Securing Meraki Wireless Networks
Sections:
- Lab Topology
- Layer 2-3 Firewall Overview
- Layer 2-3 Firewall Configuration
- Layer 7 Firewall Overview
- Layer 7 Firewall Configuration
- Traffic Shaping Overview
Resources:
- MR Firewall Rules
- Wireless Client Isolation
- Traffic & Bandwidth Shaping
- Layer 3 & 7 Firewall Processing Order
- MR Firewall Rules
- Applying Wireless Firewall & DNS Filtering
Overview:
- Meraki access points have a variety of built in security features designed to protect the network and control access
- Meraki access points and MX firewalls can work together to enhance security for your network, with both devices offering complementary features
- In this section, I will demonstrate implementing the available MR features to control access in the lab environment
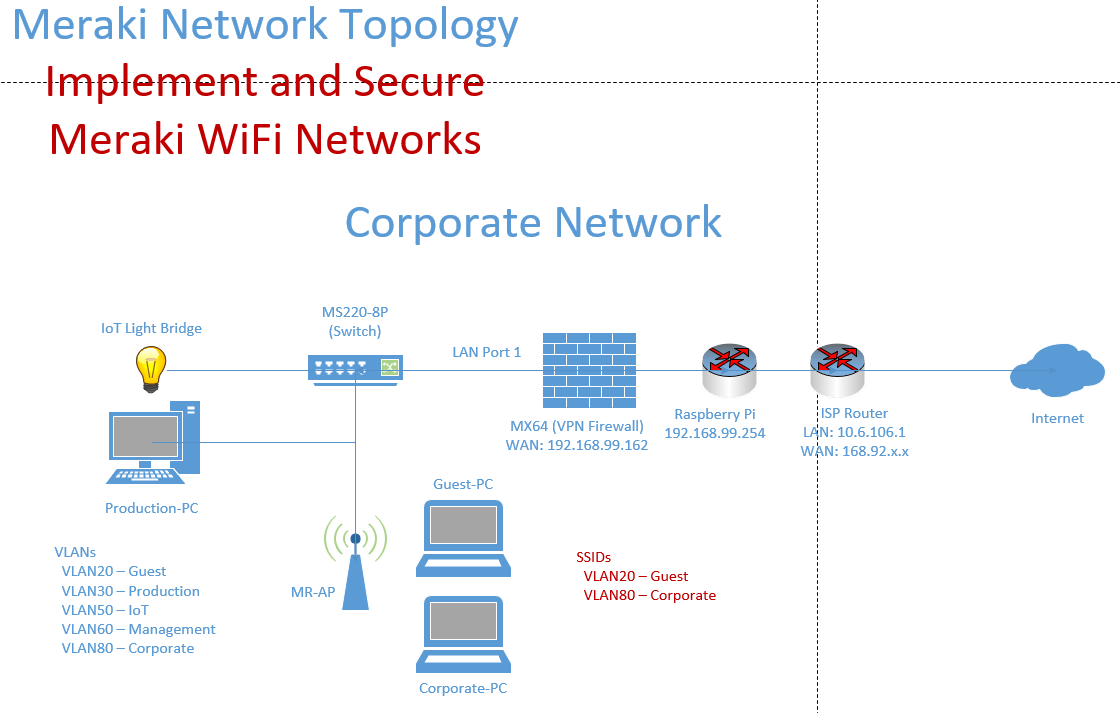
Lab Topology
Layer 2 & 3 Firewall Overview
Overview:
