VTP VLAN Trunking Protocol
Sections:
- VTP Modes
- VTP Domains
- Lab Topology
- VTP Configuration Setup
- VTP Propagation Configuration
- Packet Captures
Overview:
- VTP is a layer 2 Cisco Proprietary protocol that was created to simplify the management of VLANs across a network of Cisco switches
- VTP allows for an admin to centrally configure VLANs on a switch server in which the switch will then propagate the VLANs towards other switches automatically in the VTP domain
- VTP utilizes 3 switch modes that are used by switches to determine their role in the VTP domain
- Key Features
- Reduction of Configuration Errors
- Without VTP, VLAN configurations must be manually configured on each switch
- Centralized Management and Scalability
- VLANs are centrally managed on a switch server
- Reduction of Configuration Errors
VTP Modes
VTP uses 3 modes of operation that can be assigned to switches in a VTP domain and vary in characteristics
- Server Mode
- Can create, modify, and delete VLANs
- VTP Servers advertise their VLAN configuration to other switches in the domain
- Servers can also receive advertisement updates and sync their VLAN database from other VTP servers with a higher revision number
- Can specify the VTP version for the entire VTP domain
- Default VTP mode of all switches
- Client Mode
- Cannot create, modify, or delete VLANs
- Clients are only used to receive and forward advertisement updates from the VTP server
- Transparent Mode
- Switch does not participate in the VTP domain for VLAN propagation
- Switch does not receive or send advertisements for its local VLAN database
- Can create, modify, and delete VLANs
- Switch will advertise VTP updates from other switches along the network
- Off
- VTP is completely disabled on the switch
- Option for VTP Version 3
VTP Domains
A VTP domain is a group of switches that share the same VTP configuration.
All switches in the same VTP domain must have the same domain name configured for VTP to work.
