ-Distro-SW2 to demonstrate the effects of not implementing DHCP Snooping in the environment
- The rogue DHCP server switch consists of the same DHCP scopes as the Gateway-R1 router
- I will enable DHCP on the PC client from each VLAN and analyze the IP address assignments
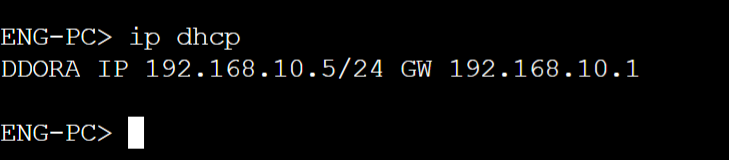
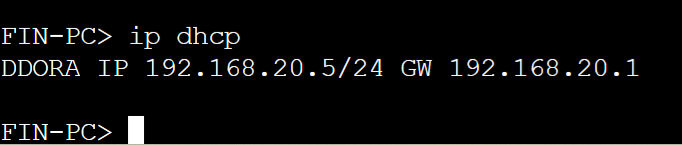
Rogue DHCP Effects
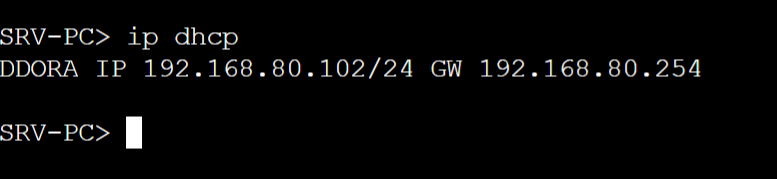
2 out the 4 PCs received an IP address from the rogue DHCP server
- Legitimate DHCP Server
- Address Range: X.X.X.100 - X.X.X.200
- Gateway IP: X.X.X.254
- Rogue DHCP Server
- Address Range: X.X.X.1 - X.X.X.254
- Gateway IP: X.X.X.1
Engineering VLAN10
Finance VLAN20
MGMT VLAN60
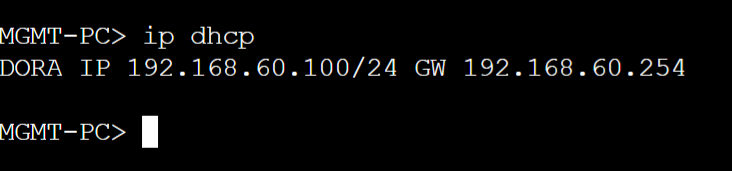
Servers VLAN80
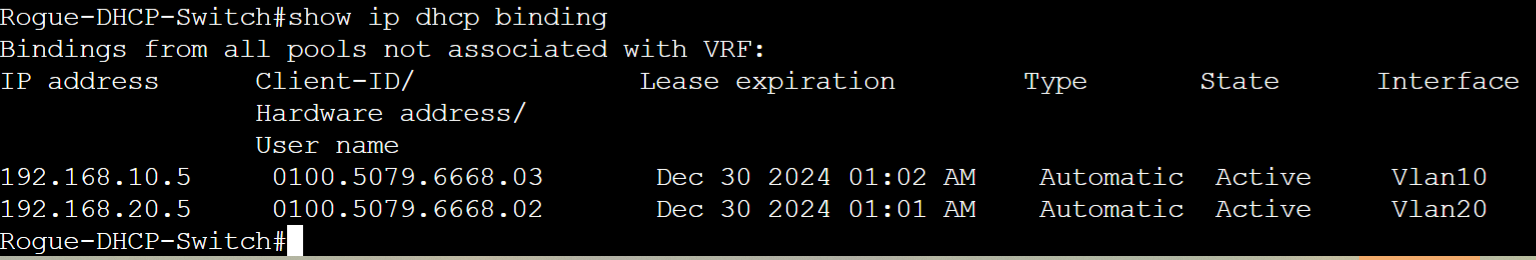
Active leases on rogue DHCP server switch.
