Backbone Fast
Sections:
Overview:
- BackboneFast helps eliminate the need for the full STP convergence recalculation time in an event of a failure within the network backbone (the core part of the network)
- BackboneFast helps speeds up the process of recovering from a root switch failure or a root port failure by quickly rerouting traffic
- BackboneFast is built into the standard by default in RSTP/RPVST+ or MST
How it Works:
- BackboneFast works by allowing a switch to detect when there is a suspected problem with the root switch or its root port
- Switches that lose connectivity to the root bridge immediately send out TCN (Topology Change Notification) messages to quickly update their topology information
- With BackboneFast enabled globally, the switch that detects the failure sends a special backbone query to neighboring switches asking whether they have heard about the failure or can see the root bridge
- If a neighboring switch has knowledge of the failure, it will inform the querying switch, which can then begin the process of quickly finding a new path or reevaluating its role on the network
- If a backbone query reveals that the failure has propagated, the affected switches can rapidly transition to a new topology instead of waiting for the full STP recalculation process
- Triggered in cases where indirect link failures at the core (root switch) occur
When to use:
- Commonly utilized on distribution or core layer switches where the failure of the root switch or root port has a significant impact on the overall network
- Beneficial in larger networks or redundant core networks where multiple potential paths can be used to reach the root bridge
- BackboneFast is manually configured in older versions of STP (802.1D STP/PVST)
- Note: BackboneFast must be enabled on all switches in the domain if implementing in older versions of STP
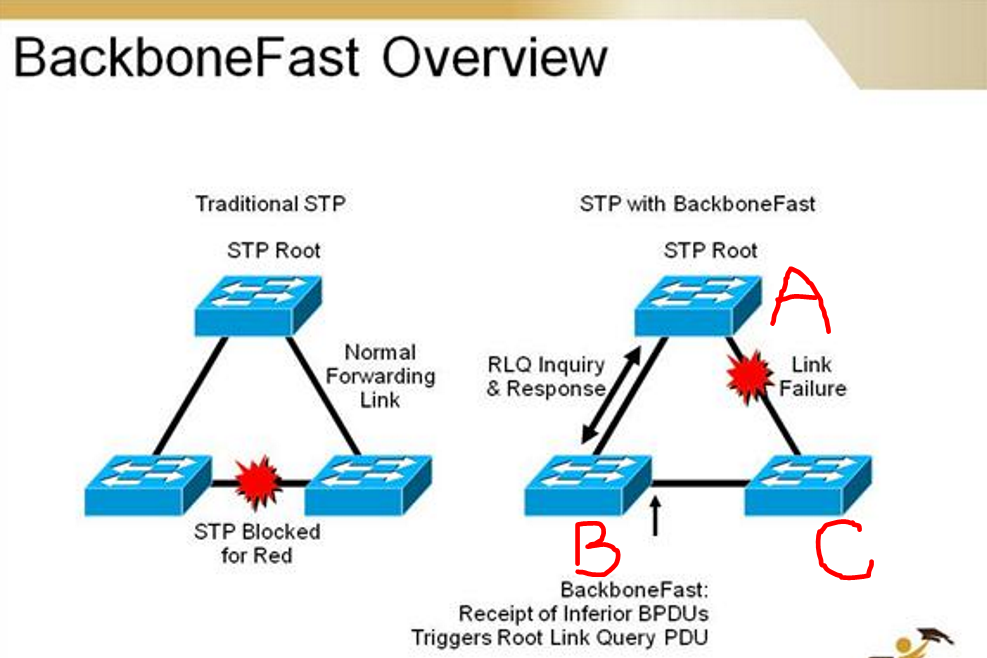
Scenario Example
- Switch (C) stops receiving BPDUs from Root switch (A)
- Switch (C) sends out TCN messages towards switch (B) claiming to be the new root switch to re-converge the STP topology
- With Switch (B) receiving superior BPDUs from switch (A), switch (B) also receives inferior BPDUs from switch (C)
- Switch (B) queries the Root switch (A) to confirm it is still the root switch
- If confirmed, Switch (B) discards the inferior BPDU from switch (C)
- Switch (B) will then transition its blocking port towards switch (C) to forwarding to adjust the STP topology due to the indirect link failure
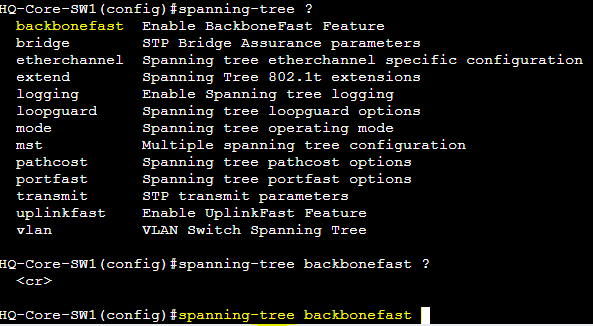
Configuration
Global Configuration command: spanning-tree backbonefast