Trunk Ports
Sections:
Overview:
- A trunk port is a switchport that is configured to carry traffic for multiple VLANs simultaneously across one or more physical links
- Efficient use of resources is a benefit to trunk links, reducing the number of physical connections needed between devices
- Trunk links are used to connect switches, routers, and other devices that need to communicate across different VLANs or subnets
- In a trunk port, the traffic that travels across the link is tagged with a VLANID using the IEEE 802.1Q trunking protocol
- 802.1Q is used to identify the VLANs on a trunk link by adding the VLAN tag to an Ethernet frame
- Note: ISL or Inter-Switch Link is a legacy Cisco proprietary trunking protocol that has since been replaced with 802.1Q
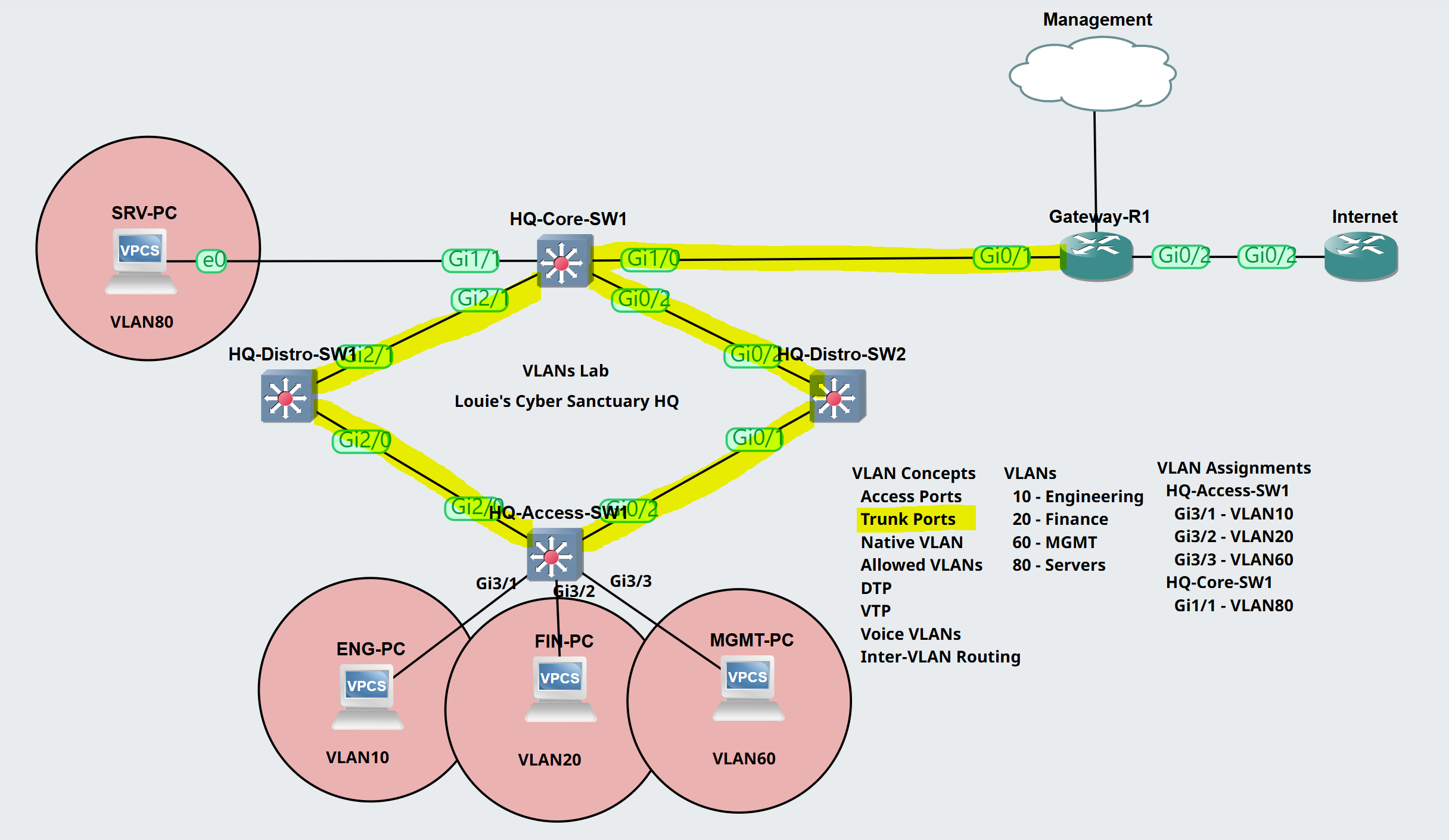
Lab Topology
Scenario:
- In this lab topology scenario I will configure trunk