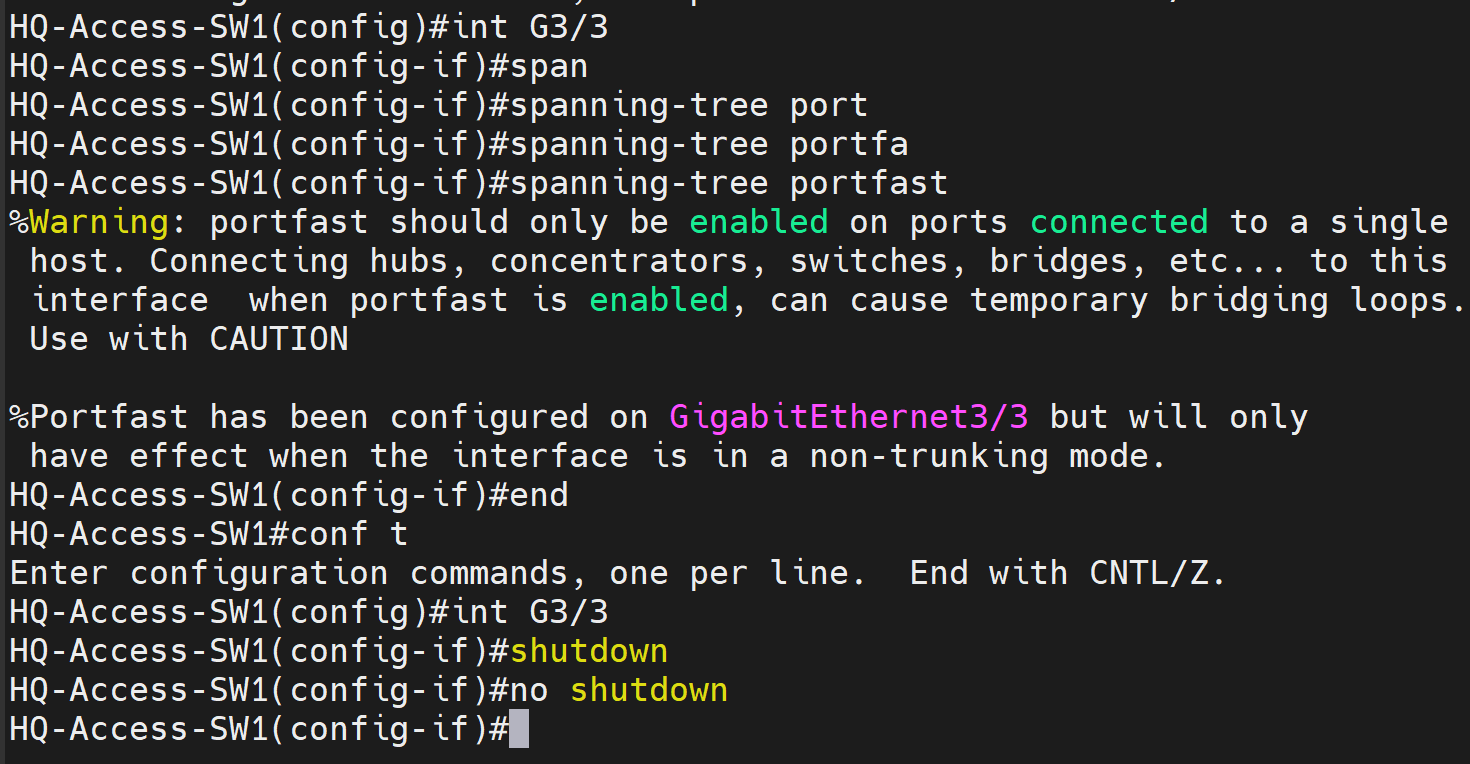
Portfast
Sections:
Overview:
- Port-Fast enables a switch port to accelerate the time it takes to transition to the forwarding state
- Enabling Port-Fast on ports allows the switchports to bypass the listening and learning states of the STP forward delay timers
- The goal of Port-Fast is to enable end user devices to connect to the network almost instantly improving the user experience
When to use:
- PortFast is recommended for access ports connected to devices like computers, printers, or other non-switch devices that don’t have the ability to cause loops by forwarding BPDUs