Rogue DHCP Server Potential Consequences
- No Network Access
- The rogue DHCP server may assign the client an incorrect subnet mask or gateway IP address, causing the client to be unable to access the rest of the network or the Internet
- Man in the Middle Attacks
- If the rogue DHCP server assigns an incorrect default gateway or DNS server address, all traffic from the affected client device can be routed through the DHCP server allowing the attacker to intercept, monitor, or manipulate the data being sent and received by the client
Trusted vs Untrusted Ports
Overview
- To configure DHCP Snooping, defining the trusted and untrusted ports on the switches is essential
Trusted vs Untrusted Ports
- By default, all Cisco switchports are considered untrusted when DHCP Snooping is enabled
- As a quick summary, untrusted ports are ports that only accept incoming DHCP Discover messages and is most commonly implemented on access ports connecting to clients
- Trusted ports are ports where incoming DHCP offer and acknowledgement messages are allowed, typically implemented on trunk links or point to point links between switches or routers
DHCP Snooping Binding Table
- The binding table contains information about DHCP lease assignments for client devices on the network
- The table is built dynamically after enabling DHCP Snooping and provides the switch a trusted record of which MAC Addresses are associated with which IP addresses, VLANs, and interfaces
- Helps prevent rogue DHCP server attacks
- By associating MAC addresses with IP addresses and interfaces, the binding table helps detect and prevent IP spoofing and Man in the Middle attacks
Information Option 82
