Root Bridge Election Process
Sections:
Overview:
- The Root Bridge Election process is a critical aspect of the Spanning Tree protocol as it determines the foundation of the network topology and ensures that STP can prevent network loops while providing optimal data paths
- The Root Bridge switch serves as the central reference point in the network for all STP calculations
- Once the Root Bridge is elected, all other switches in the network determine the best path to the Root Bridge based on their cost to reach it
- In this section, lets demonstrate the key steps in the Root Bridge Election Process
Summary:
- The Root Bridge switch with the lowest numeric BID or BridgeID value is elected as the root bridge for the STP domain
- The BID value consists of the switch's MAC address in addition to a Priority value
- All Cisco switches have a priority of 32768 by default if not changed manually
Default Bridge Examples
Scenario:
- By default, all switches have a Spanning Tree priority value of 32768 if not changed manually
- For Cisco environments running the PVST and RPVST standards of 802.1D and 802.1w, a VLANID numeric tag is appended at the end of the priority value to classify the STP VLAN instance
- Priority values can be manipulated to designate a root switch and is recommended to prioritize switches at the core of the network to become designed root switches
- Assuming the priorities values are set to the defaults on all switches, the switch with the lowest MAC address value is the tie-breaker to win the root election
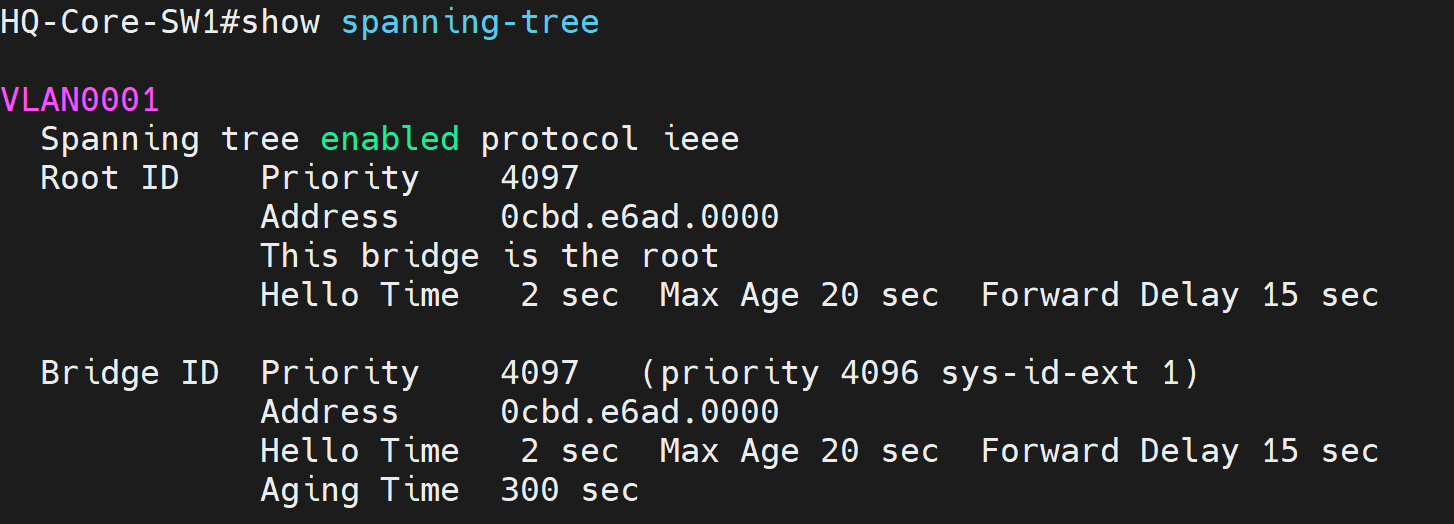
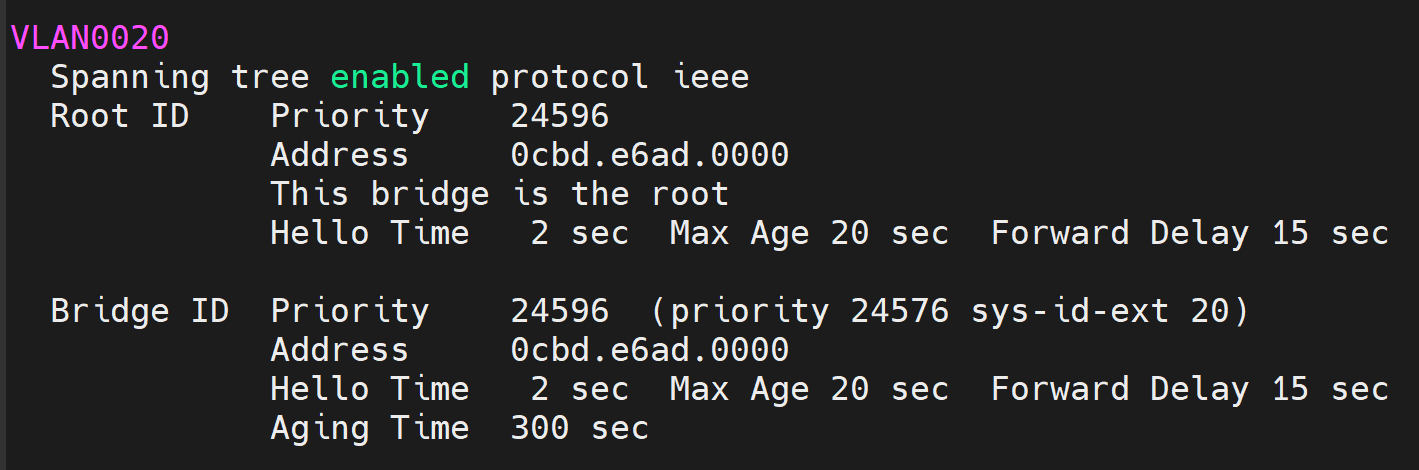
- In this lab exercise, lets verify the default Spanning Tree priority values on the HQ-Core-SW1 for VLANs 1 and 20
VLAN1 default priority: 32768 + 1 for VLAN 1

VLAN20 default priority: 32768 + 20 for VLAN 20
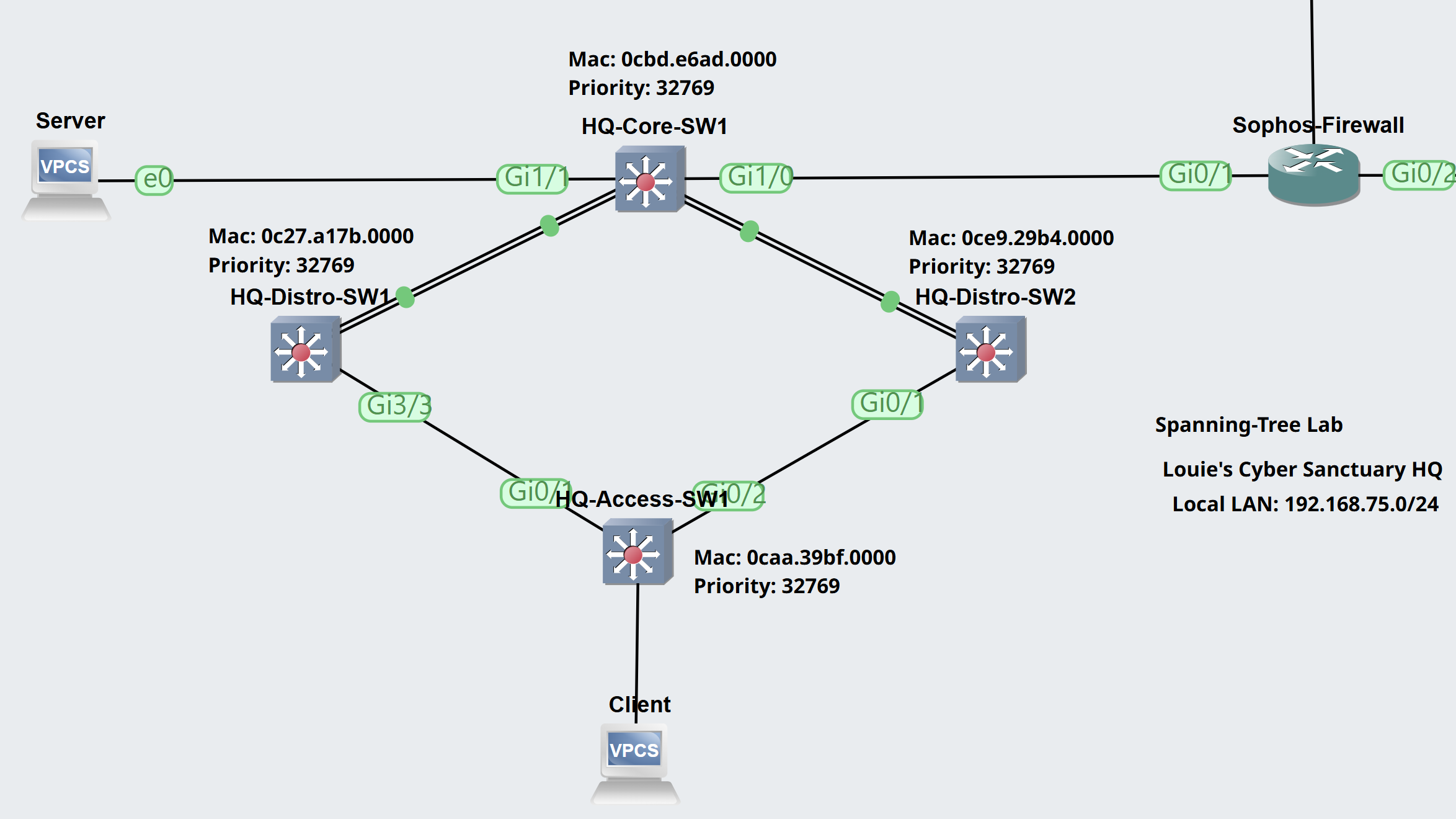
Lab Topology
Scenario:
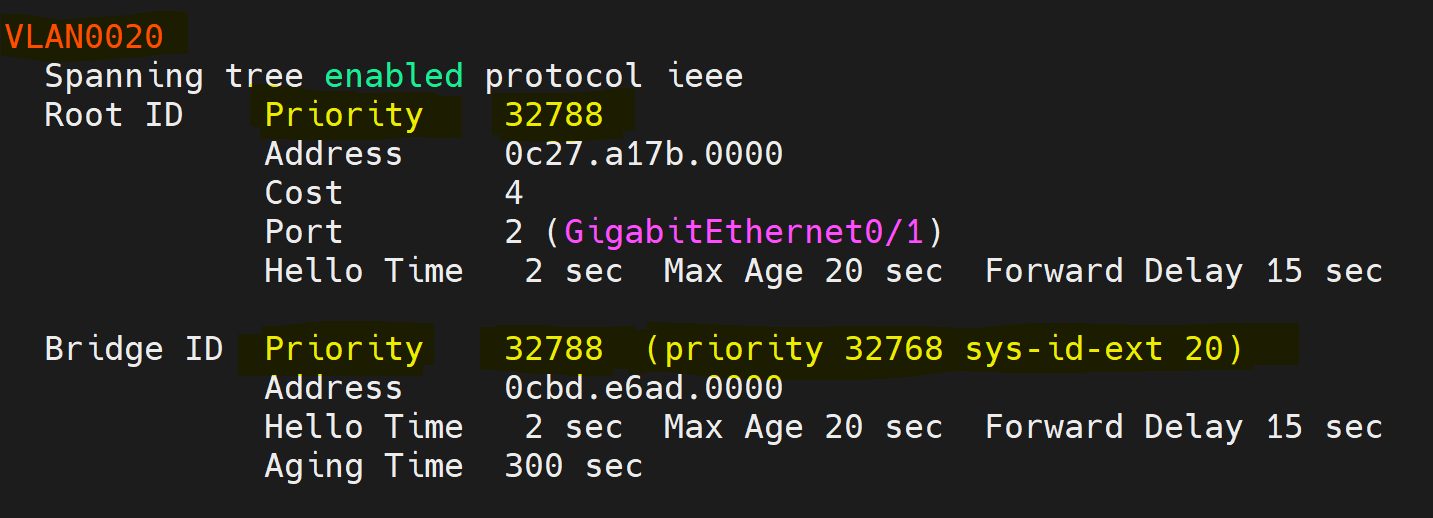
- Based on the Lab Topology diagram, all switches in the Spanning Tree domain are set to the default priority values. HQ-Distro-SW1 will win the Root Bridge election based on its lowest MAC address value out of all of the switches
Root Bridge Configuration
