Connected Routes
Sections:
Overview:
- Connected Routes are routes that are created when a router is directly connected to a network or subnet through various mediums including Ethernet, Serial, or Wireless
- Connected Routes represent networks that are physically accessible via those interfaces
- With each network being segmented off, inter-network communications will have to pass through a router or another layer 3 device such as a layer 3 switch or firewall
- Note: Connected routes alone will not will not make routing work because other routers in the path will need instructions on how to reach those networks that are not directly connected
- Note: In a later section we will discuss adding static routes and eventually dynamic routing protocols to instruct routers on how to reach other networks
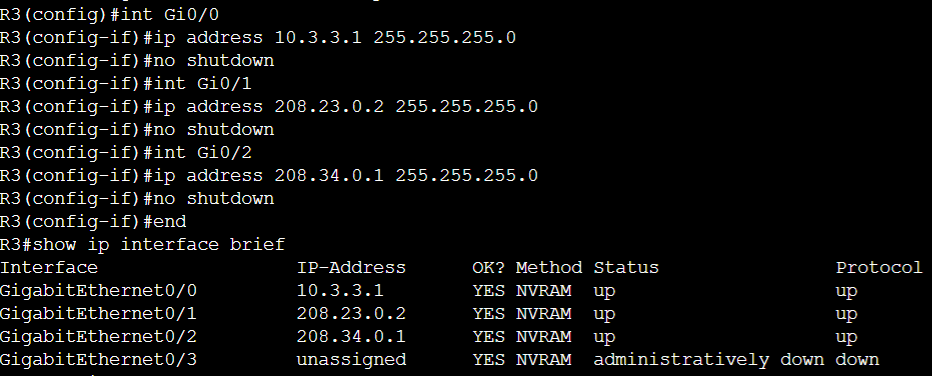
- For example in the topology below, if PC1 intends to communicate with PC3 located on a different network, PC1 would have to let its default gateway R1, send the traffic towards R2, then from R2 to R3, then from R3 to PC3 off its directly connected network
- In this lab scenario, lets define the directly connected networks of R1, R2, and R3 respectively