- Information option 82 is enabled by default when DHCP snooping is enabled
- Option 82 is used in the DHCP snooping process to insert information about a client's location into the DHCP request message that is forwarded by a DHCP relay agent
- Information option 82 is designed for and only used by DHCP relay agents
- Must be disabled globally if not using a DHCP relay agent
DHCP Snooping Configuration
HQ-Access-SW1
Enable DHCP Snooping globally and on specific VLANs.
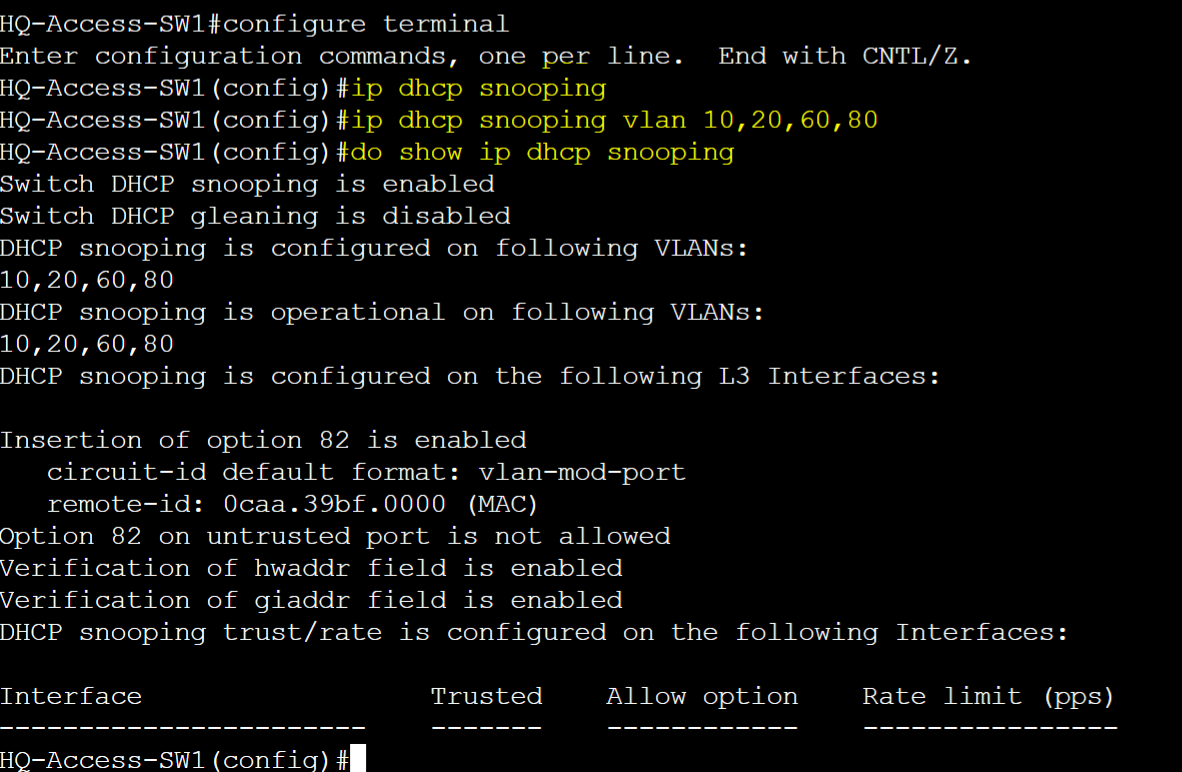
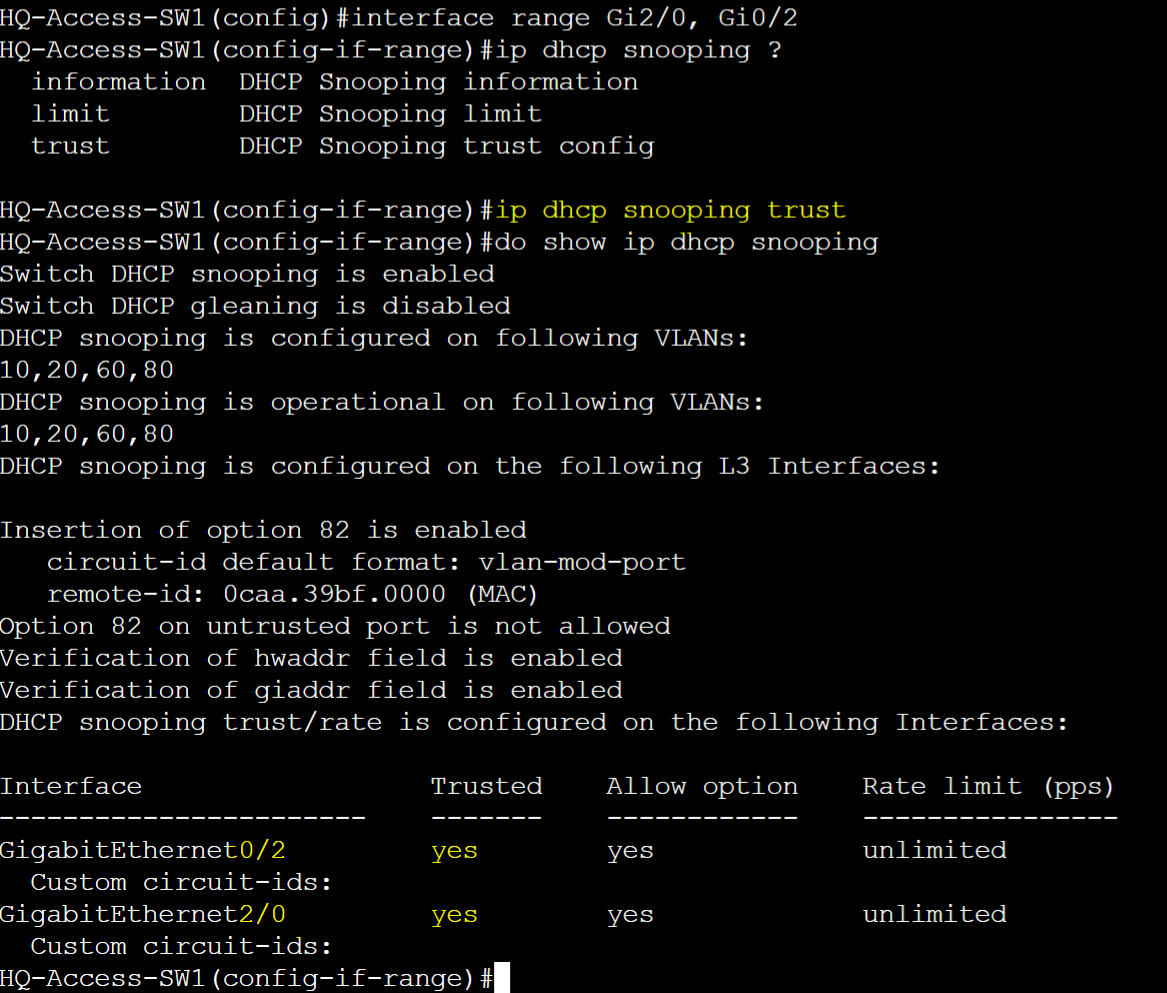
Define trusted ports.
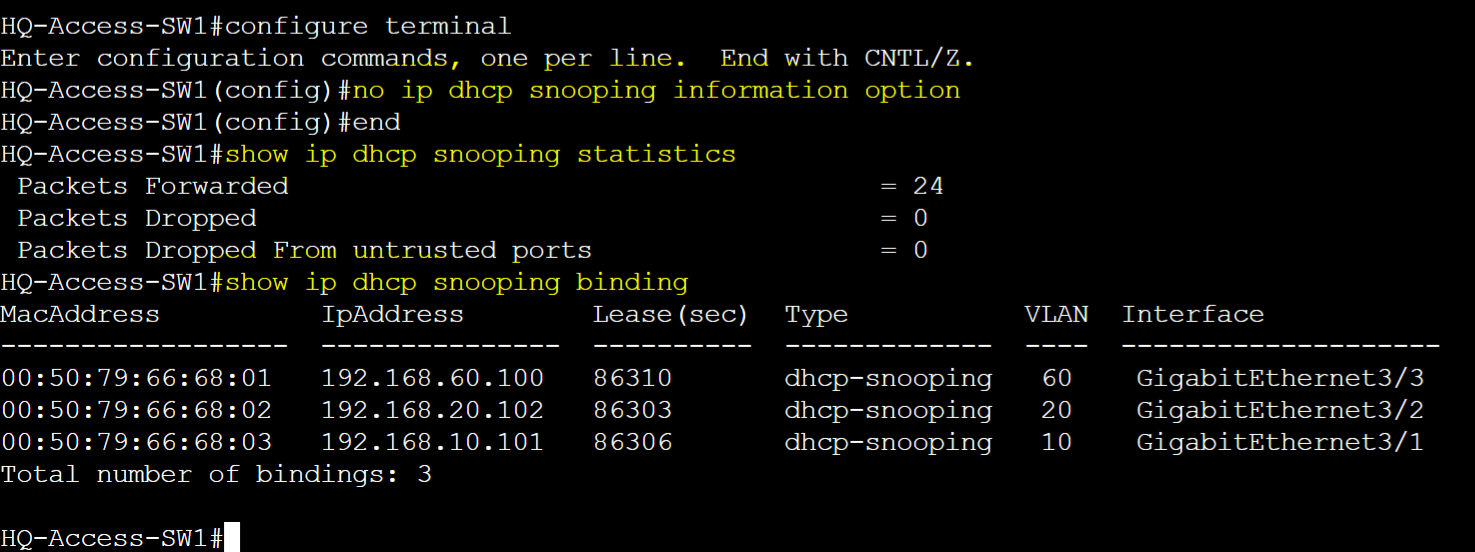
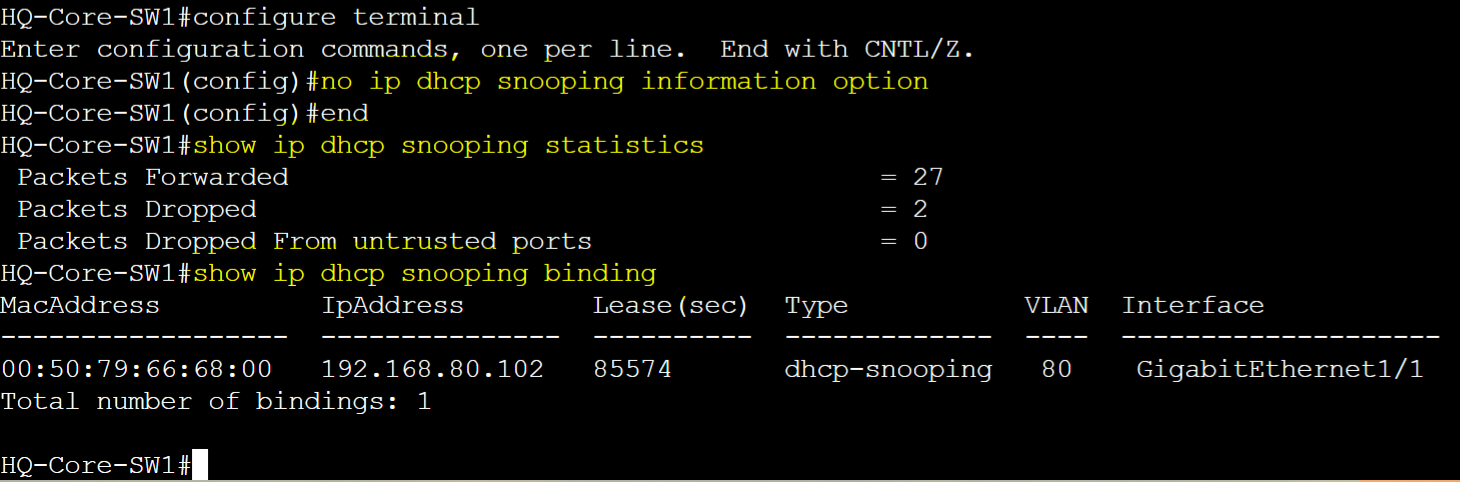
Disable information option 82 and verify DHCP binding table & statistics.
HQ-Distro-SW1
Enable DHCP Snooping globally and for specific VLANs in addition to defining trusted ports.