- Cisco Meraki APs provide a range of Layer 2 and Layer 3 security features to ensure that the wireless network is secure from unauthorized access
- In this section, I will go over the available settings for the Layer 2 and 3 security features of a Meraki MR access point
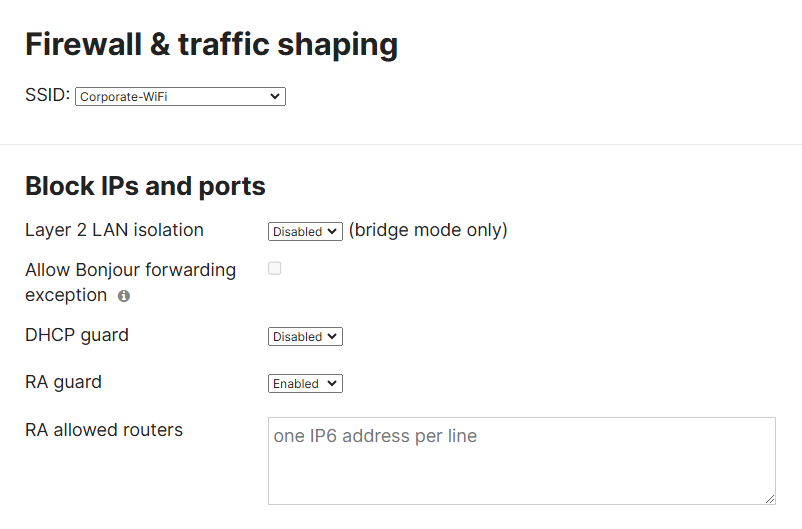
Firewall & Traffic Shaping Menu
Overview of Settings
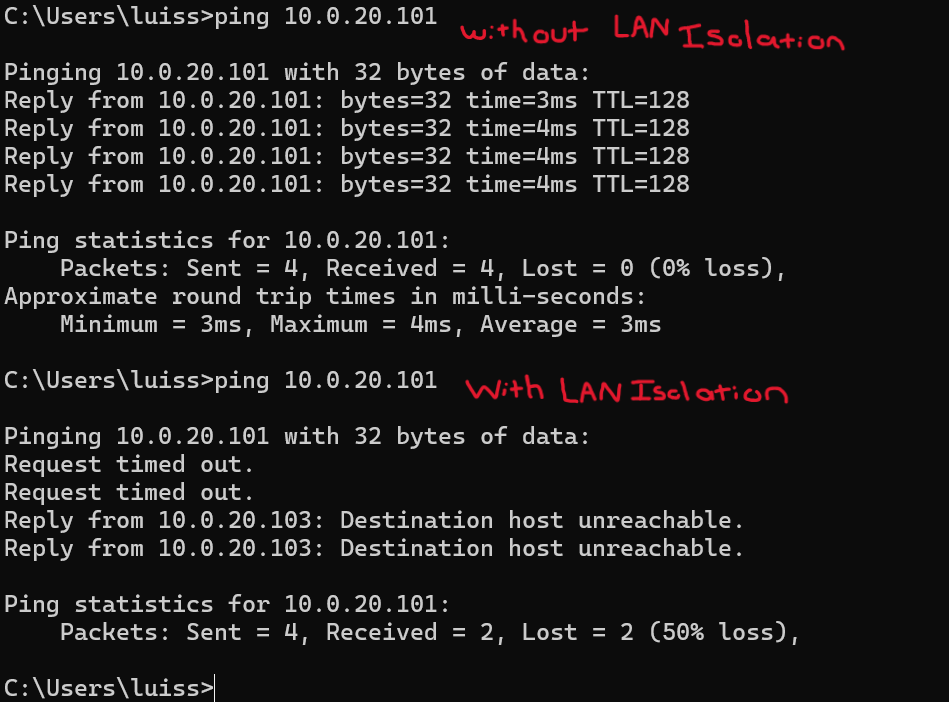
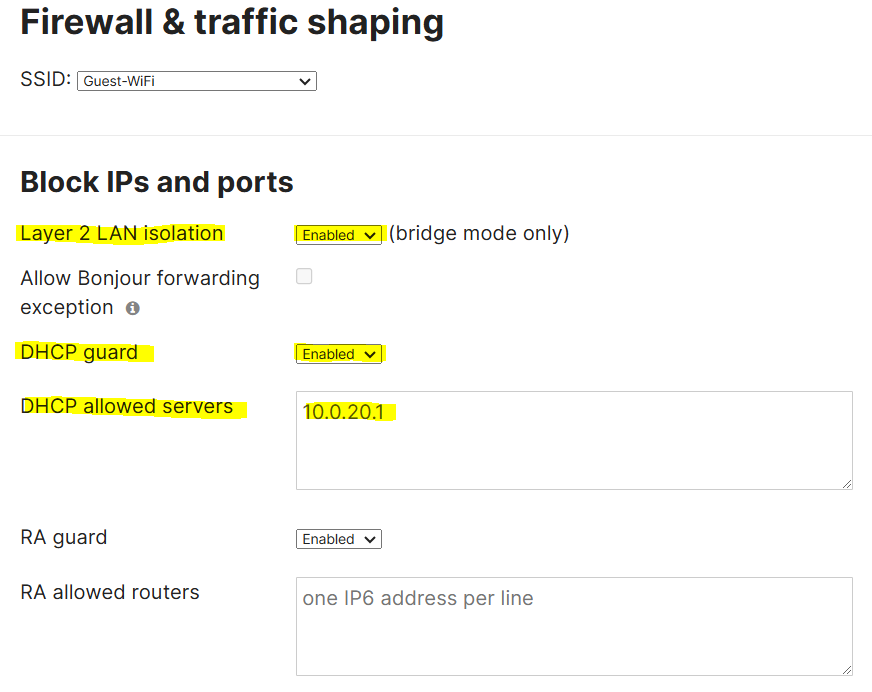
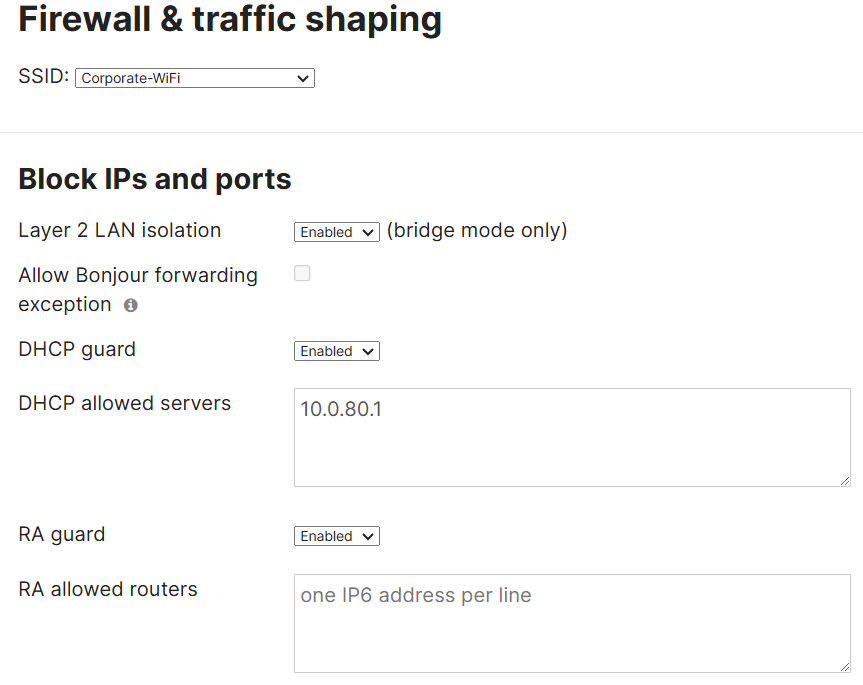
Layer 2 LAN Isolation
- When enabled, this feature prevents clients from communicating with one another on the same SSID
- Useful in public networks or guest access environments where you don't want clients to interact with one another
- This feature isolates clients at the data link layer, meaning they can't send traffic directly to each other even if on the same VLAN
Allow Bonjour Forwarding
- Also known as Apple's Zero Configuration Networking protocol, this feature allows Apple devices to discover each other including printers, file sharing, and AirPlay