Lab Topology
Configuration
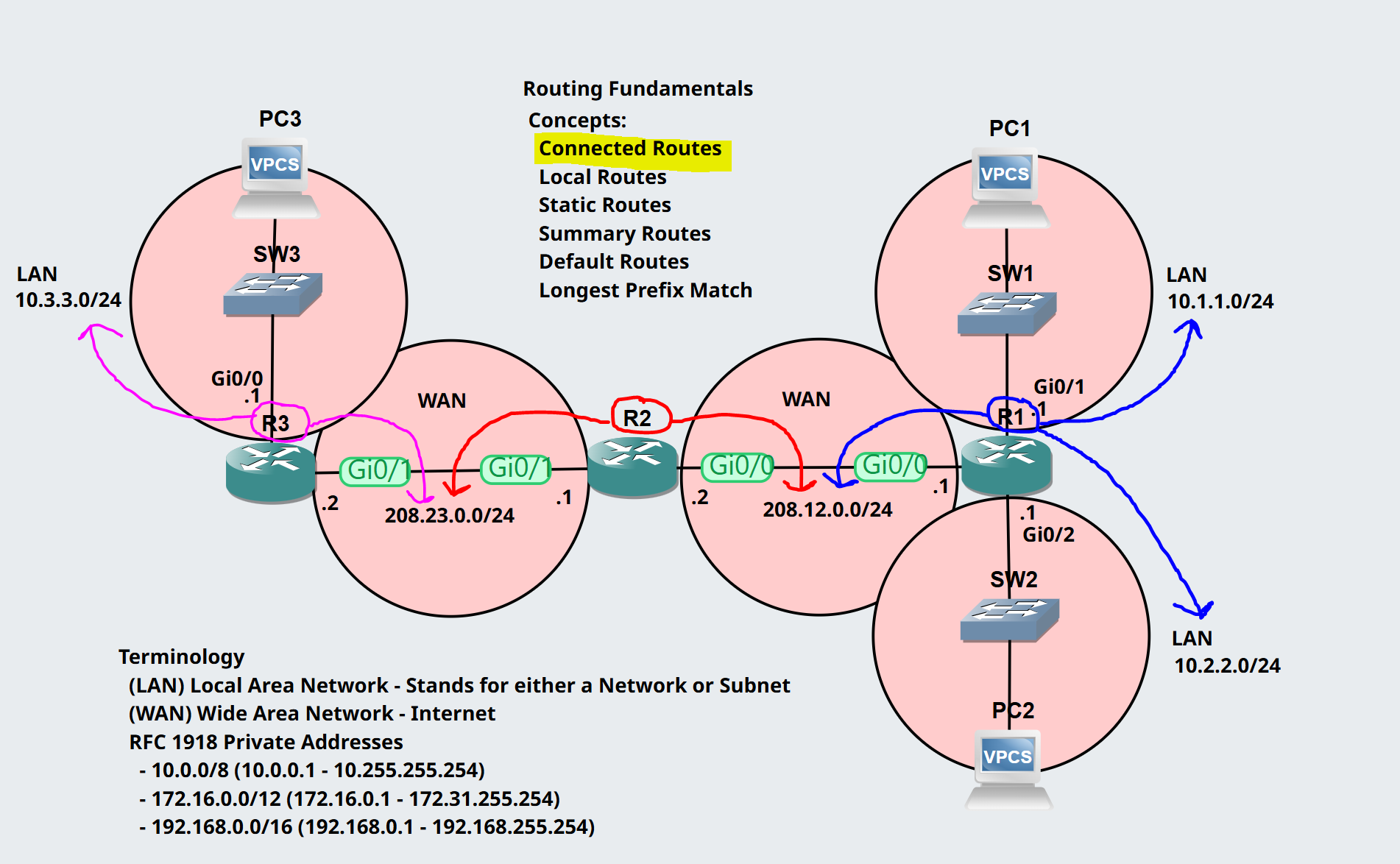
Connected Routes: R1
Notes:
- From R1, we have defined networks on interfaces Gi0/0, Gi0/1, Gi0/2
- You can view any configured IP addresses using the 'show ip interface brief' command
- You can view all available networks using the 'show ip route' command
- From the 'show ip route' command, the 'C' routes indicate directly connected networks and the interfaces mapped to each
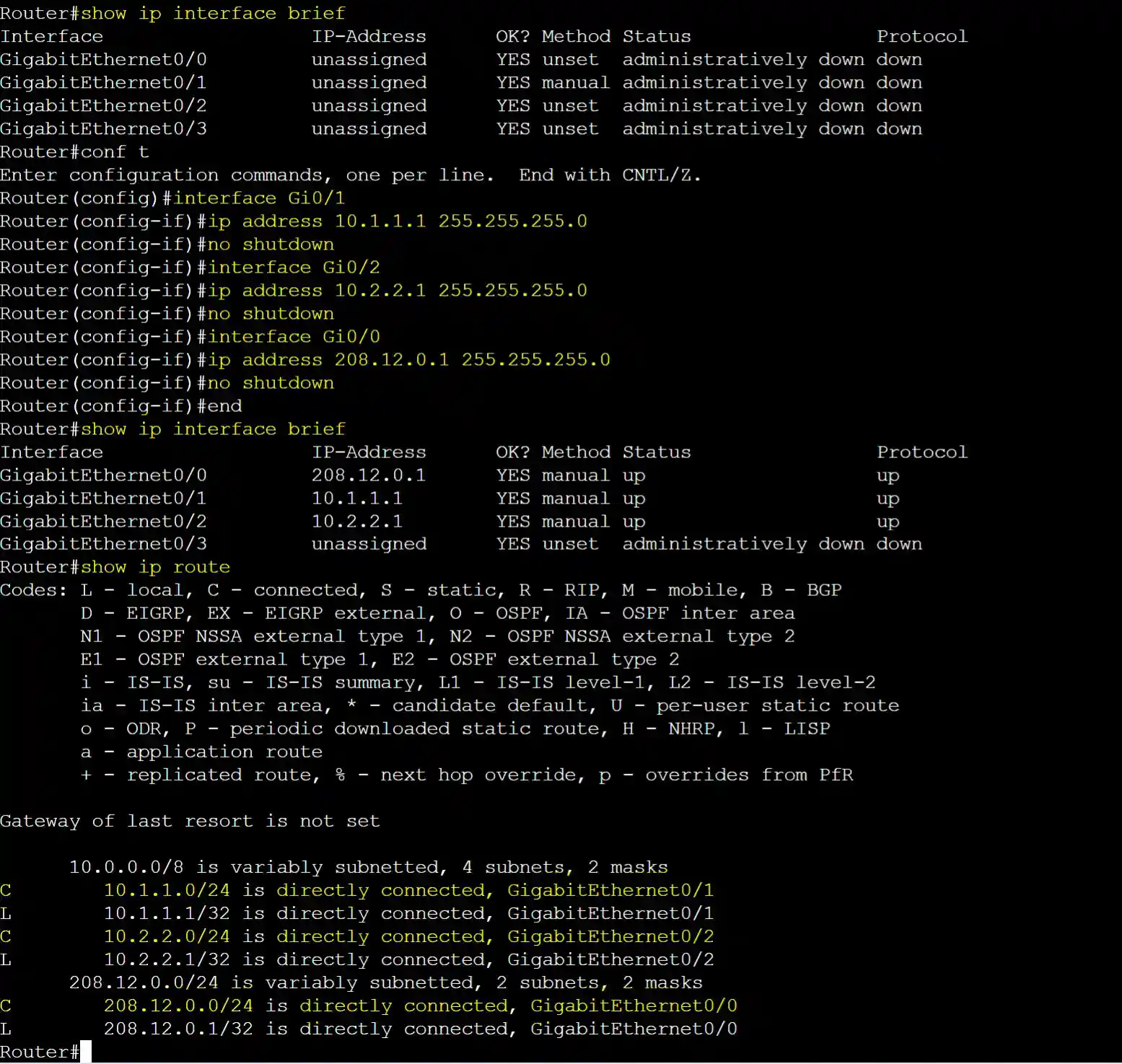
Connected Routes: R2
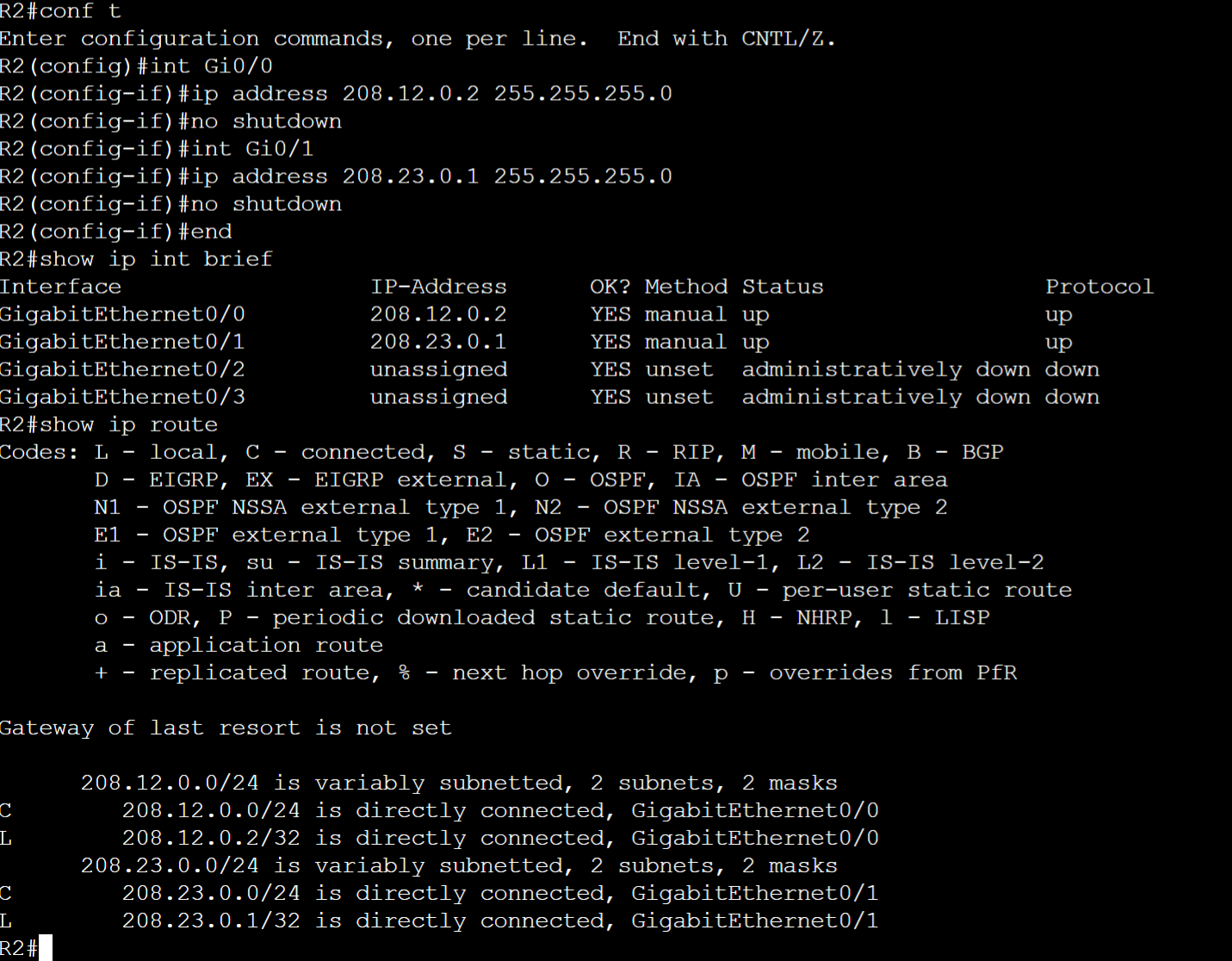
Connected Routes: R3