Overview
Sections:
- (HSRP) Hot Standby Router Protocol
- (VRRP) Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
- (GLBP) Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
Overview:
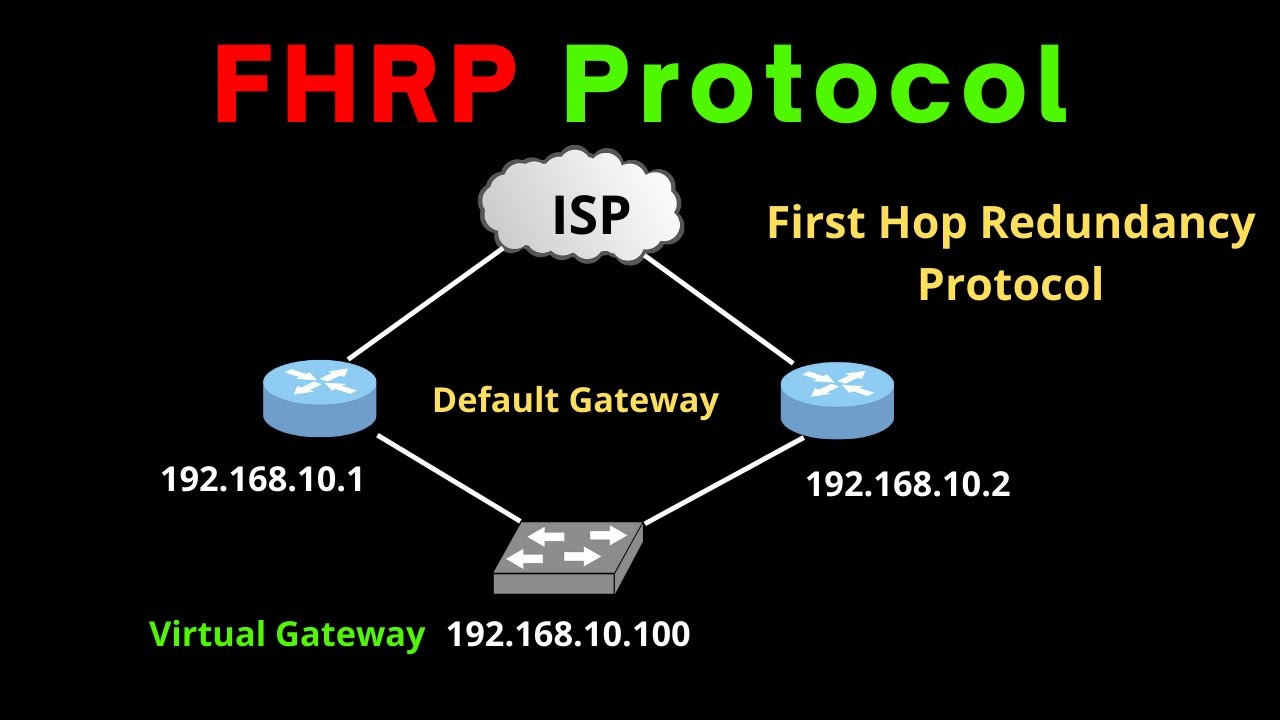
- FHRP or the First Hop Redundancy Protocol consists of a family of protocols used in networking to provide redundancy for the default gateway on a network
- FHRP ensures that if the primary gateway device fails, a backup device can take over and continue to provide network connectivity without disrupting service for the clients on the network
- FHRPs are essential in fault-tolerant network designs as it eliminates single points of failure at the WAN edge
- FHRP allows multiple routers to appear as a single virtual default gateway to the clients on the network
- In this lesson, lets analyze and dive deep into the different types of FHRPs available
(HSRP) Hot Standby Router Protocol
HSRP Overview
- The Hot Standby Router Protocol was developed by Cisco and is one of the most widely used FHRPs. However HRSP is proprietary and unable to be used across different vendors
- Terminology
- Active Router
- The Active router in a HSRP configuration handles the traffic for the virtual IP Address
- Standby Router
- The Standby router in a HSRP configuration is ready to take over in case of Active router failure
- (VIP) Virtual IP Address
- A VIP is a virtual IP address that network clients use as their default gateway
- Both the Active and Standby routers are put into an HSRP group and assigned a virtual IP address
- A virtual MAC address is also used in conjunction with the VIP
- Hello Packets
- Hello packets are multicast messages that routers in a HSRP group exchange to maintain communication and establish active and standby roles
- If a standby router fails to receive Hello packets from the active router, it will trigger a failover and assume the active role
- Hello packets are sent to multicast address 224.0.0.2
- Hello packets contain a UDP payload on port 1985 for the source and destination
- Hello Packet Timers
- Hello Timer
- By default hello packets are sent every 3 seconds
- Hold Timer
- By default the hold time for missed hello packets is 10 seconds
- Hello Timer
- Priority
- Used by routers in a HSRP group, the priority value determines which router will become the active or standby router
- By default, the priority value is set to '100' of each router in an HSRP group
- The router with the highest priority becomes the active router
- Priority values range between 0 and 255
- Preemption
- Used in conjunction with Priority, Preemption allows a router to take over the active role if it has a higher priority than the current active router even if the current active router is still functioning
- By default, preemption is disabled in HSRP
- Active Router
- HSRP States
- Initial
- The starting state for all routers in the HSRP group
- In this state, routers are waiting to start the HSRP process
- Learn
- The state in which the router is in the process of learning the VIP from the active or standby router
- Listen
- State in which the VIP is known but is not yet the active or standby router
- Router listens for Hello messages from the other routers to determine active or standby role
- Speak
- In this state, the router sends hello packets to other routers in the HSRP group
- The router actively participating in the election process to become either the active or standby router
- Standby
- Router is in the Standby role ready to take over if the active router fails
- Standby router actively monitors the active router's hello packets
- Active
- Router is in the Active role and is responsible for handling traffic to and from the VIP
- Initial
- Version Differences
- HSRPv1
- Multicast Address
- HSRPv1 uses multicast address 224.0.0.2
- The multicast address represents the 'All Routers' address meaning that any packet sent to this address will reach every router on the local network
- Address is less efficient than HSRPv2
- Virtual MAC Address
- HSRPv1 uses the format '0000.0c07.ACxx' for the virtual mac address of the HSRP group
- The 'xx' stands for the HSRP group number in hexadecimal