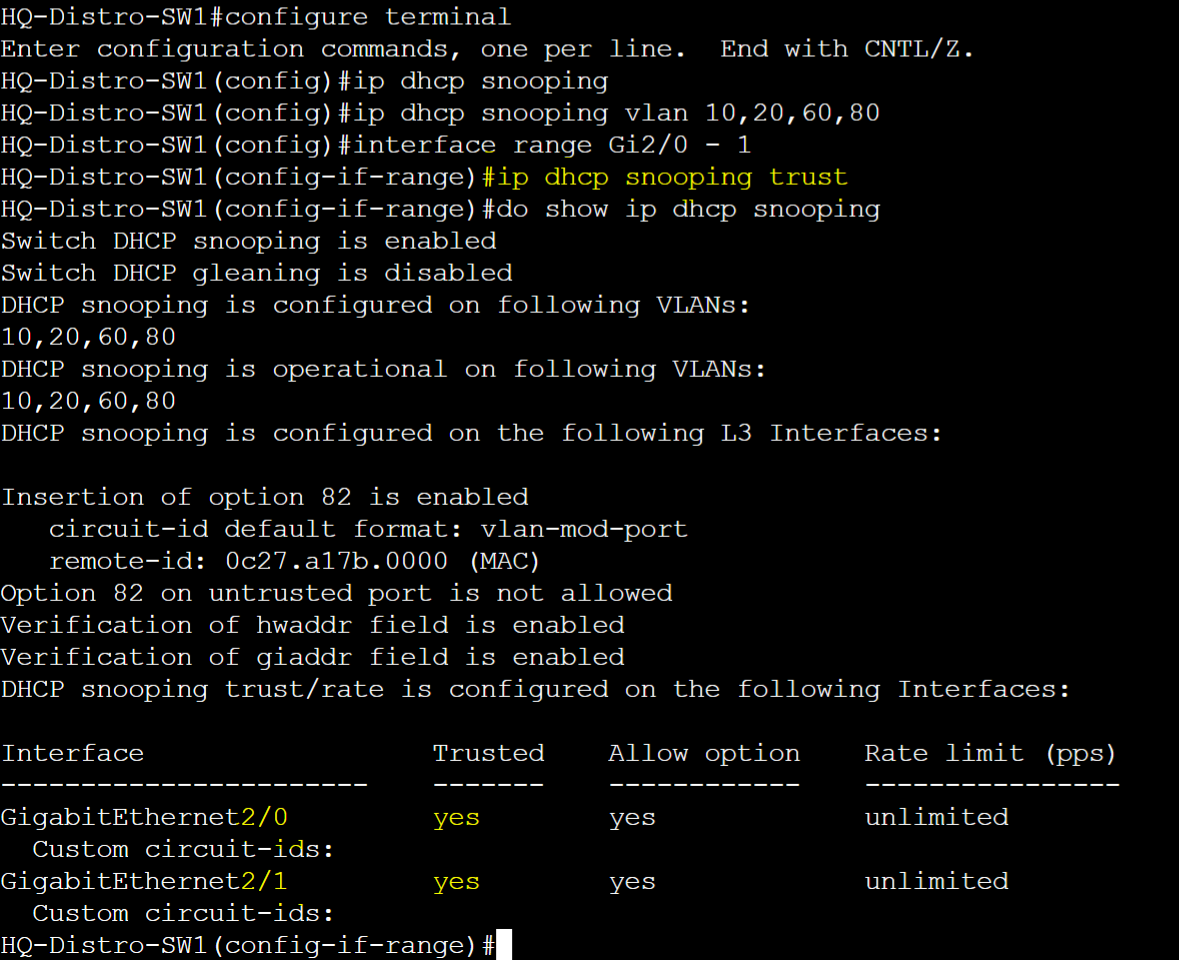
Disable information option 82 and verify DHCP Snooping statistics.
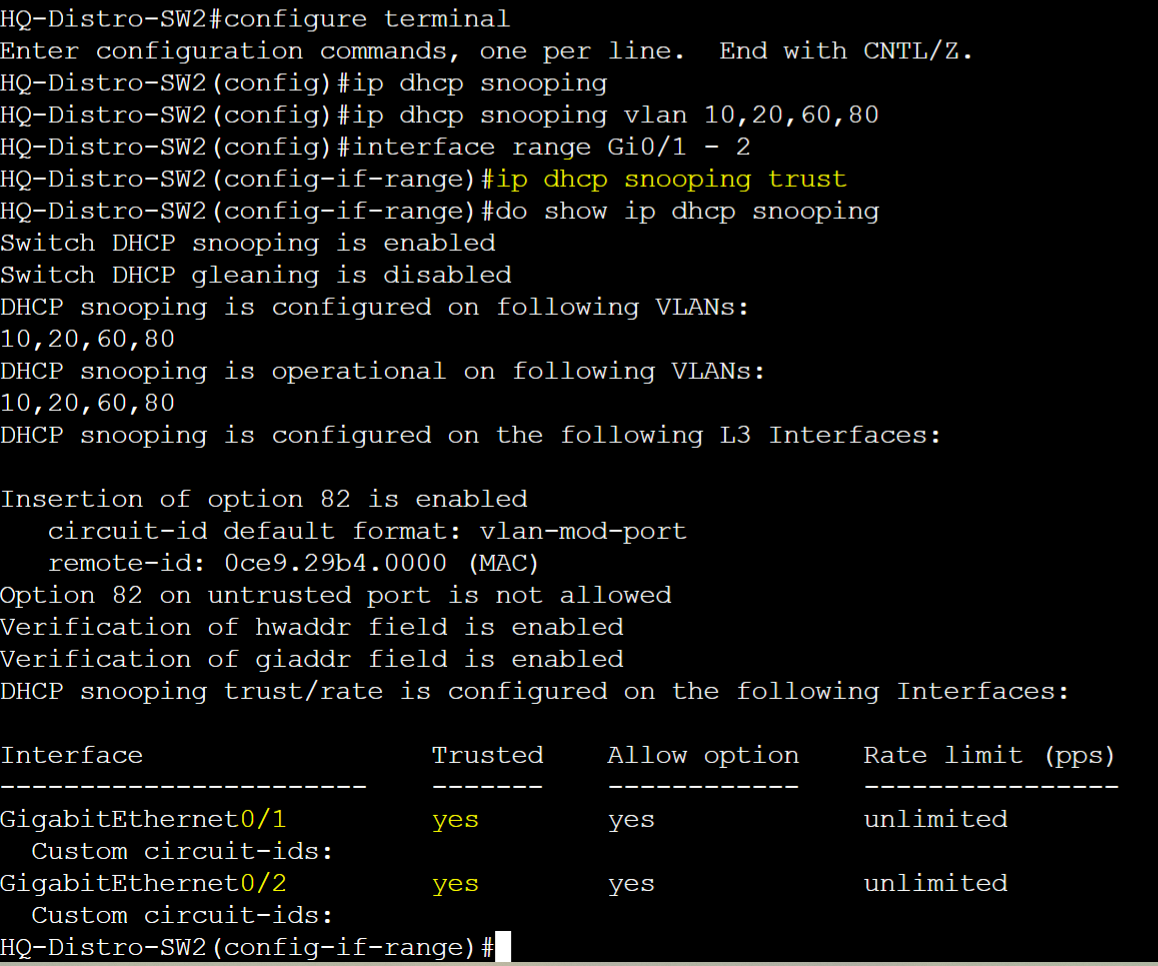
HQ-Distro-SW2
Enable DHCP Snooping globally and for specific VLANs in addition to defining trusted ports.