RootID vs BridgeID
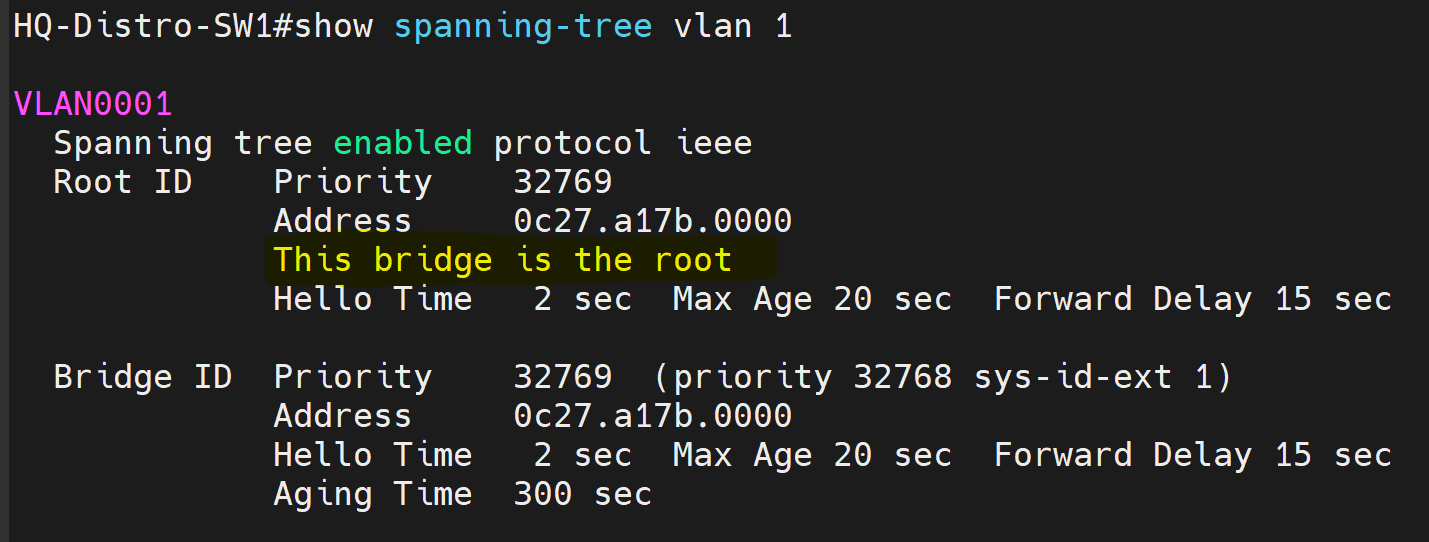
Examining the command output syntax below - let's define 'RootID' and 'BridgeID'.
RootID - Defines the root switch of the vlan1 spanning tree instance
- Note: 'This bridge is the root' identifies this local switch as the root being HQ-Distro-SW1
- Note: Mac address of the RootID and BridgeID sections match up giving another indicator that the HQ-Distro-SW1 is the root switch
BridgeID - Defines the local switch in which you're issuing the show command on
Root Bridge Configuration
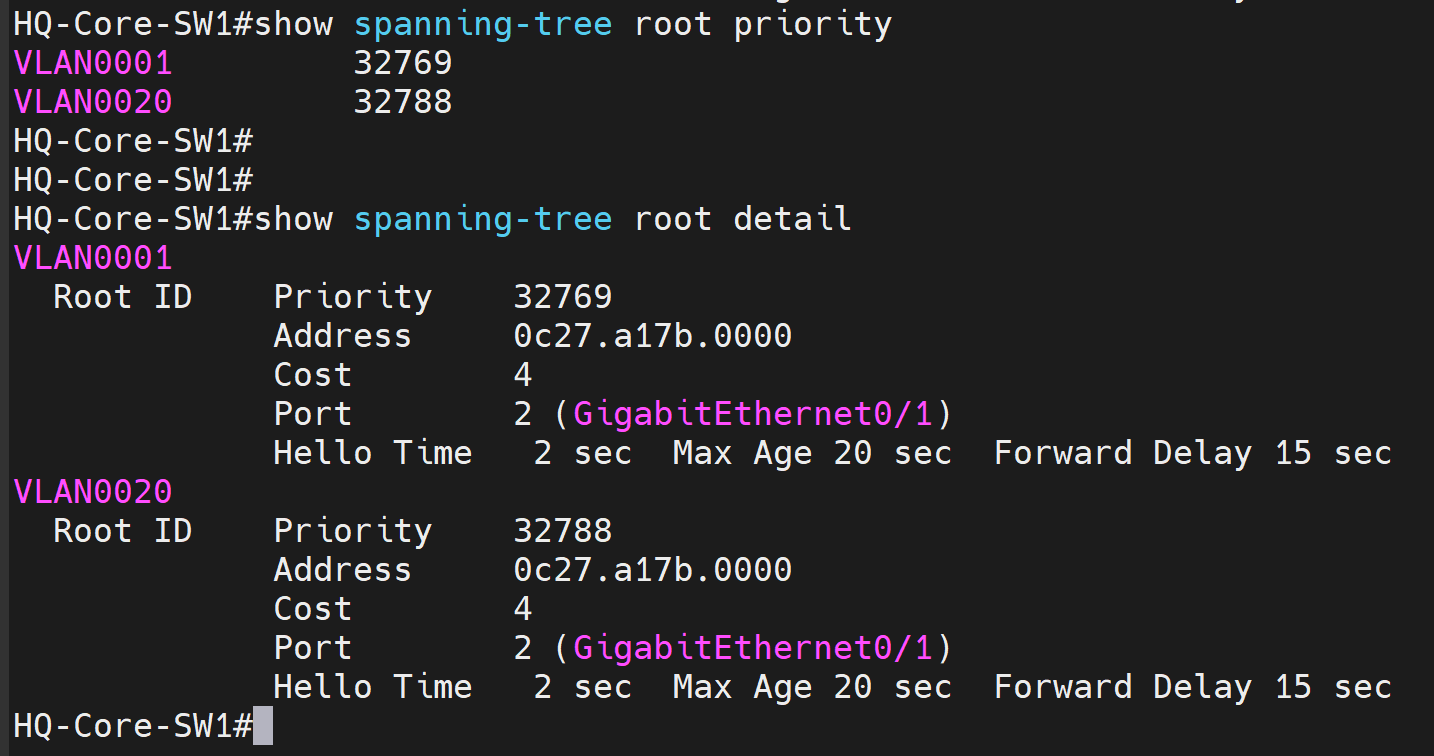
Scenario 1: Lowering the priority value, let's manipulate the root bridge election by making HQ-Core-SW1 the Root Bridge for VLANs 1 and 20.