Until a VTP domain name is specified or learned, you cannot create or modify VLANs on a VTP server, and VLAN information is not propagated over the network.
How VTP Propagates VLAN Information
- VTP Advertisements
- VTP servers send advertisements containing VLAN information to other switches in the VTP domain
- VTP advertisements are sent in multicast frames
- Note: By default, Cisco switches are in a VTP null domain name state until it receives an advertisement for a domain to inherit over a trunk link or until you configure a domain name on the switch
- VTP Revision Number
- Each VTP advertisement consists of a revision number that is incremented with each update (example: adding/removing a VLAN)
- All switches except for Transparent switches compare the revision number in incoming advertisements to determine if the information is newer than their current configuration
- The higher the revision number, switches will update their VLAN database to reflect itself to match the VLAN configuration of the VTP server with the highest revision number
VTP Versions & Notable Features
- VTP version 1
- Original version
- Default version
- VTP version 2
- Version-Dependent Transparent Mode
- Version 1: domain name and version must match to relay advertisments
- Version 2: only domain name must match to relay advertisements
- Version-Dependent Transparent Mode
- VTP version 3
- Added Enhanced Authentication
- All domain switches must share the same password in the domain
- Authentication password must be configured on each switch in the VTP domain
- If a switch does not have the correct password configured for the domain, the switch is unable to receive VTP advertisements
- Provides support for extended range VLANs (1006-4094)
- Ability to turn off VTP globally or on a per-trunk (per-port) basis
- VTP Primary & Secondary Servers
- Primary Server
- Ability to make changes to the VLAN database and send advertisements
- Secondary Server
- Receives and stores these advertisement updates from the primary server and acts as a backup
- Does not initiate sending advertisements itself