Disable information option 82 and verify DHCP Snooping statistics.
HQ-Core-SW1
Enable DHCP Snooping globally and for specific VLANs in addition to defining trusted ports.
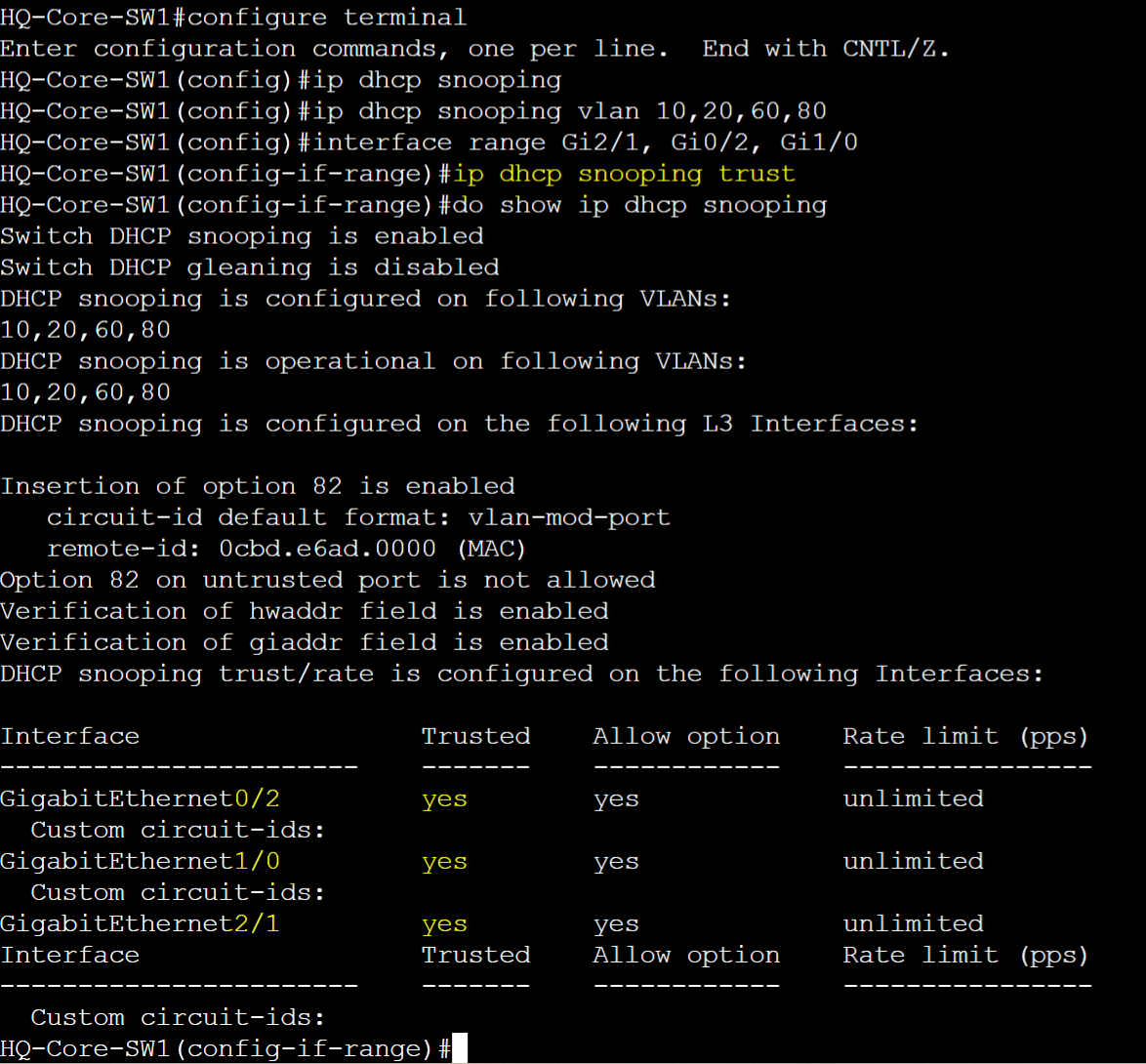
Disable information option 82 and verify DHCP binding table & statistics.