- Groups
- HSRPv1 supports up to 255 group instances
- HSRPv1 cannot interoperate with HSRPv2
- Multicast Address
- HSRPv2
- Multicast Address
- HSRPv2 uses multicast address 224.0.0.102
- Multicast address represents all HSRPv2 and GLBP routers
- Address is more efficient than HSRPv1
- Virtual MAC Address
- HSRPv2 uses the format '0000.0c9f.fxxx' for the virtual mac address of the HSRP group
- The 'xxx' stands for the HSRP group number in hexadecimal
- Groups
- HSRPv2 supports up to 4095 group instances
- HSRPv2 cannot interoperate with HSRPv1
- HSRPv2 supports IPv6 networks
- Supports Authentication features
- Multicast Address
- HSRPv1
- Advanced Features
- Object Tracking
- Line Protocol
- Tracked IP Route Object
- Tracked IP SLA Object
- Authentication
- Plain-Text
- MD5
- Key Chain Keys
- Multigroup Load Sharing
- Implementing Two HSRP Groups
- Object Tracking
(VRRP) Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol
VRRP Overview
- The Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol is an open standard FHRP and is used amongst multi-vendor environments. Although not Cisco proprietary, VRRP and HSRP are closely related in terms of command structure and strive towards the same goal of providing reliable automatic failover for gateway devices on the network.
- Terminology
- Master Router
- The Master router in a VRRP configuration handles the traffic for the virtual IP Address
- Backup Router
- The Backup router in a VRRP configuration is ready to take over in case of Master router failure
- (VIP) Virtual IP Address
- A VIP is a virtual IP address that network clients use as their default gateway
- Both the Master and Backup routers are put into a VRRP group and assigned a virtual IP address
- A virtual MAC address is also used in conjunction with the VIP
- In VRRP, the physical IP address of a VRRP router is able to be used as the vIP of a group
- Advertisement Packets
- Advertisement packets are multicast messages that the master router in a VRRP group sends to maintain communication and establish master and backup roles
- Unlike HSRP, the master router in VRRP is the only device that sends Advertisement/Hello packets
- If a backup router fails to receive Advertisement packets from the master router, it will trigger failover and assume the master role
- Advertisement packets sent to multicast address 224.0.0.18
- Advertisement Packet Timers
- Advertisement Interval Timer
- By default advertisement packets are sent every 1 second
- Down Interval
- By default the down interval for missed advertisement packets is 3 seconds
- Advertisement Interval Timer
- Priority
- Used by routers in a VRRP group, the priority value determines which router will become the master or backup router
- By default, the priority value is set to '100' of each router in a VRRP group
- The router with the highest priority becomes the master router
- Priority values range between 0 and 255
- Preemption
- Used in conjunction with Priority, Preemption allows a router to take over the master role if it has a higher priority than the current master router even if the current master router is still functioning
- By default, preemption is enabled in VRRP
- Master Router
- VRRP States
- Initial
- The starting state for all routers in the VRRP group
- In this state, routers are waiting to start the VRRP process
- Backup
- Router is in the Backup role ready to take over if the master router fails
- Backup router actively monitors the master router's advertisement packets
- Master
- Router is in the Master role and is responsible for handling traffic to and from the VIP
- Initial
- Version Similarities and Differences
- Similarities
- Multicast Address
- VRRPv2 and VRRPv3 use multicast address 224.0.0.18
- Address represents the 'VRRPv2 and VRRPv3' address meaning that any packet destined to this address will reach all VRRPv2 and v3 routers on the local network
- Virtual MAC Address
- VRRPv2 and VRRPv3 use the format '0000.5e00.01XX' for the virtual mac address of the VRRP group
- The 'xx' stands for the VRRP group number in hexadecimal
- Groups
- VRRPv2 and VRRPv3 support up to 255 group instances