Analyzing the show commands below - we will need to set a priority value of HQ-Core-SW1 to a value less than 32768 for both VLAN instances to satisfy the Root Bridge preference as all switches are using the default priority value.
There are two ways to manipulate the priority values:
- First method is to explicitly configure the priority value in increments of 4096
- Second method is to utilize and configure the root primary command to have the STP protocol auto adjust the priority value of HQ-Core-Sw1 to become the preferred root switch of the Spanning Tree domain
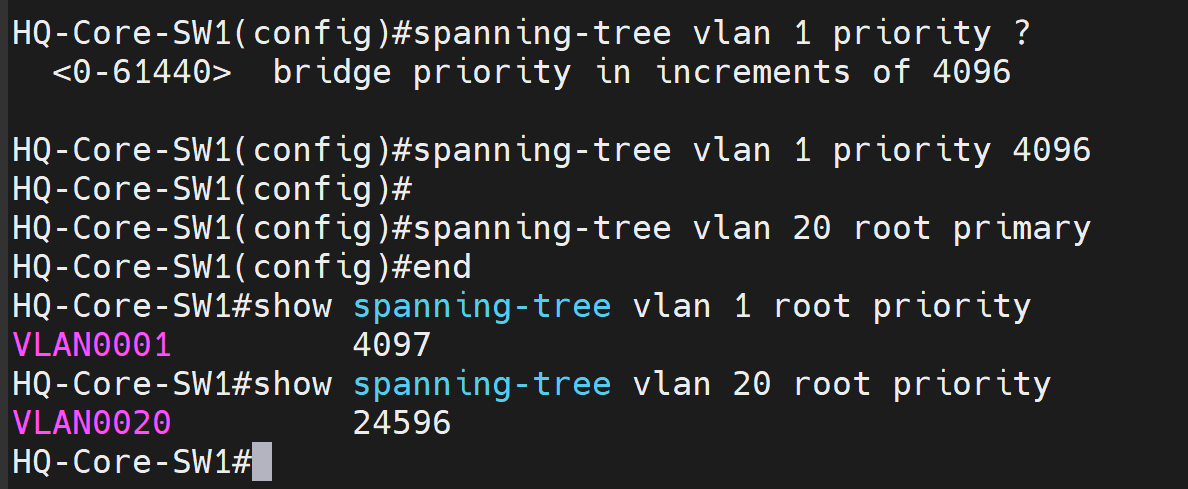
Verification show commands to prove HQ-Core-SW1 was elected as the new root bridge for VLANs 1 and 20 after defining a lower priority value.