- Bonjour Forwarding allows traffic to be forwarded between VLANs or subnets on the network
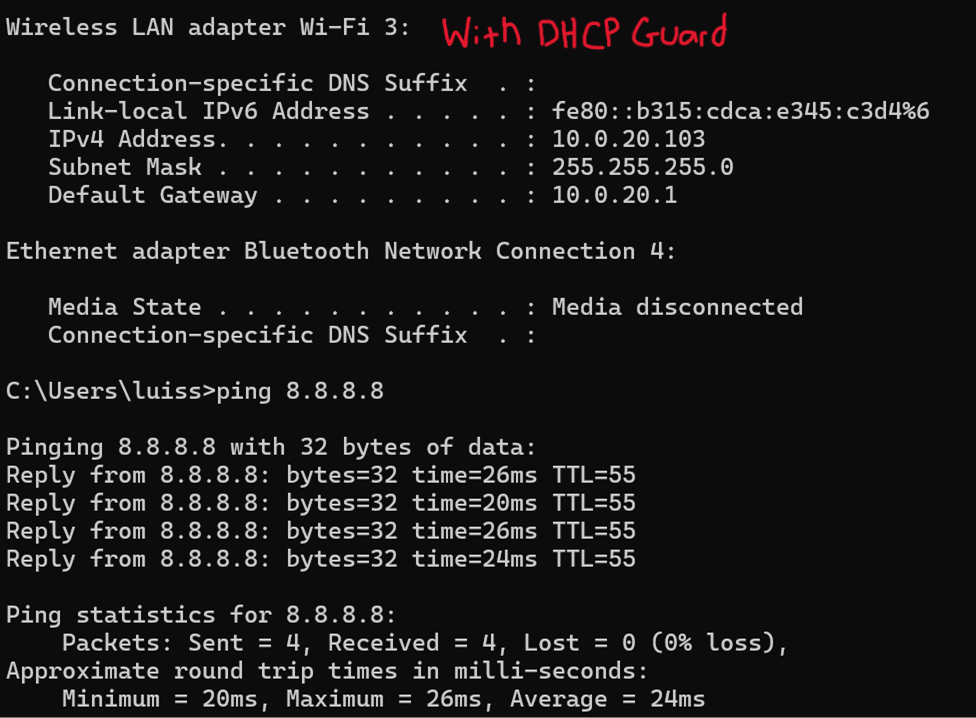
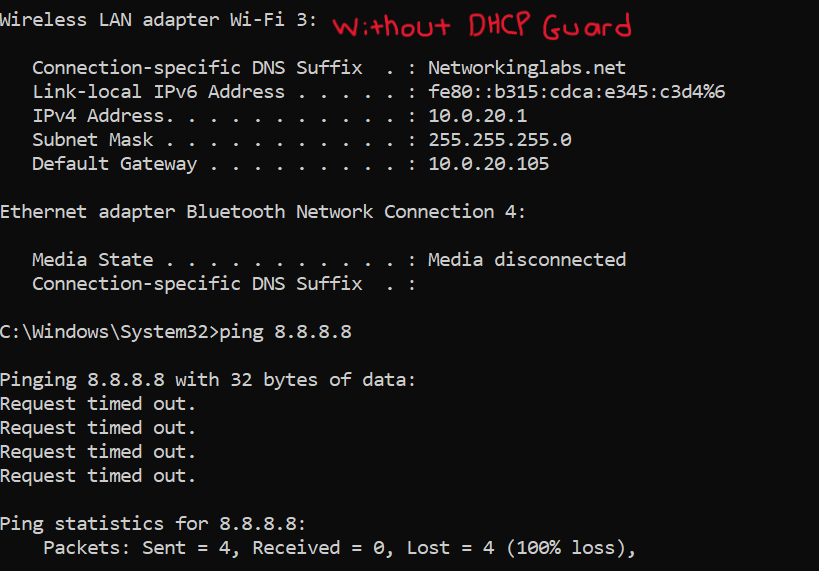
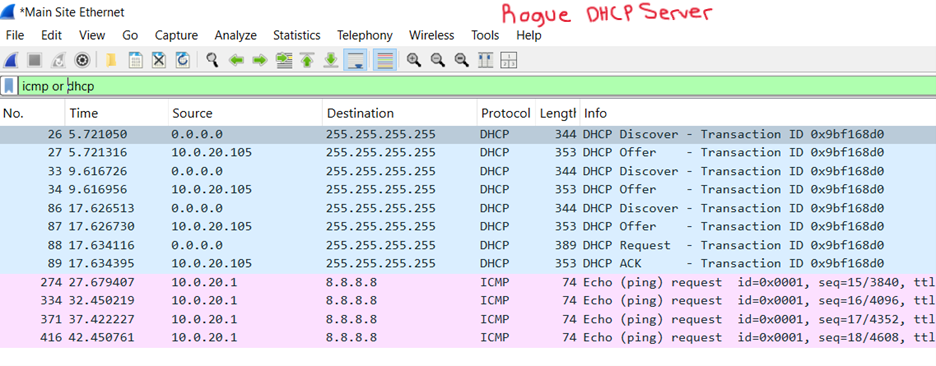
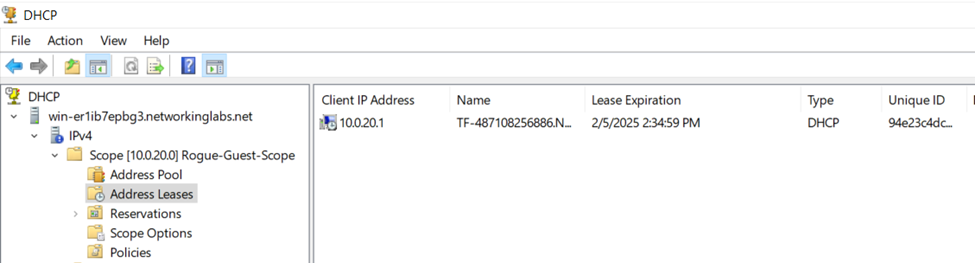
DHCP Guard
- DHCP Guard is a security feature that is designed to prevent rogue DHCP servers from operating on the network and handing out DHCP leases
- This feature ensures only the legitimate DHCP server is providing IP addresses to clients
RA Guard
- RA Guard or Router Advertisement Guard on a Meraki MR access point is a security feature designed to protect the network from rogue router advertisements in IPv6 networks
- In an IPv6 network, RAs are sent by routers to advertise information about the network such as the IP prefixes that devices can use, the default gateway, and other configuration information like DNS servers