- Default server mode when version 3 is configured on a switch
- Primary Server
- Added Enhanced Authentication
VTP Limitations
With VTP, there are several factors to note before implementing VTP in your network
- VTP Version Compatability
- With the 3 different versions of VTP, certain features are only available in specific versions and is important to implement the same version across all switches in the VTP domain for consistency
- Risk of Overwriting VLAN Configurations
- It's important to note that if the revision number of an advertisement is higher than the local revision number on a switch, VTP advertisements can overwrite existing VLAN information leading to the loss of VLAN configurations
- Requires Trunk Links
- VTP requires trunk links to propagate VLAN information and will not work with access ports
Lab Topology
Scenario: In this lab scenario, we will configure VTP version 3 on all four switches and use the following configuration parameters to ensure switches behave correctly in the VTP domain.
- VTP Domain: NetworkLabs
- VTP Version: Version 3
- VTP Version 3 Authentication
- Verification Show Commands
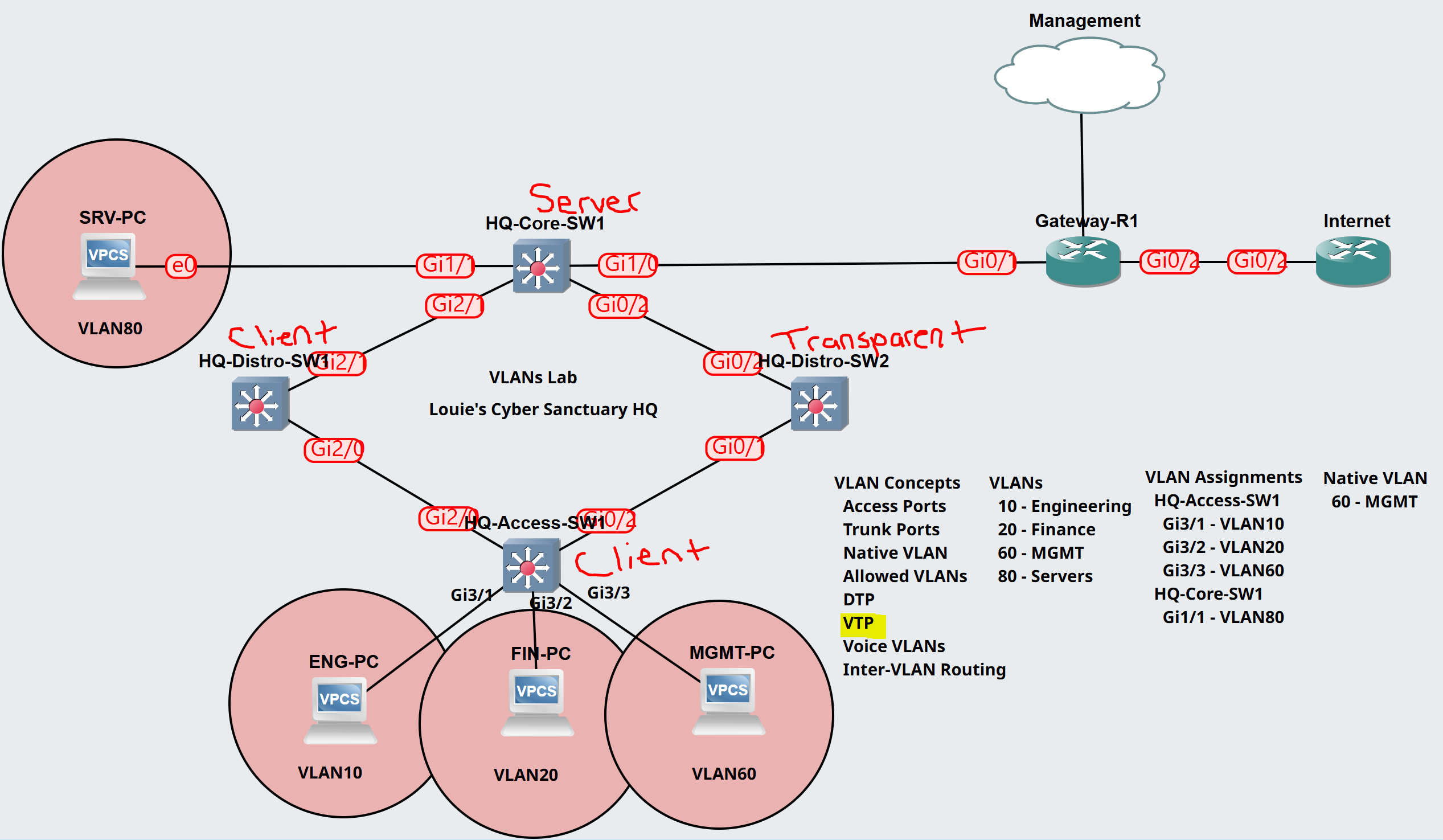
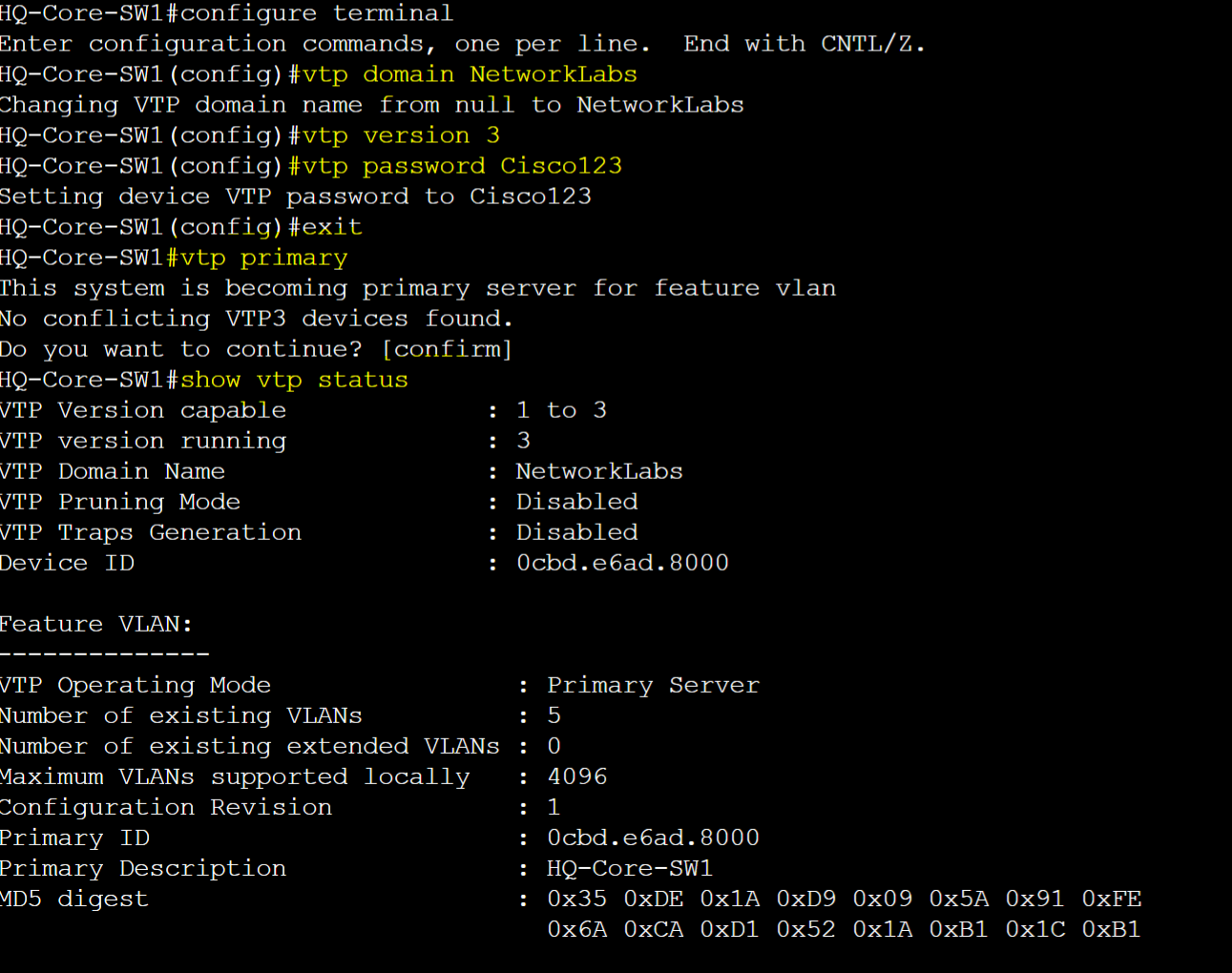
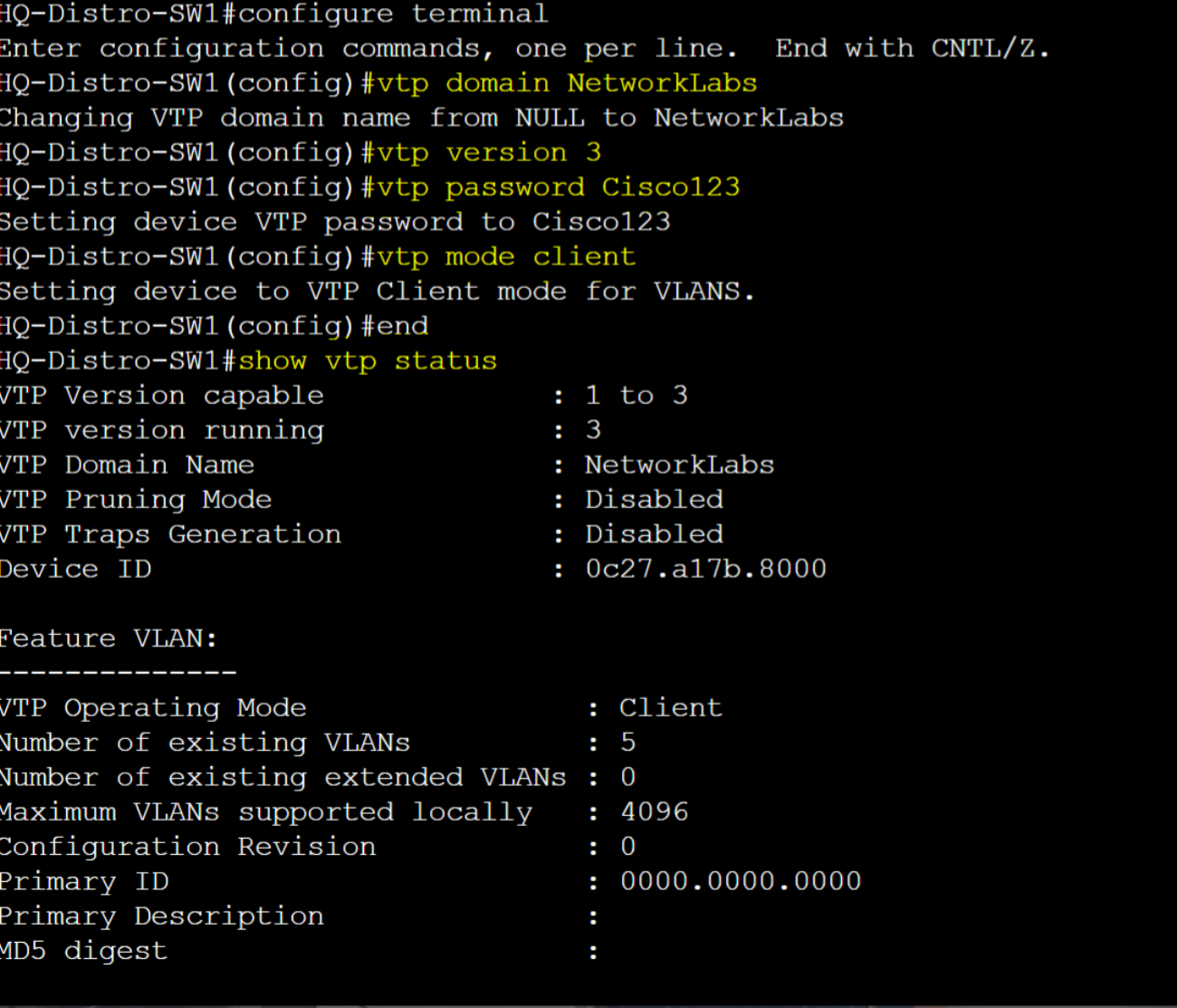
VTP Configuration Setup
HQ-Core-SW1 - Server
HQ-Distro-SW1 - Client
HQ-Distro-SW2 - Transparent
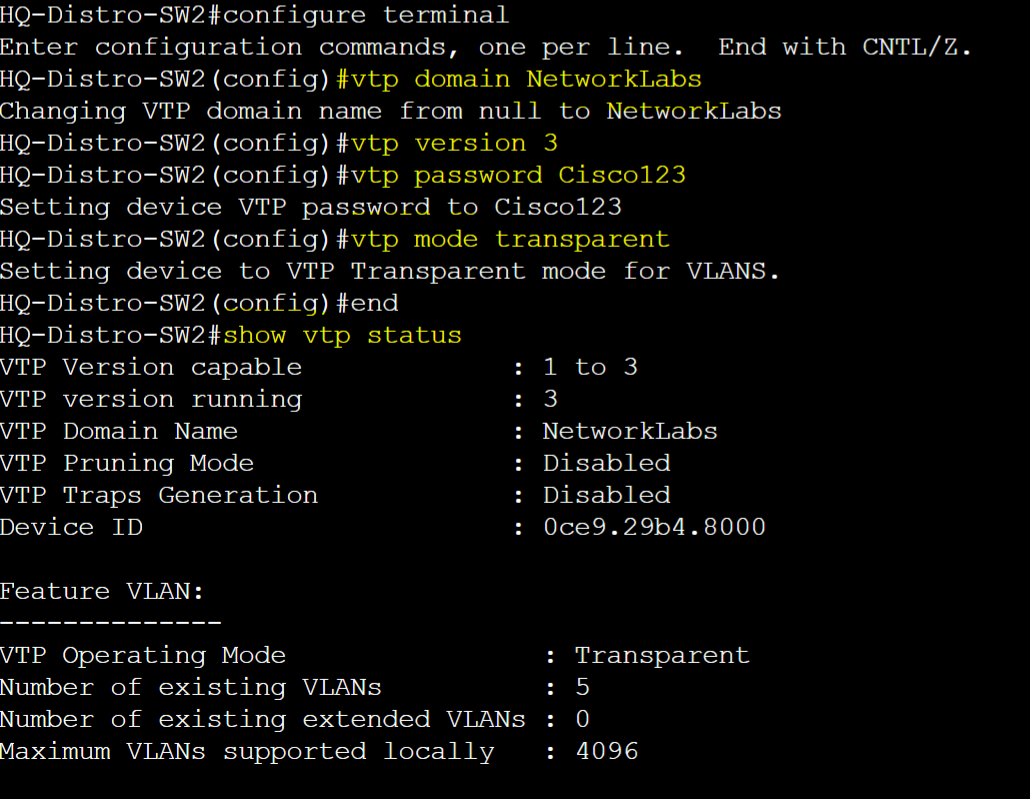
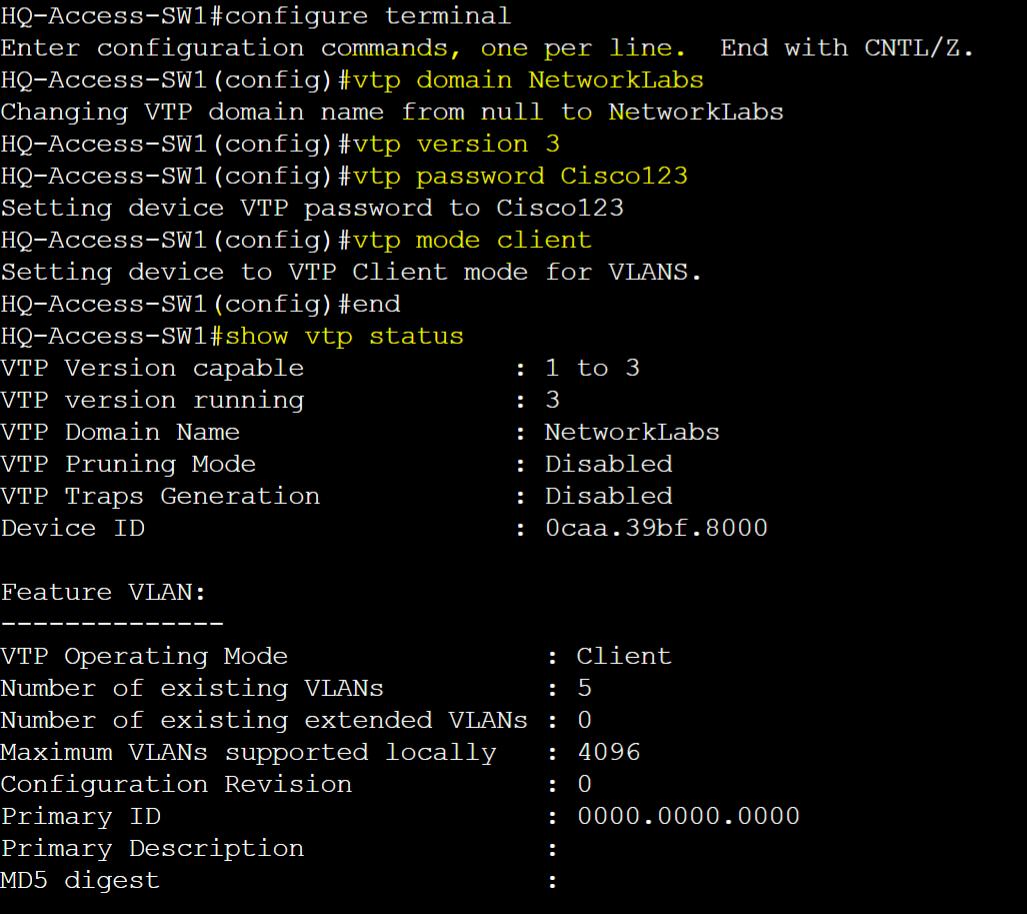
HQ-Access-SW1 - Client
VTP Propagation Configuration
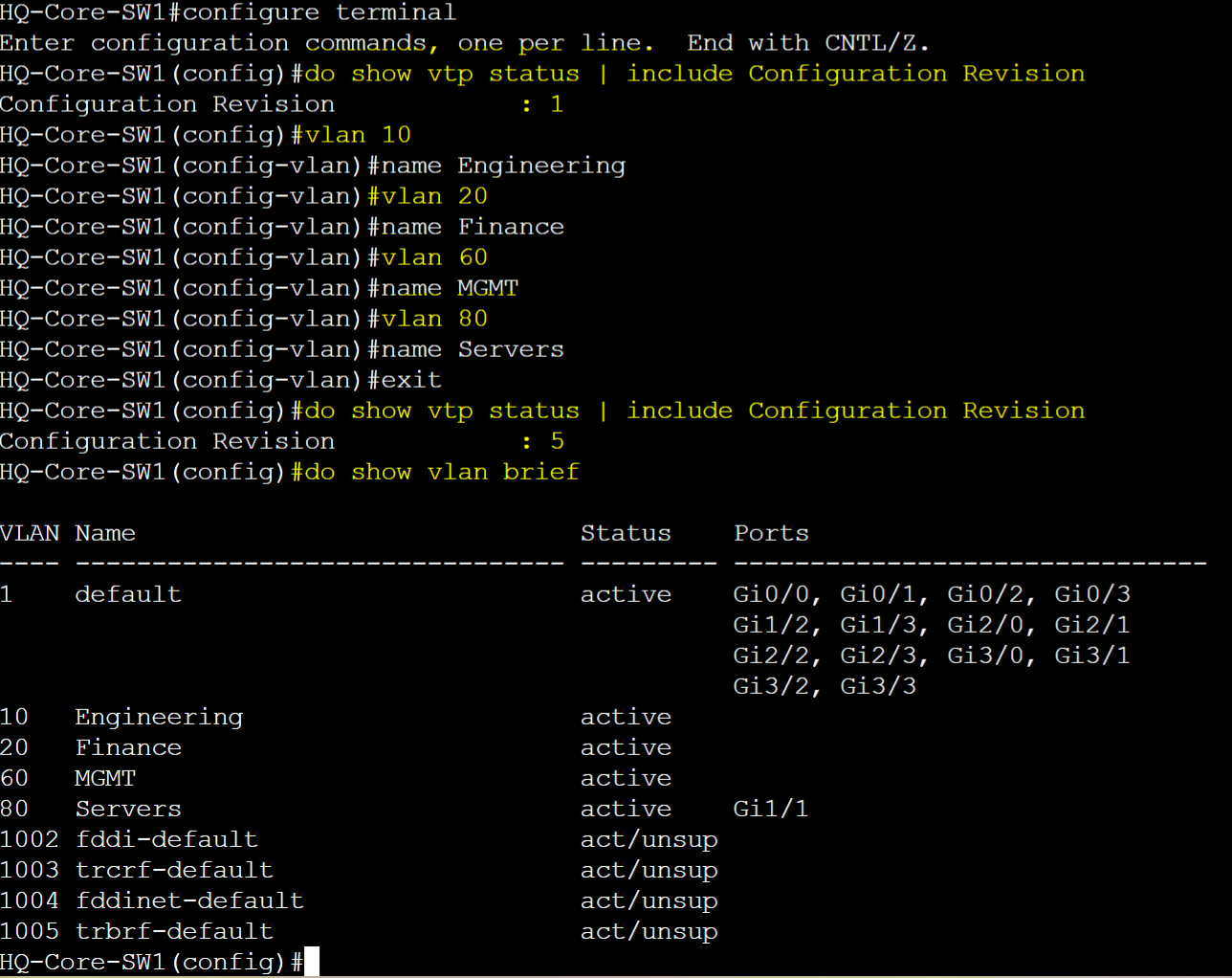
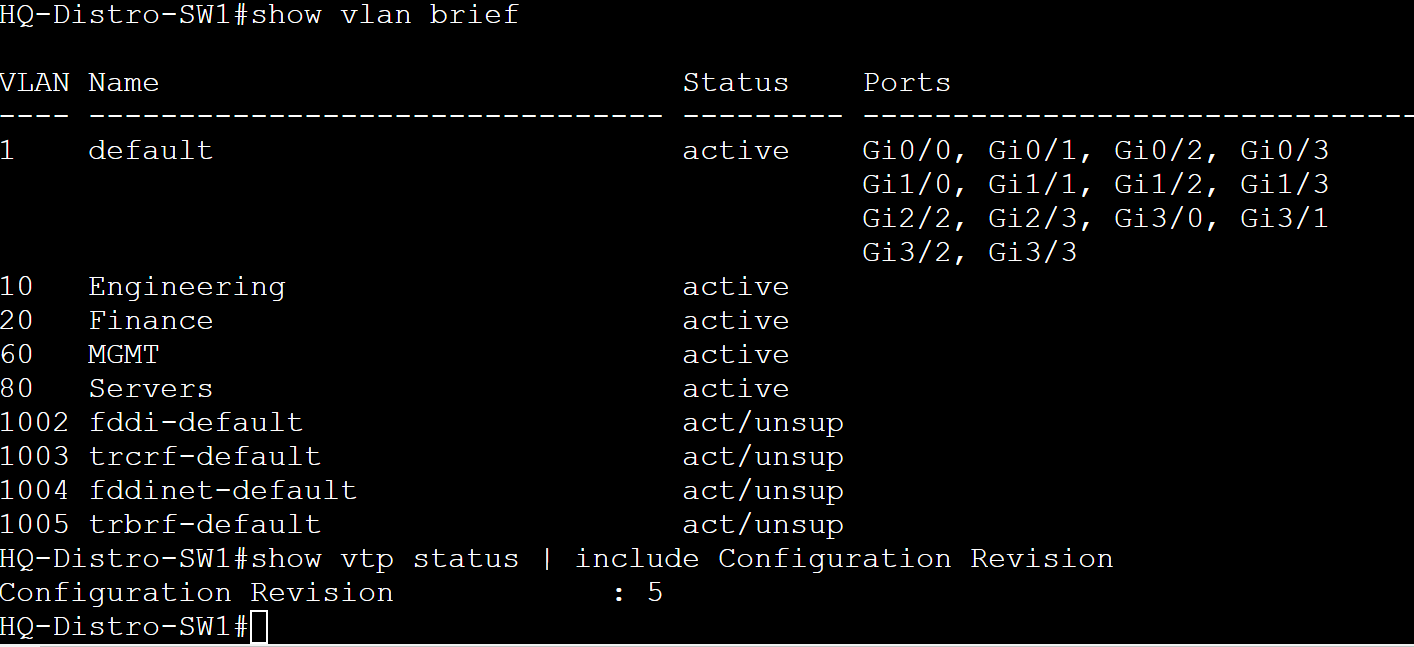
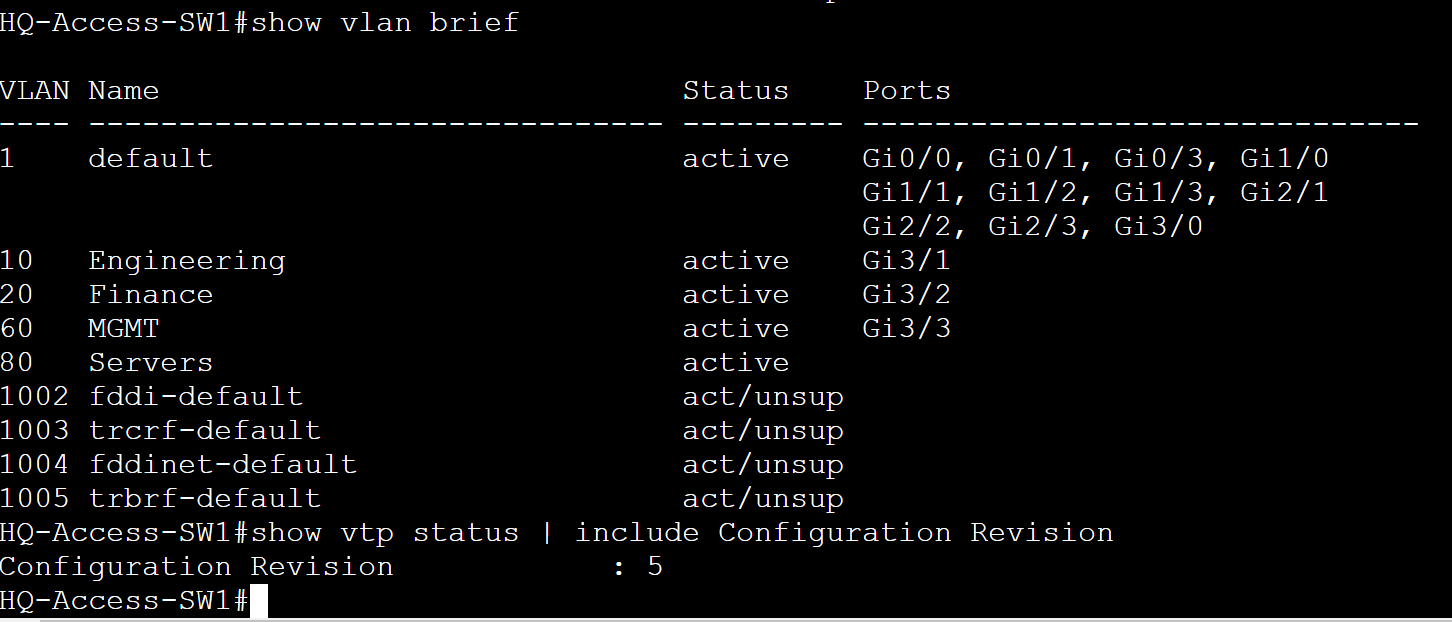
Scenario: In this lab scenario, we will create VLANs on the VTP server HQ-Core-Sw1 and verify the VLANs have been propagated and advertised towards all switches in the VTP domain except for the Transparent switch HQ-Distro-SW2.
HQ-Core-SW1 - Server
HQ-Distro-SW1 - Client
HQ-Distro-SW2 - Transparent
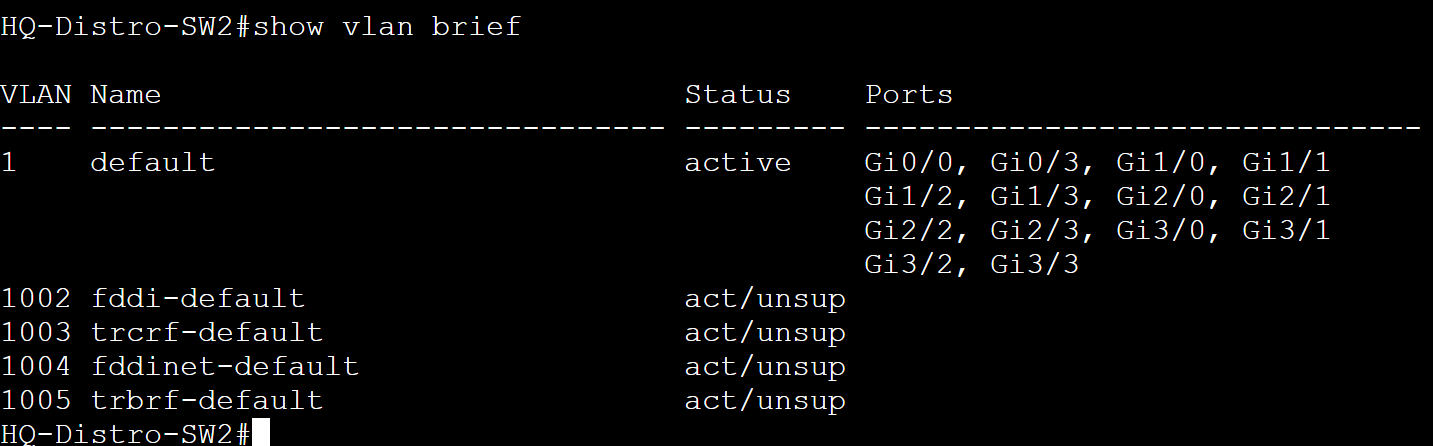
HQ-Access-SW1 - Client
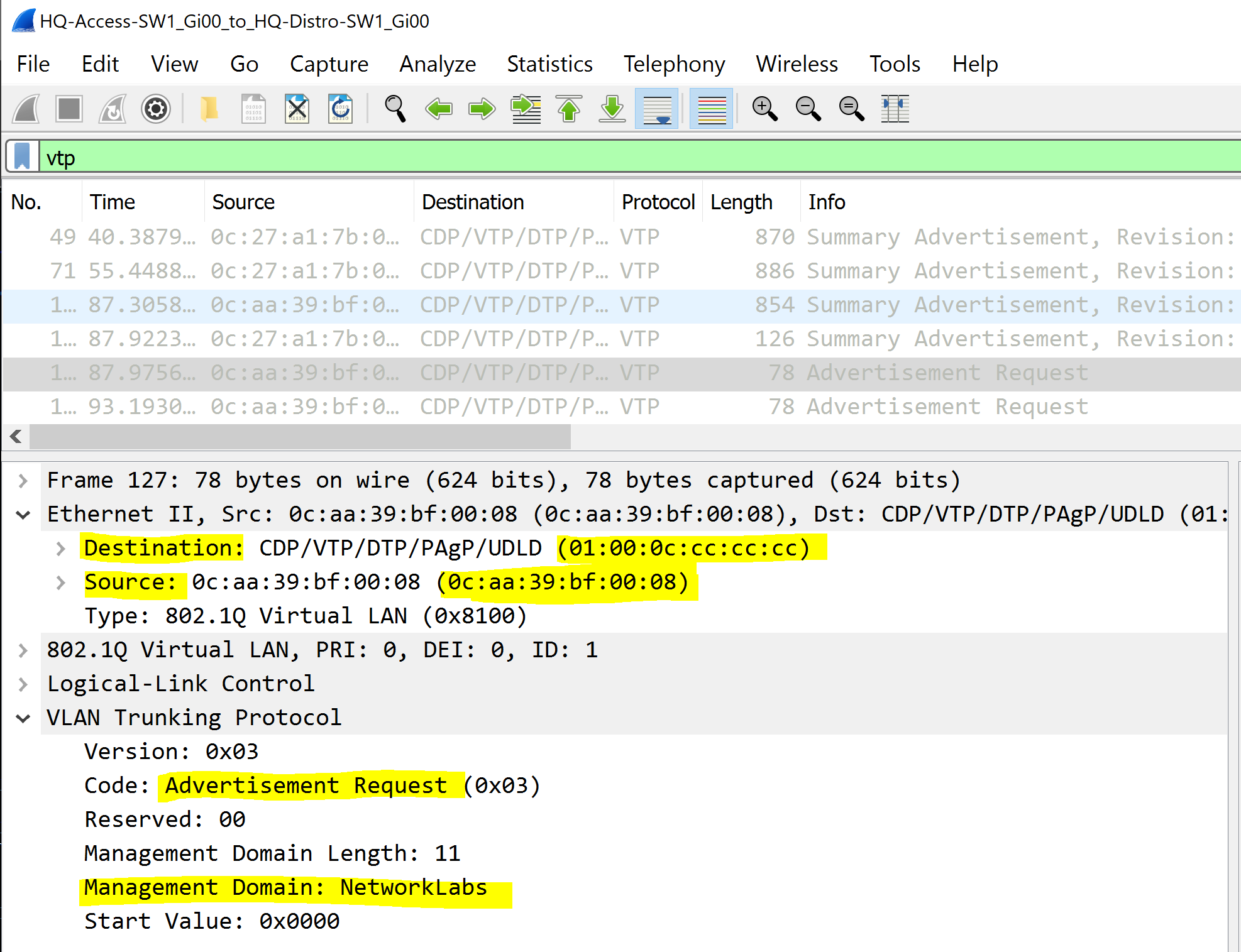
VTP Packet Captures
Scenario:
- In this scenario, we will review the different packet types using our Wireshark Analyzer
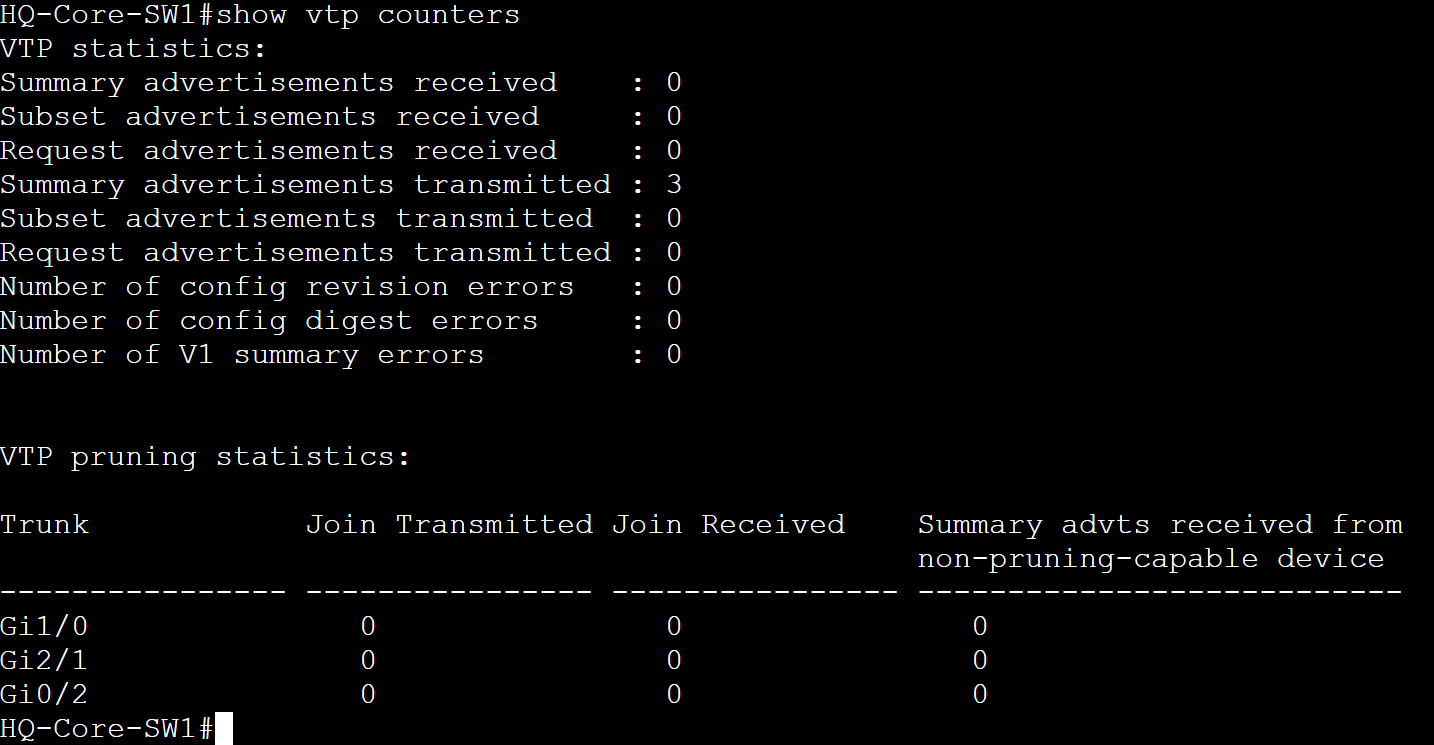
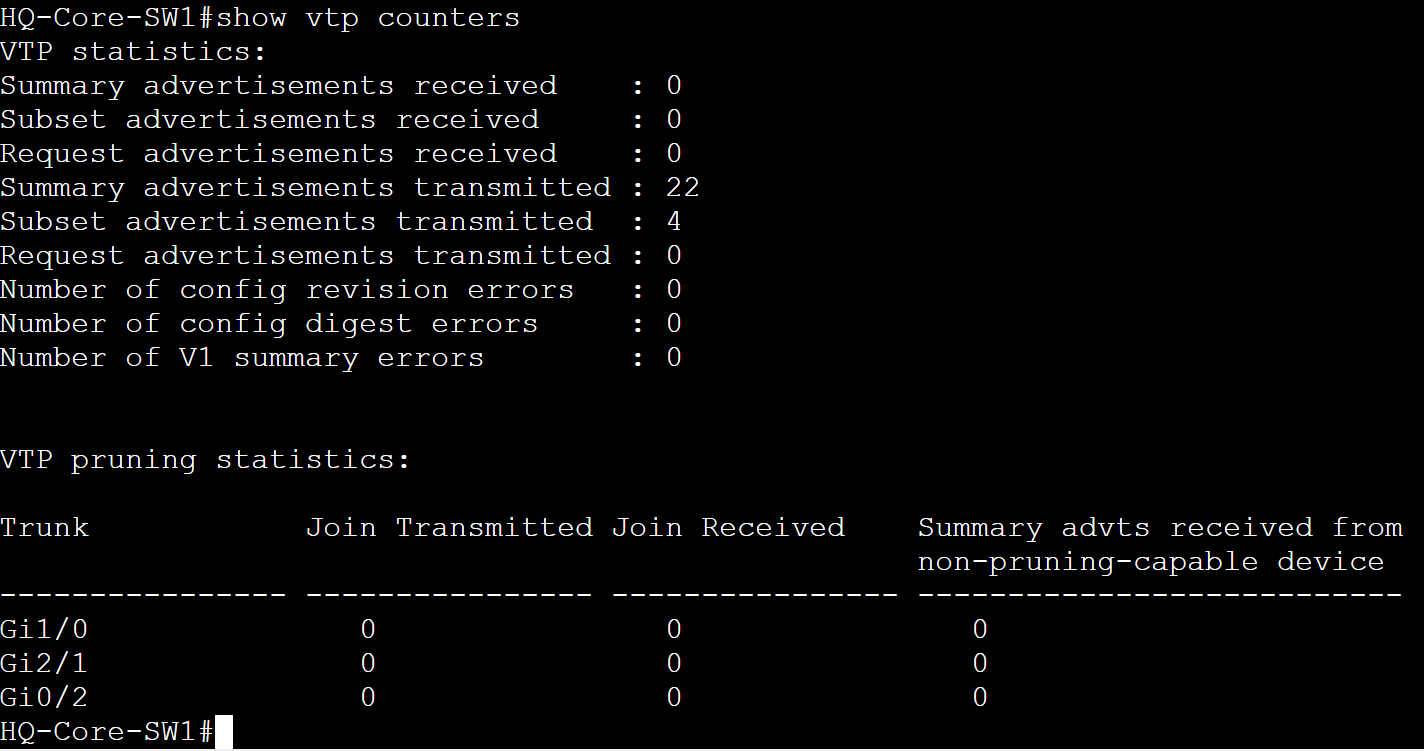
- In the example images below, you can view the VTP counters by using the 'show vtp counters' command
- This command allows you to view the sent and received advertisements and can be used to aid troubleshooting if VLANs are not being propagated towards the switches in the VTP domain
Before VLANs configured on HQ-Core-SW1 Server
After VLANs configured on HQ-Core-SW1 Server
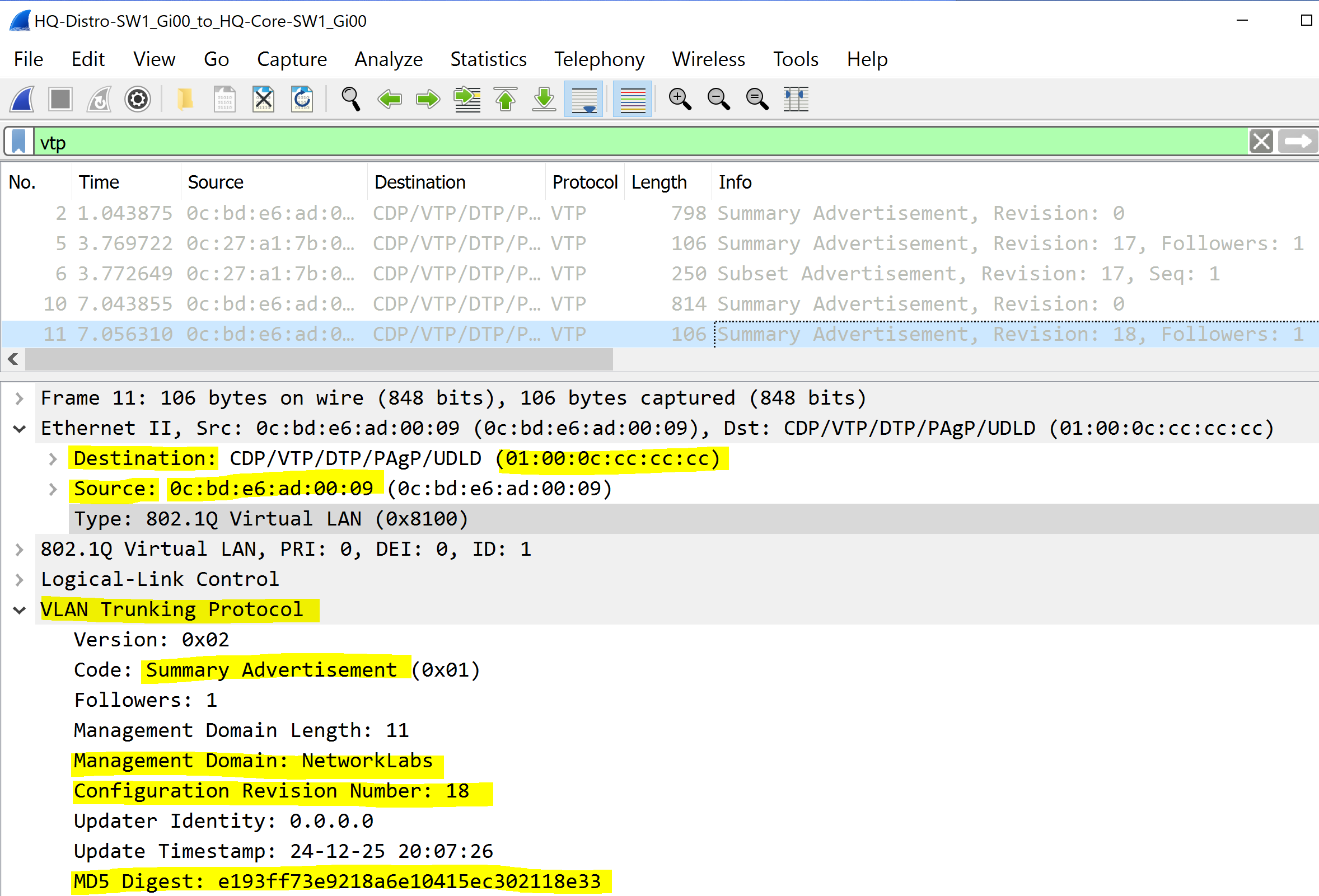
Summary Advertisement
By default Summary Advertisements are sent every 5 minutes or when a change in the VLAN database occurs. Although these summary advertisements don't include the information about the individual VLANs, they include information about the VTP domain and are sent to multicast address 01.00.0c.cc.cc.cc. The MD5 digest is a hash that is used to verify the integrity and authenticity of the VTP messages exchanged between switches.