DHCP Snooping Additional Features
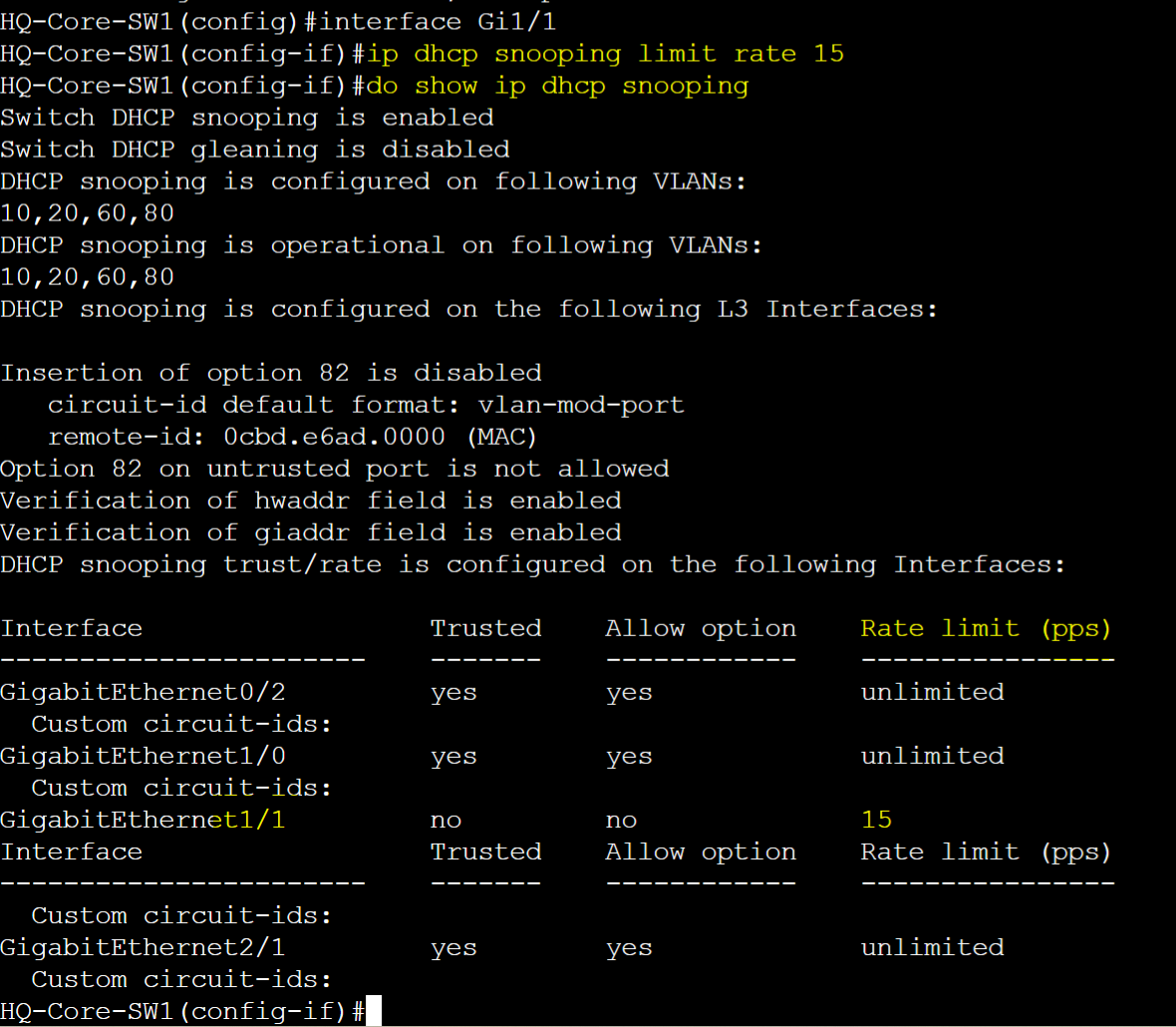
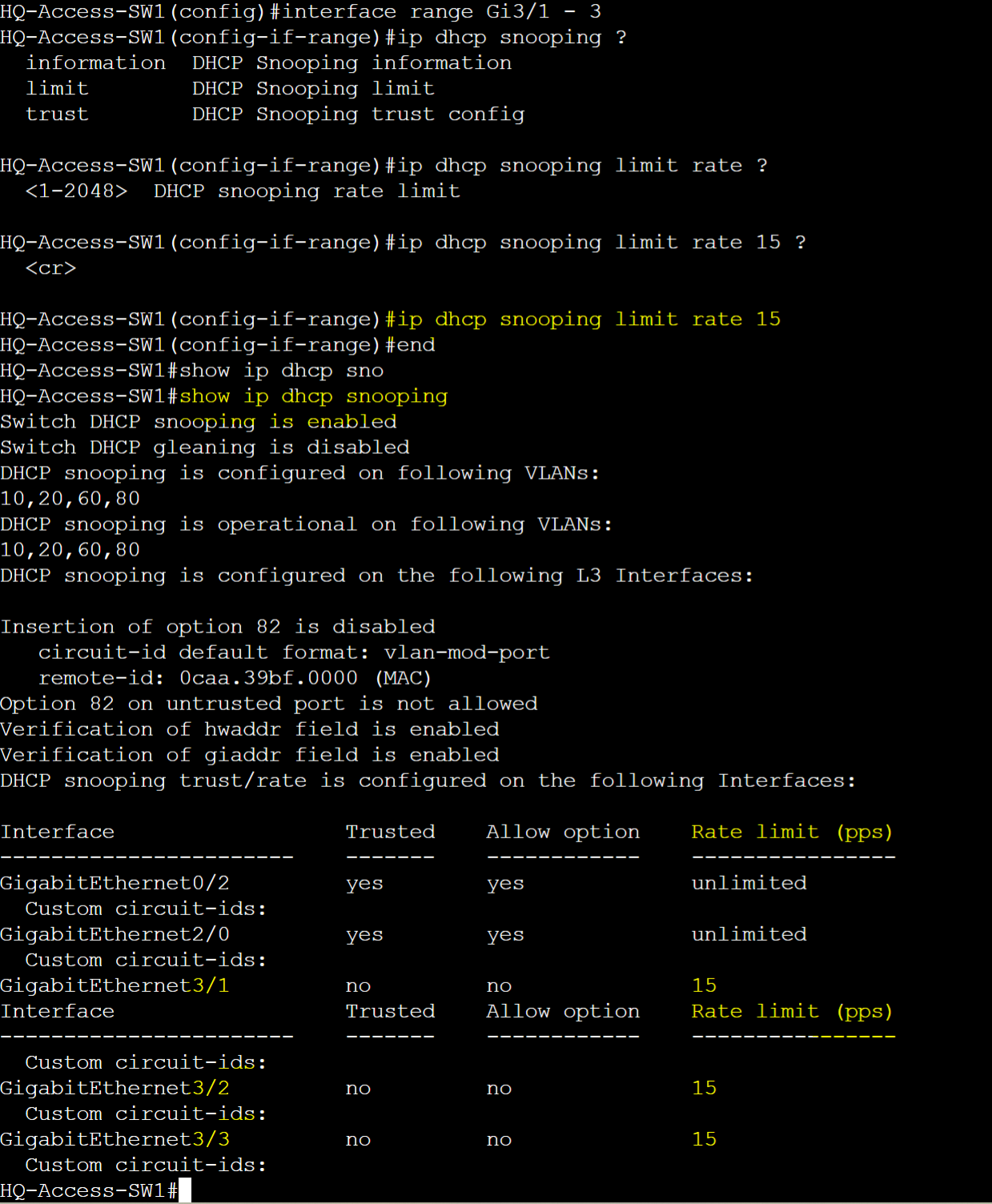
DHCP Snooping Rate Limit
- The Cisco DHCP Snooping Rate Limit is a security feature used to protect a network from DHCP denial of service attacks that involve flooding the network with excessive DHCP request messages
- The rate limit command specifies the number of DHCP requests allowed per second on a given port
- Best practice is to configure rate limiting to around 15 packets per second on access ports / untrusted DHCP Snooping ports connecting to clients
HQ-Access-SW1
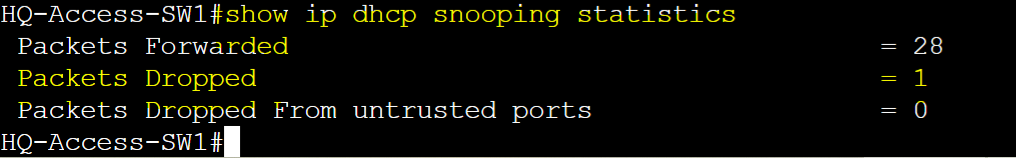
Example of HQ-Access-SW1 dropping DHCP packets when rate limit exceeds.
HQ-Core-SW1