- It's important to note that IPv6 networks do not use IPv4's ARP protocol and as a replacement, rely on RA and NS messages
RA Allowed Routers
- Used in conjunction with RA Guard, this feature is used to specify which devices are allowed to send RA messages in an IPv6 network
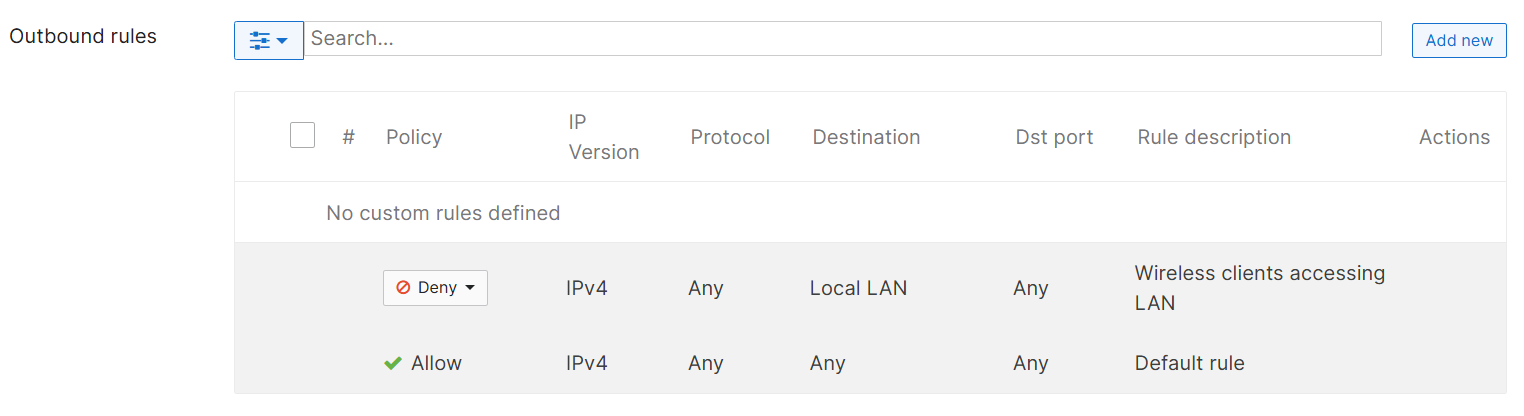
Outbound Rules
- The layer 3 firewall ACL ruleset table
- An admin can define a set of firewall rules that is evaulated for every request sent by a wireless user associated to that SSID
- These layer 3 rules are evaluated from top to bottom like a typical Cisco ACL
- Unlike the 'stateful' nature of the Meraki MX appliances, MR access points are 'stateless' in nature and can be based on destination address and port
Layer 2 & 3 Firewall Configuration
Overview:
- In this lab exercise, I will be enabling LAN isolation for the Guest & Corporate wireless networks in addition to DHCP Guard
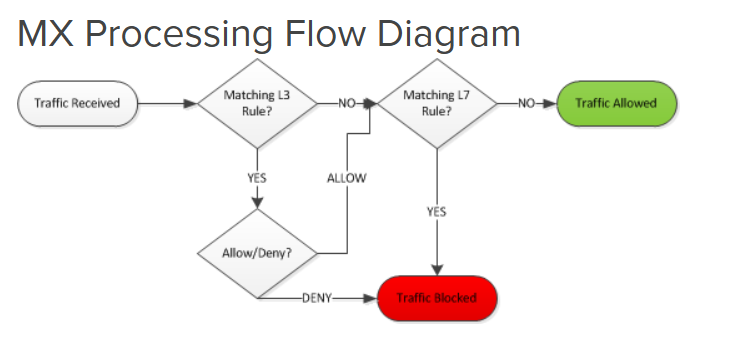