- PortFast should never be enabled on switch to switch links as this could lead to Spanning Tree loops and inconsistencies on the network
Lab Topology
Portfast Configuration
Scenario1 - Without Portfast
Scenario:
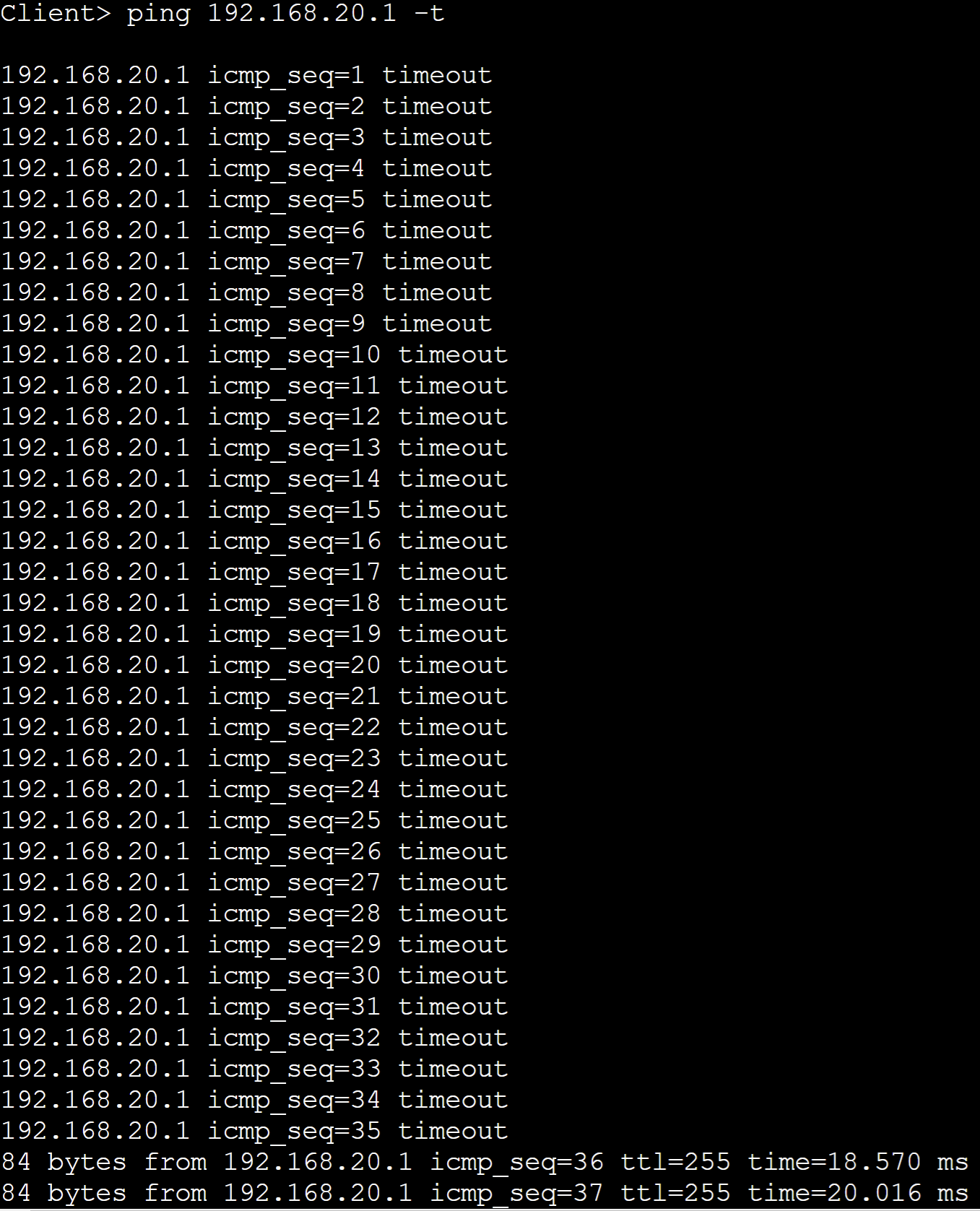
- Intention is to shutdown the Gi3/3 port on AccessSW1 towards the client PC in VLAN20
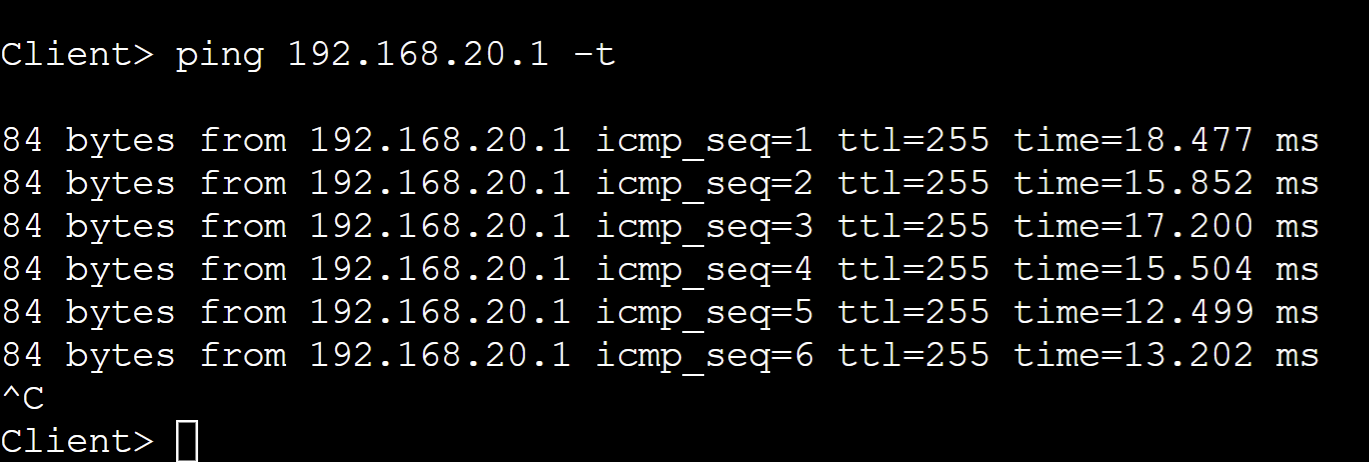
- Re-enabling the port will transition to the forwarding state after going through the Spanning Tree timers
- As you can see, clients on the network will have to wait for these timers to expire before being able to send any traffic on the network