ports on the switch uplinks to allow all defined VLANs to be carried across the links
- When all trunk links are configured, I will demonstrate a Wireshark capture to analyze a 802.1Q VLAN tag in an Ethernet frame
Trunk Link Configuration
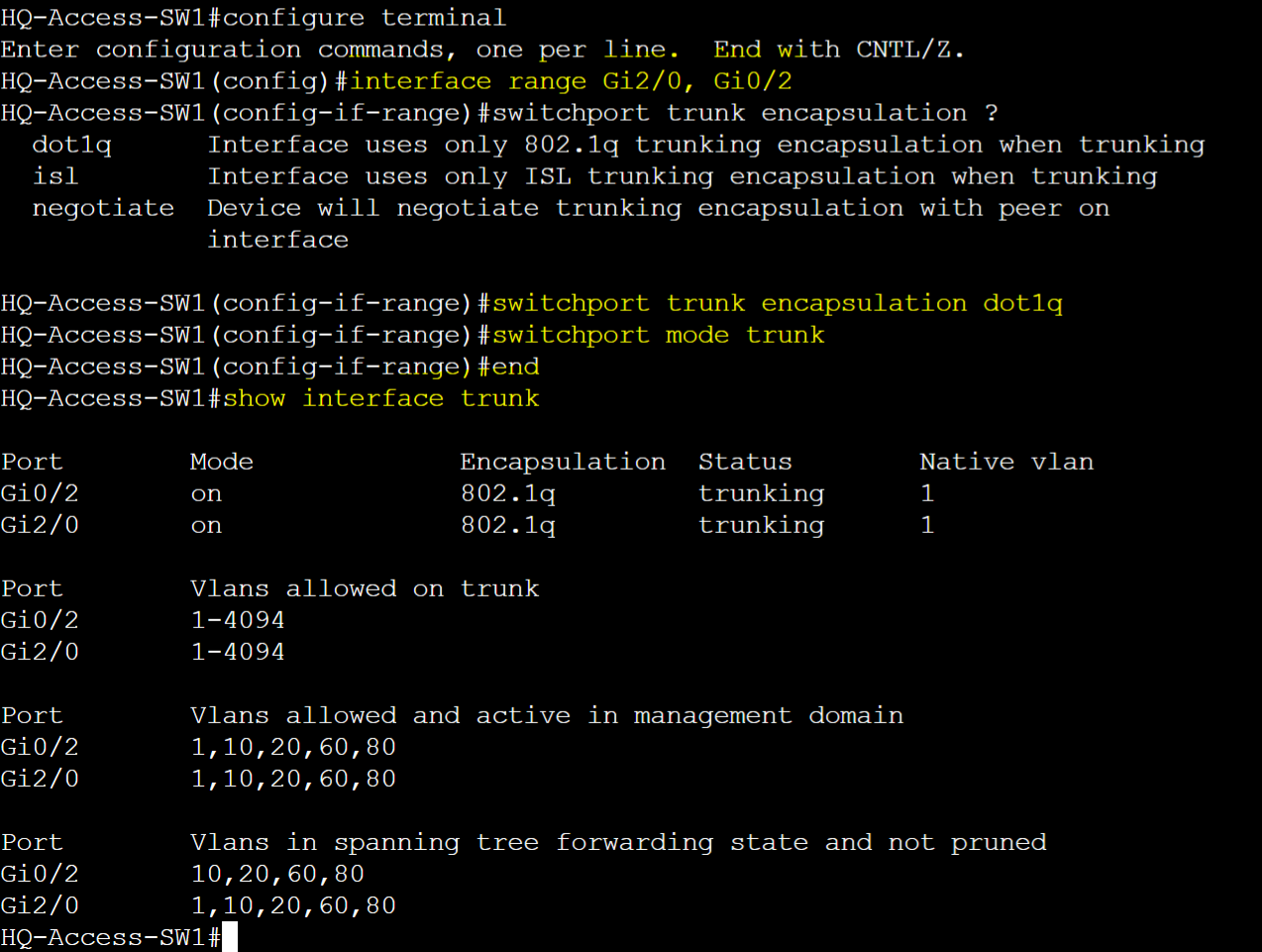
HQ-Access-SW1