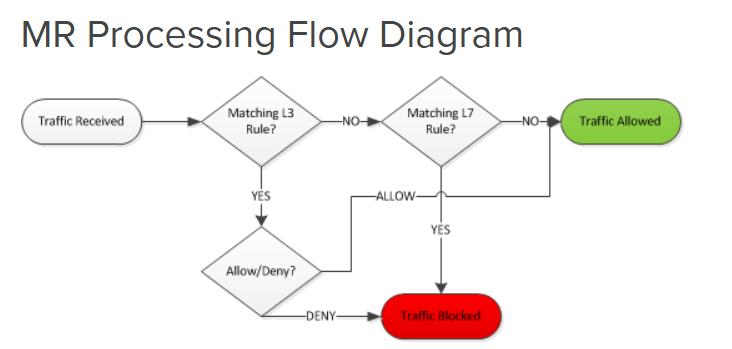
- When defining Layer 3 and 7 rules, it's important to understand the processing logic of the rules as they differ between the MX security appliances and MR access points
- On an MR access point, the default layer 3 rules do not act as a bypass for layer 7 rules. Traffic that matches a custom defined layer 3 rule will automatically bypass layer 7 rules
- As for an MX security appliance, if traffic matches an allow rule on the layer 3 firewall, it can still be blocked by a layer 7 rule
- For this lab exercise, I will leave the default layer 3 firewall rules for each SSID to demonstrate the layer 7 rules in the next section
MR vs MX Processing Flow Diagram:
Guest Wireless Configuration
Corporate Wireless Configuration
Layer 7 Firewall Overview
Overview:
- The Cisco Meraki MR access points include integrated layer 7 firewall capabilities offered through the Meraki Dashboard