- Multicast Address
- Differences
- VRRPv2 is the default version when configuring VRRP
- VRRPv3 supports IPv4 and IPv6 networks
- Similarities
- Advanced Features
- Object Tracking
- Line Protocol
- Tracked IP Route Object
- Tracked IP SLA Object
- Authentication
- Plain-Text
- MD5
- Key Chain Keys
- Multigroup Load Sharing
- Implementing Two VRRP Groups
- Object Tracking
(GLBP) Gateway Load Balancing Protocol
GLBP Overview
- The Gateway Load Balancing Protocol is a Cisco proprietary FHRP that is used across Cisco gateway devices. GLBP helps distribute the traffic load across multiple routers or gateway devices on a network. GLBP ensures that if one router fails, another can take over without disrupting network connectivity. By default out of the three FHRPs (HSRP, VRRP, and GLBP) GLBP provides load balancing out of the box
- Terminology
- AVG Router
- The AVG router in a GLBP configuration responds to client ARP requests for the AVF gateway virtual MAC address
- GLBP can support up to 1 AVG per group
- Optionally 3 standby AVGs can be configured
- The AVG plays the role of the AVF and AVG
- AVF Router
- The AVF router in a GLBP configuration has a unique vMAC from other AVFs and routes client traffic
- If one AVF fails, another AVF picks up the responsibility of the failed AVF by taking over its virtual MAC address
- GLBP can support up to 4 AVFs per group
- AVFs play a role as active and standby AVFs
- (VIP) Virtual IP Address
- A VIP is a virtual IP address that network clients use as their default gateway
- Both the Active and Backup AVG/AVF routers are assigned a virtual IP address
- A virtual MAC address is also used in conjunction with the VIP
- vMAC format: 0007.b4xx.xxYY
- x = Group
- y = AVF
- vMAC format: 0007.b4xx.xxYY
- Hello Packets
- Hello packets are multicast messages that all routers in a group exchange to maintain communication and establish active and standby roles
- If the backup AVG router fails to receive Hello packets from the active AVG router, it will trigger failover and assume the active role
- Hello packets sent to multicast address 224.0.0.102
- Hello Packet Timers
- Hello Timer
- Hello packets are sent every 3 seconds
- Hold Timer
- By default the down interval for missed hello packets is 10 seconds
- Hello Timer
- Load Balancing Methods
- Round Robin
- Weighted ratio %
- Host Dependent
- Timer Intervals
- Redirect Timer
- How long the AVG will forward new requests to AVFs
- Timeout Timer
- Backup AVF time of taking over virtual MAC address of failed AVF
- Redirect Timer
- Priority
- Used by routers in a GLBP group, the priority value determines which router will become the active and backup AVG router
- By default, the priority value is set to '100' on each router in a GLBP group
- The router with the highest priority becomes the active AVG router
- Priority values range between 0 and 255
- Preemption
- Used in conjunction with Priority, Preemption allows a router to take over the active role if it has a higher priority than the current active AVG router even if the current active router is still functioning
- By default, preemption is disabled in GLBP
- AVG Router
- GLBP States
- Initial
- The starting state for all routers in the GLBP group
- In this state, routers are waiting to start the GLBP process
- Listen
- State in which the VIP is known but is not yet the active or standby router
- Router listens for hello messages from the other routers to determine active or standby role
- Speak
- In this state, the router sends hello packets to other routers in the GLBP group
- The router actively participating in the election process to become either the active or standby router
- Standby
- Router is in the Standby role ready to take over if the Active router fails
- Standby router actively monitors the Active router's hello packets
- Active
- Router is in the Active role and is responsible for handling traffic to and from the VIP
- Initial
- Advanced Features
- Weighted Object Tracking
- Line Protocol
- Tracked IP Route Object
- Tracked IP SLA Object
- Authentication
- Plain-Text
- MD5
- Key Chain Keys
- Supports IPv6 networks
- Weighted Object Tracking