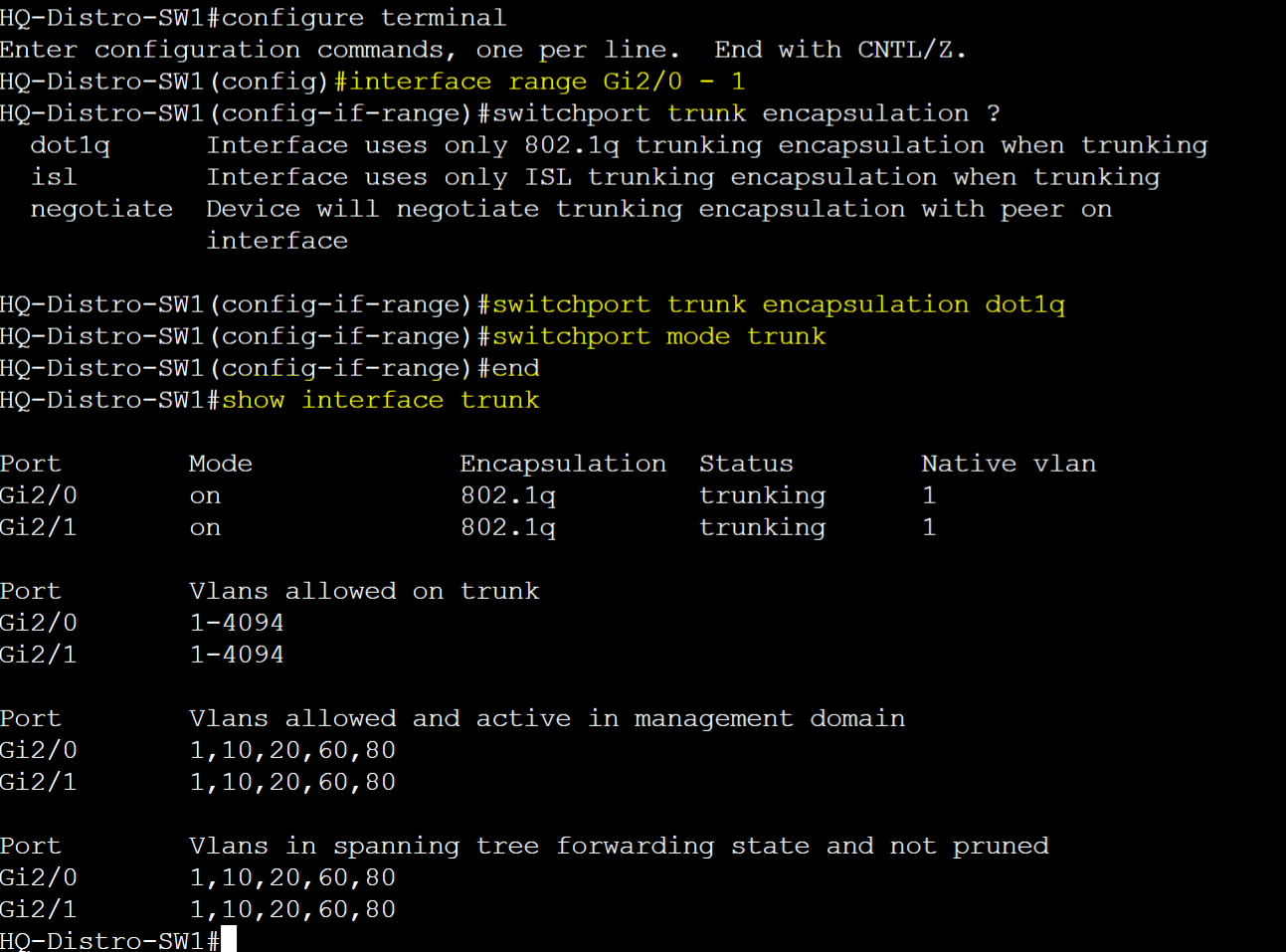
HQ-Distro-SW1
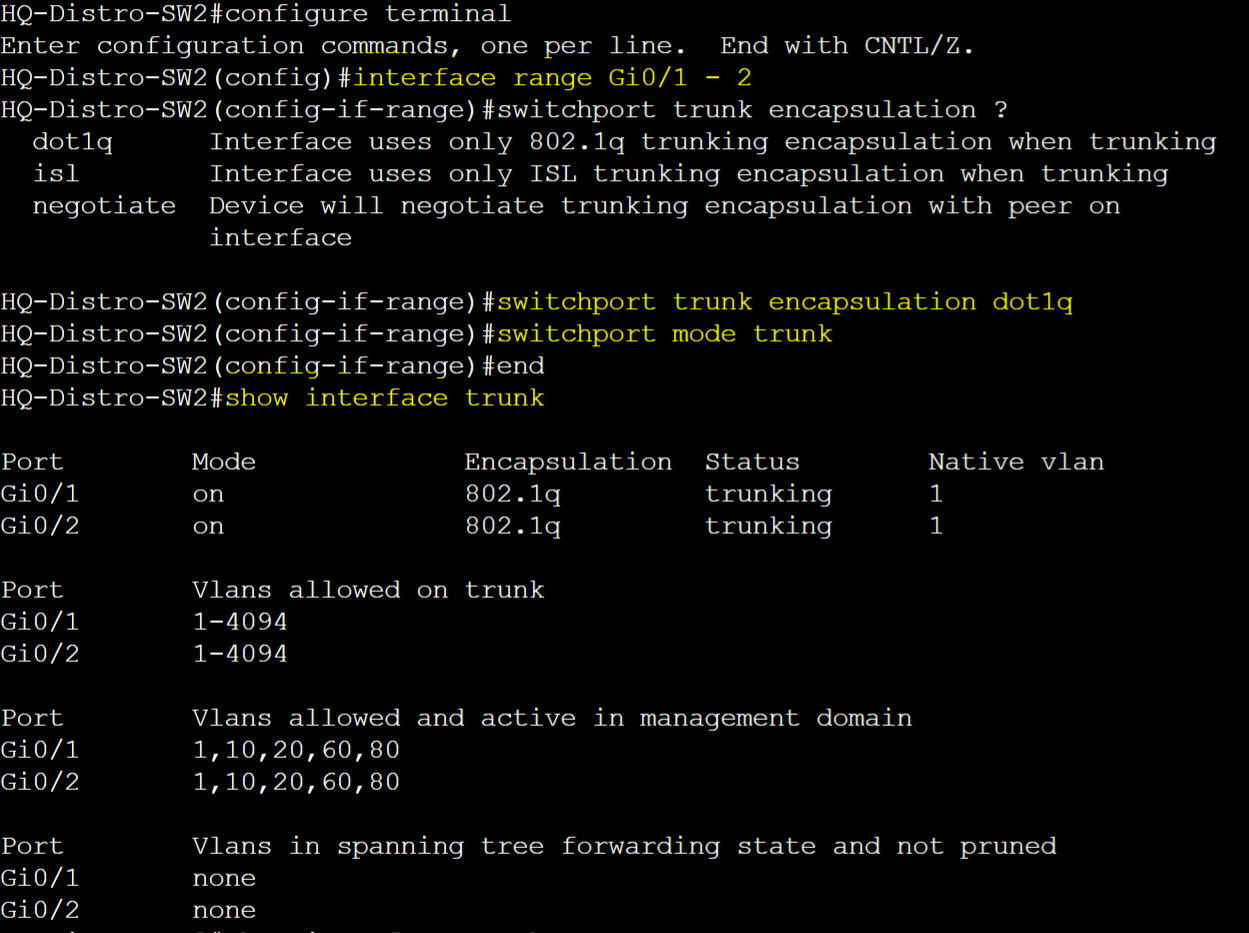
HQ-Distro-SW2
HQ-Core-SW1
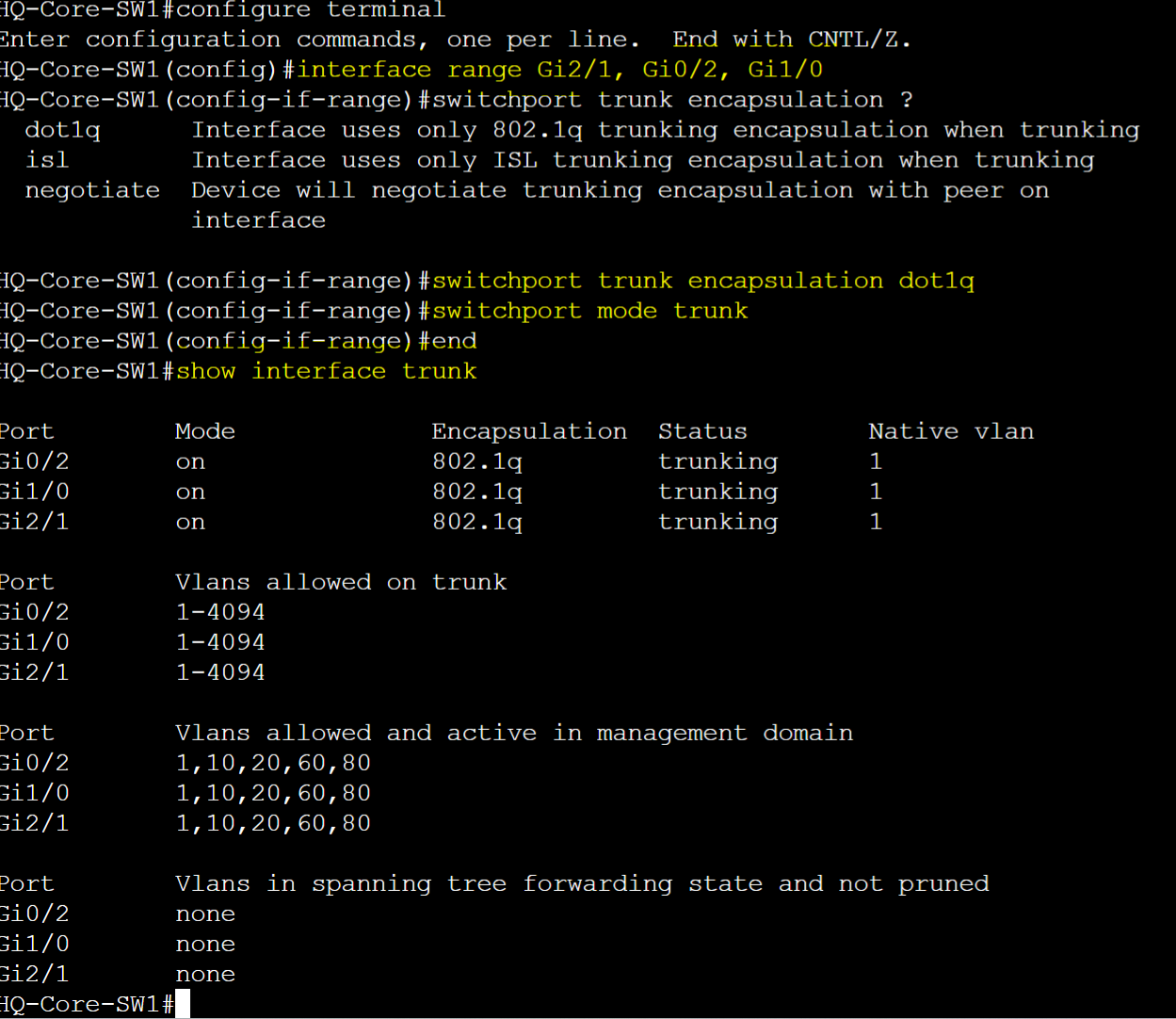
To summarize the scenario, trunk links have been configured on all switch uplinks to carry multiple VLANs on the physical links.