Global Domain Information
- VTP Domain Name
- VTP Configuration Revision Number
- MD5 Digest VLAN Configuration
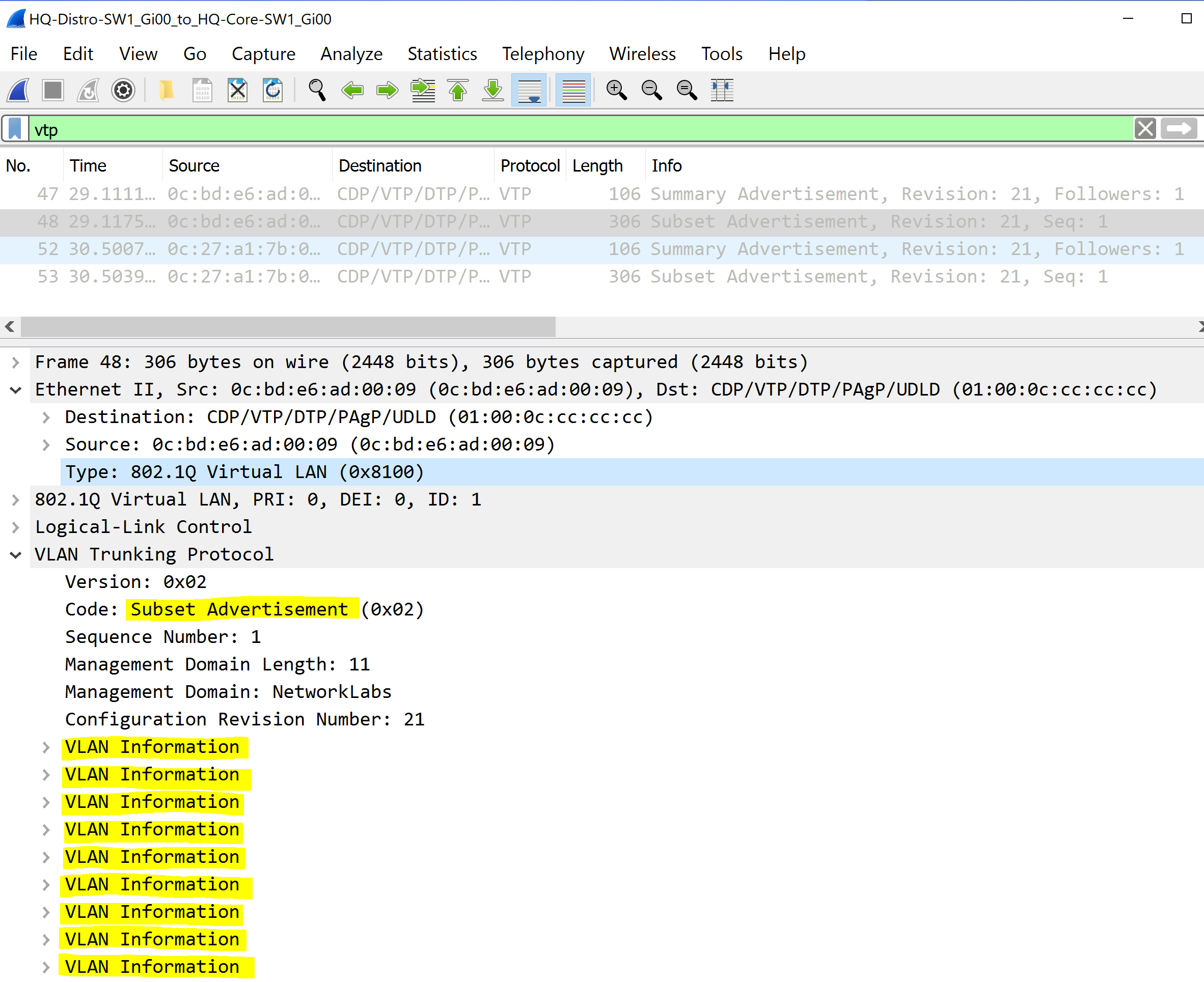
Subset Advertisements
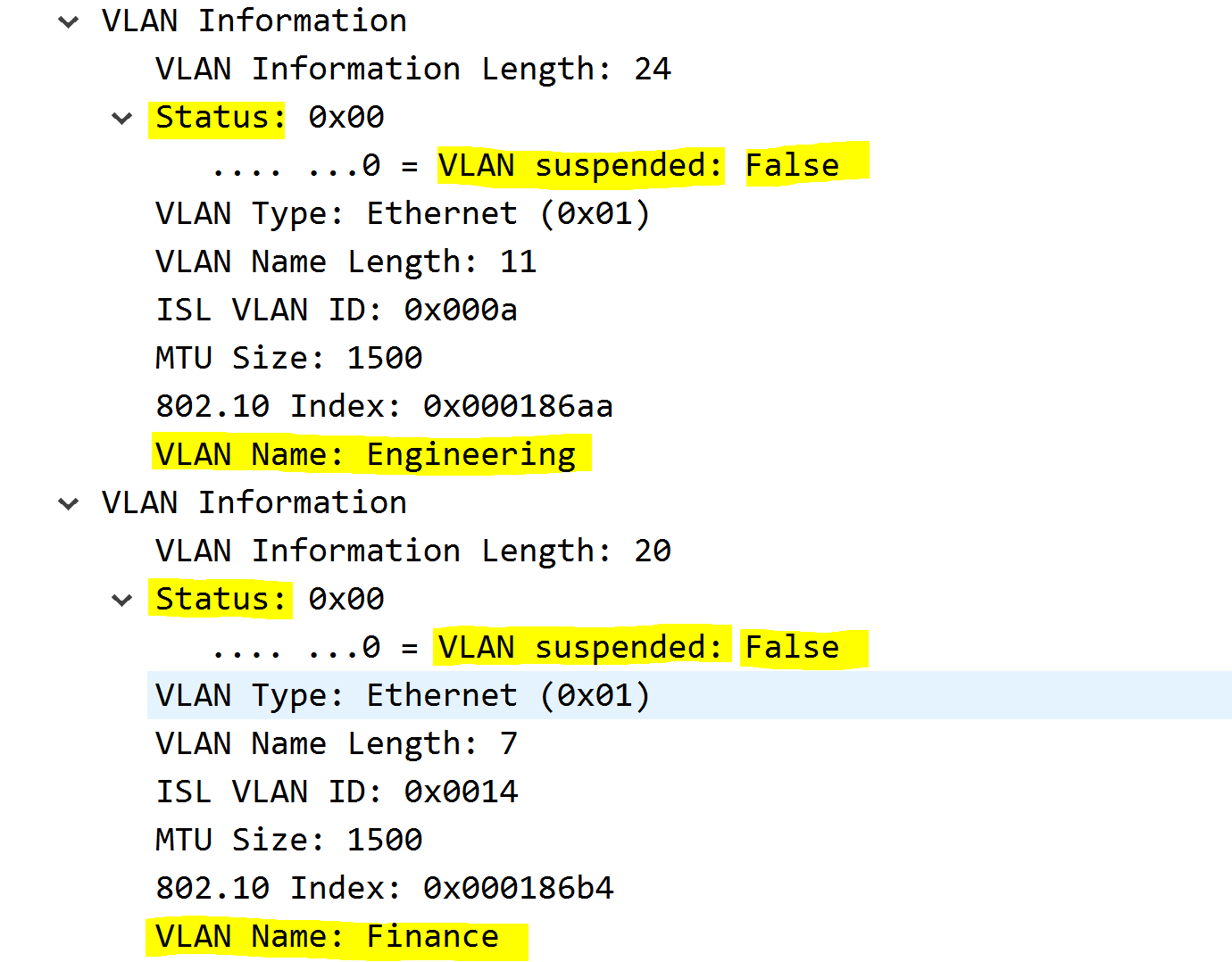
Subset Advertisements follow summary advertisements if there's a change to the VLAN database. These advertisements include the detailed information about the individual VLANs and are sent to the multicast address of 01.00.0c.cc.cc.cc.
VLAN Inforomation
- VLAN IDs
- VLAN Name
- VLAN Type
- VLAN State
Advertisement Requests
Advertisement Requests are sent by a switch when it requires information, prompting other switches in the VTP domain to send summary and subset advertisements. In most cases, this type occurs when a client requests for VLAN information in cases in which the switch lost its VLAN configuration or hears a higher revision number than what is locally stored.