- Default 802.1D Spanning Tree Timers:
- Listening State: 15sec
- Learning State: 15sec
- Overall: 30sec until the client can send traffic
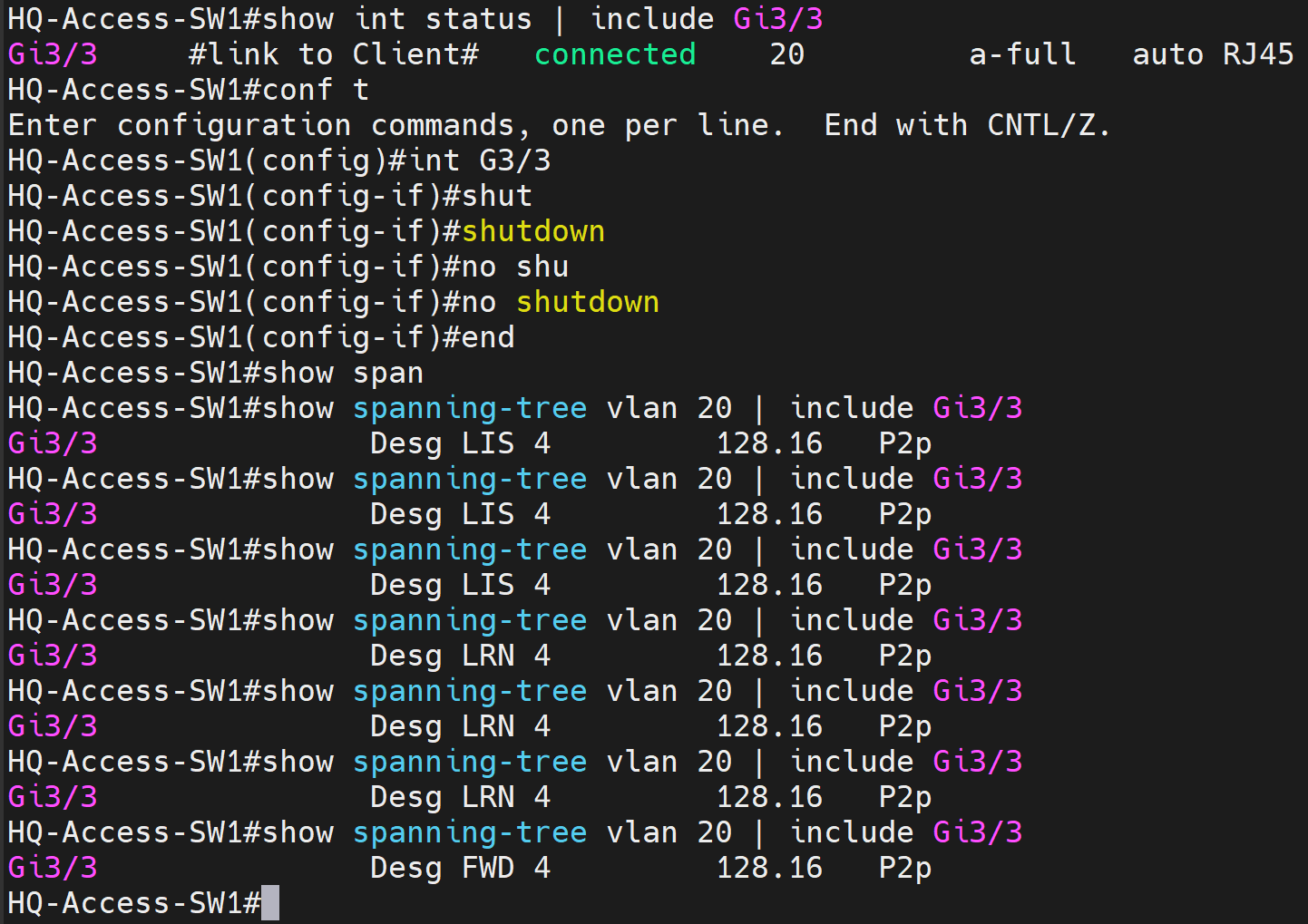
Scenario2 - Portfast Configuration
Scenario:
- Intention for this lab scenario is to enable Portfast on the Gi3/3 port on AccessSW1 towards the client PC in VLAN20
- As you can see, clients on the network are able to send traffic on the network almost immediately bypassing the Listening and Learning forward delay timers of the Spanning Tree protocol