- Interface Configuration Commands
- To specify trunking protocol
- switchport trunk encapsulation <protocol>
- To assign interface port to a trunk port
- switchport mode trunk
- To verify configured trunk ports
- show interfaces trunk
- To specify trunking protocol
Packet Captures
802.1Q Wireshark Capture
Scenario:
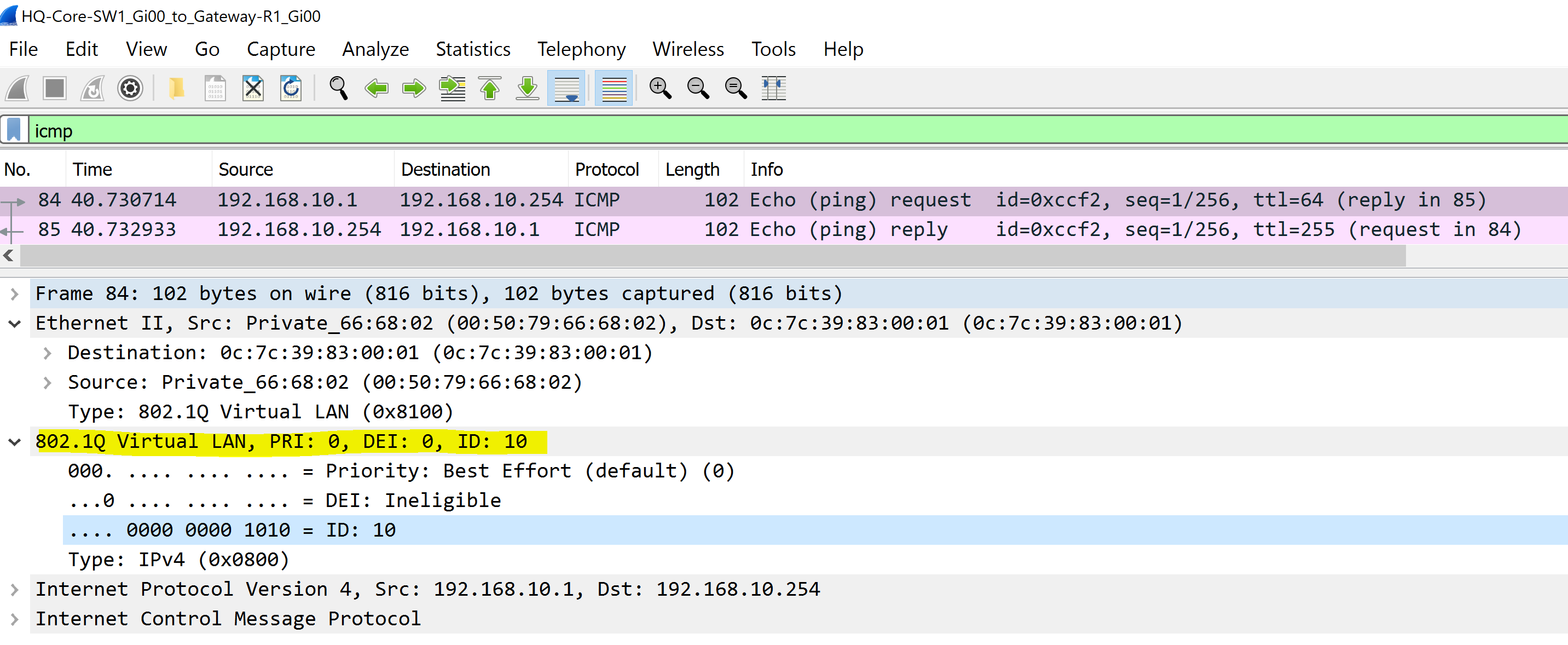
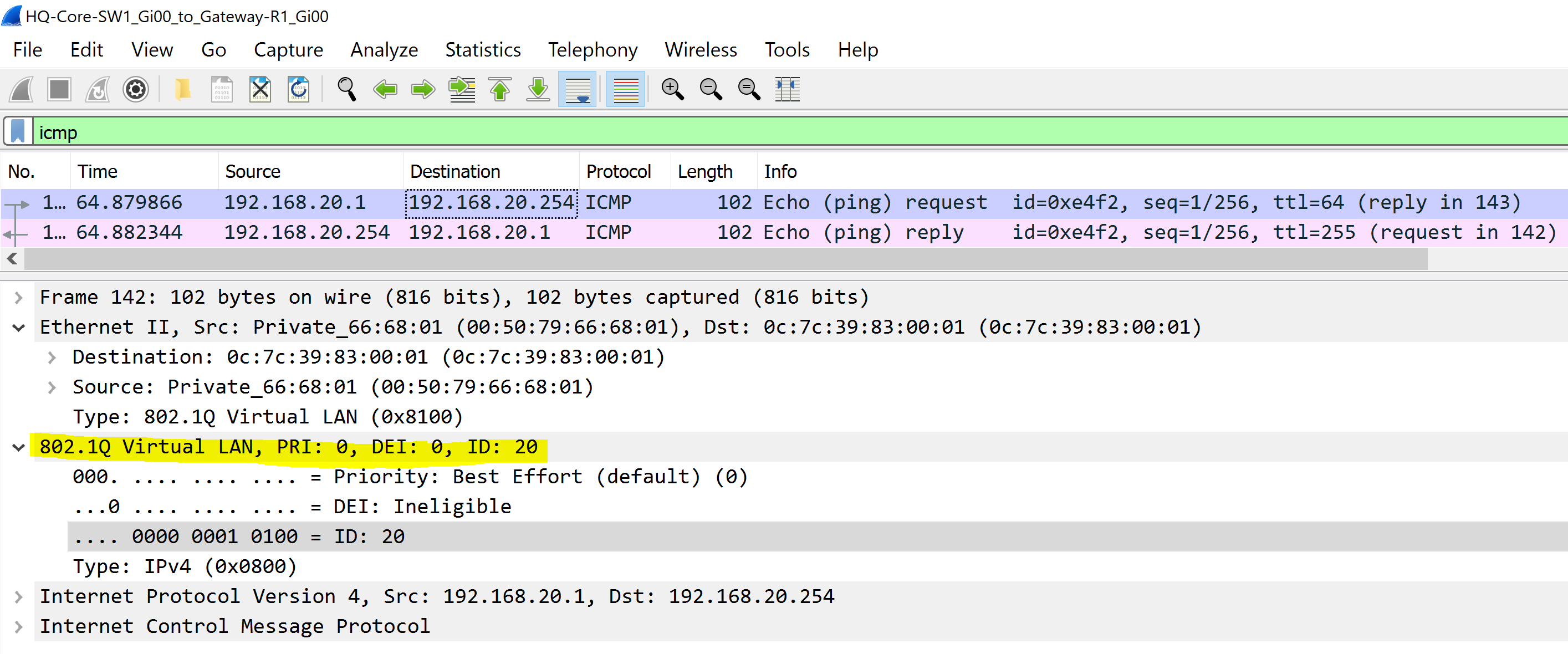
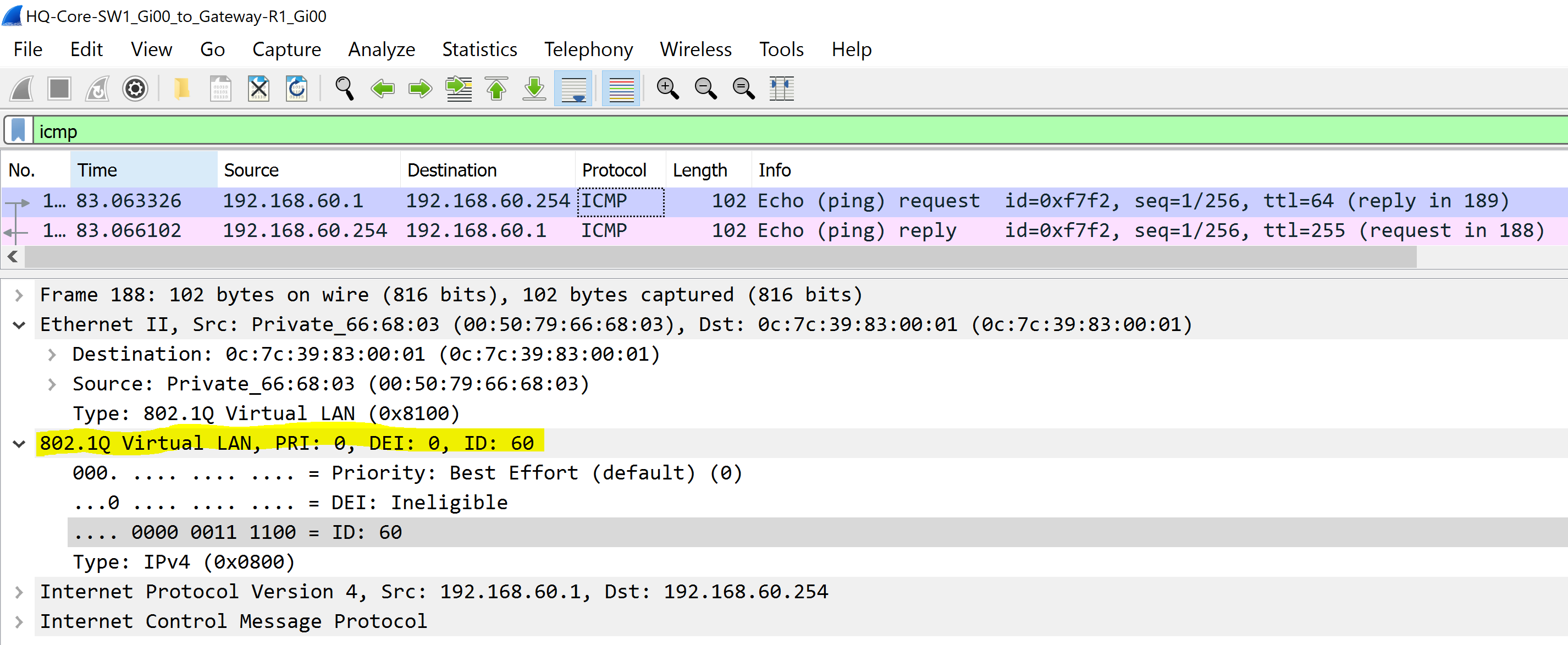
- In this scenario we will examine several Ethernet frames with a 802.1Q tag by sending ICMP traffic towards the Gateway-R1 router from the PCs in VLANs 10, 20, 60, and 80