- The Layer 7 firewall, also known as an application layer firewall, allows for traffic filtering based on the application type rather than just IP addresses and ports
- In this section, I will go over the available settings for the Layer 7 capabilities of a Meraki MR access point
Overview of Settings
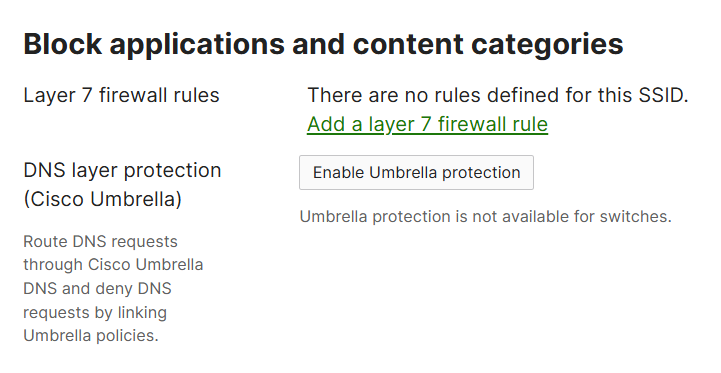
Layer 7 Firewall Rules
- Meraki MR access points allow you to implement Layer 7 firewall rules to control traffic based on application types
- These rules go beyond traditional IP-based firewall filtering and enable you to define policies based on the type of application traffic rather than just source/destination IPs or ports
- This feature can be useful when applications use multiple or changing IP addresses or port ranges
- Firewall rules can be applied for a given SSID or as part of a group policy
DNS Layer Protection (Cisco Umbrella)
- This feature provides an additional layer of security by leveraging Cisco Umbrella's cloud based DNS filtering capabilities