802.1Q VLAN 10 - Engineering
802.1Q VLAN 20 - Finance
802.1Q VLAN 60 - MGMT
802.1Q VLAN 80 - Servers
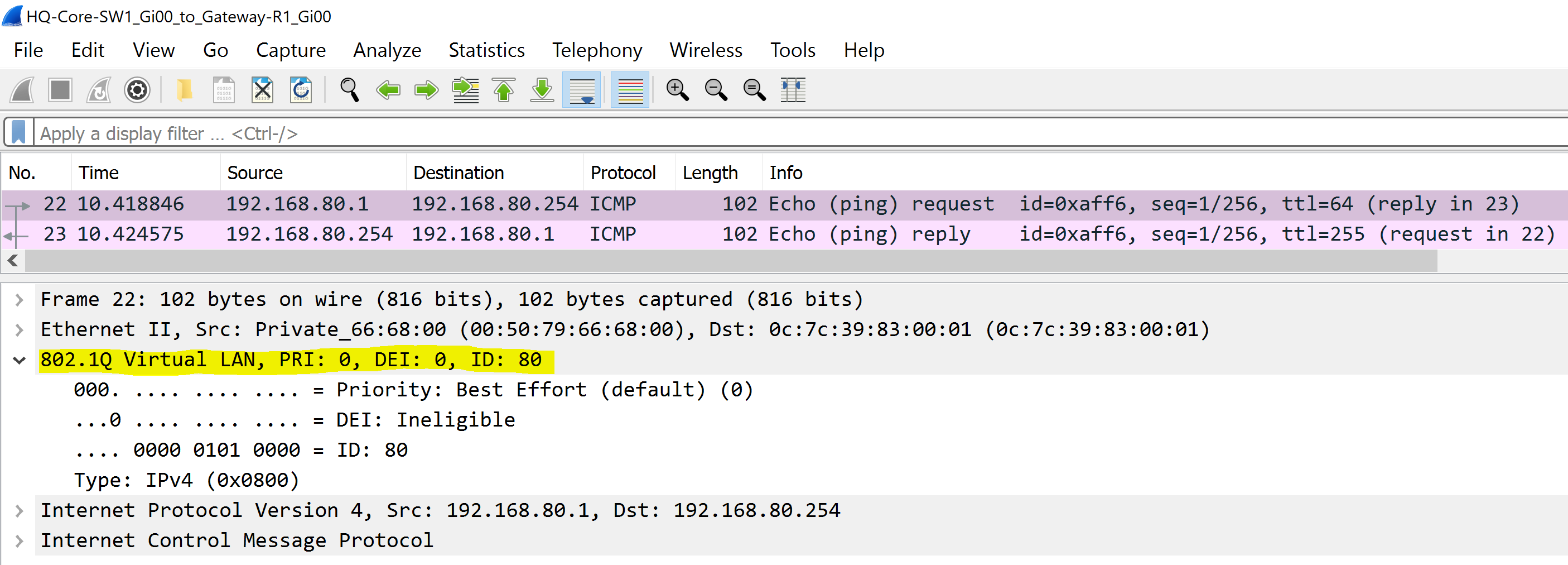
To summarize the scenario, there is a VLANID tag in a 802.1Q header to differentiate the VLAN traffic is sourced from.