- This feature helps protect your network by blocking access to malicious websites and domains at the DNS layer before a device connects to harmful content
Layer 7 Firewall Configuration
Overview:
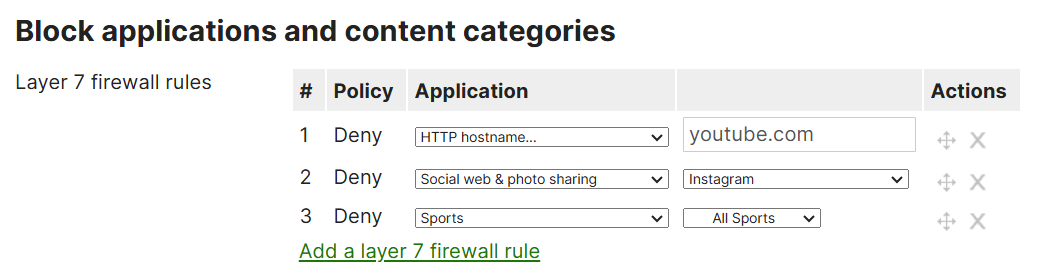
- In this lab exercise, I will be configuring application layer firewall rules for the wireless Guest and Corporate networks
- Based on the snippet below, I will restrict certain categories of websites that are not allowed to be accessed by clients in this lab environment from both networks
- Cisco Meraki offers different 'Application' types including the general categories to define these rules including the following:
- Port
- HTTP Hostname
- Remote IP Range
- Remote IP Range & Port
Guest & Corporate Wireless Configuration
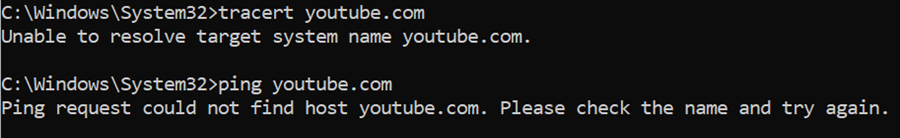
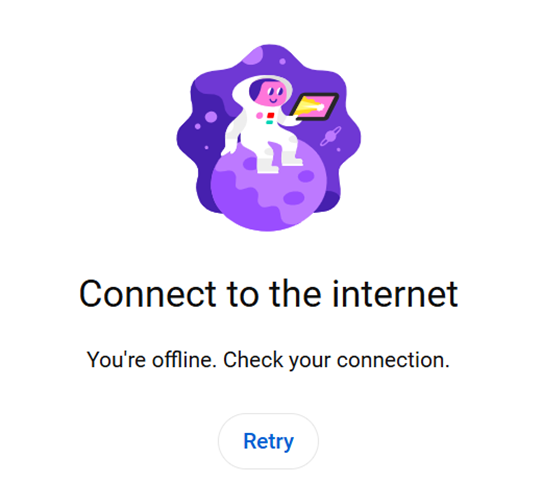
Verification
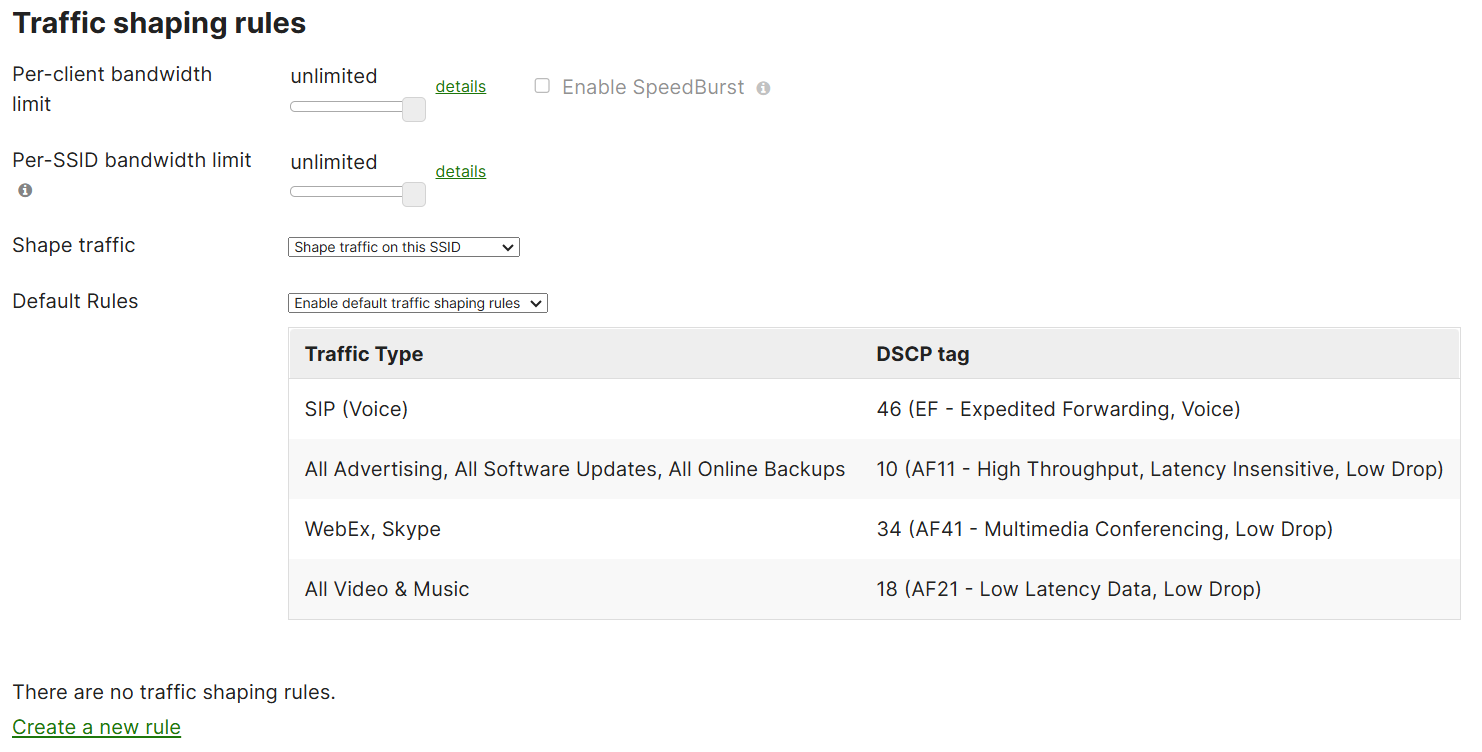
Traffic Shaping Overview
Overview:
- Bandwidth and Traffic Shaping ensures that users do not consume more bandwidth than they should
- Administrators can create shaping policies to apply per user on a per-application basis
- Traffic shaping rules for applications are applied per flow (setting a 5Mbps bandwidth limit to three different applications will allow 5Mbps down to each application)
- Custom defined traffic shaping rules may be used with or without the default rules being applied
Overview of Settings
Per-Client Bandwidth Limit
- This setting allows you to set a maximum upload or download rate per client device connected to the access point
Per-SSID Bandwidth Limit
- This setting allows you to set a total amount of bandwidth available to users on a particular SSID
Shape Traffic
- This setting allows you to enable or disable traffic shaping based on the traffic shaping rules
Default Rules
- Cisco Meraki's default QoS rules for traffic type and DSCP priority tags