Configuring General Settings
Sections:
- Renaming Network Settings
- Traffic Analysis Settings
- Device Configuration Settings
- Reporting Settings
- Firmware Upgrade Settings
Resources:
- Renaming Network Settings
- Traffic Analysis Settings
- Device Configuration Settings
- Reporting Settings
- Firmware Upgrade Settings
Overview:
- In Cisco Meraki, the Network-Wide General settings refer to the global settings that apply to the entire network, impacting all the devices within the network
- These settings are found under the Network-Wide section of the Meraki Dashboard and are essential for managing the overall behavior, security, and configuration of the network
- In this section, I will give a brief explanation of the available Network-Wide General settings that can be modified within the Meraki Dashboard
General Settings Overview
General Page Menu
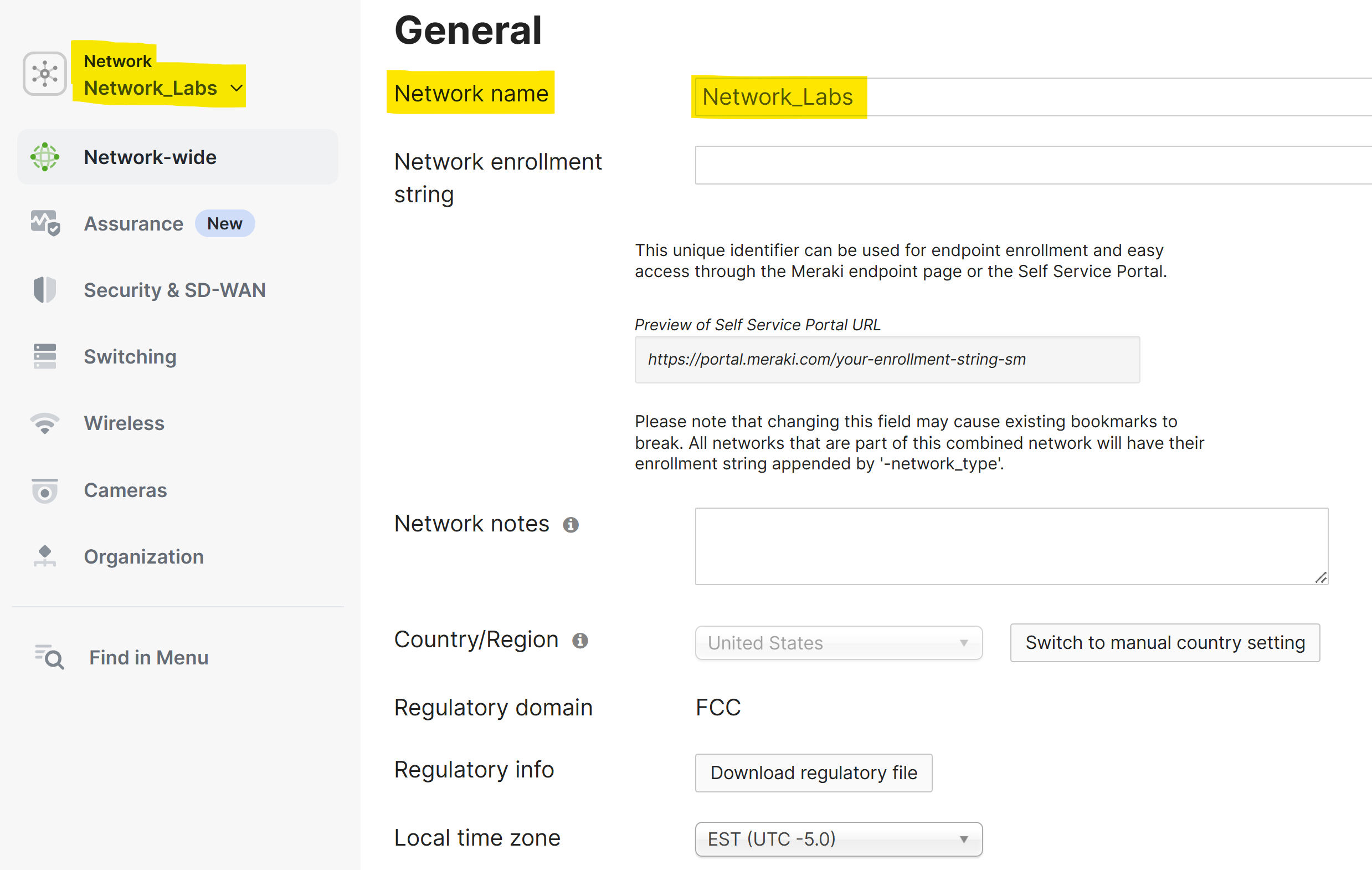
Renaming a Network or Organization
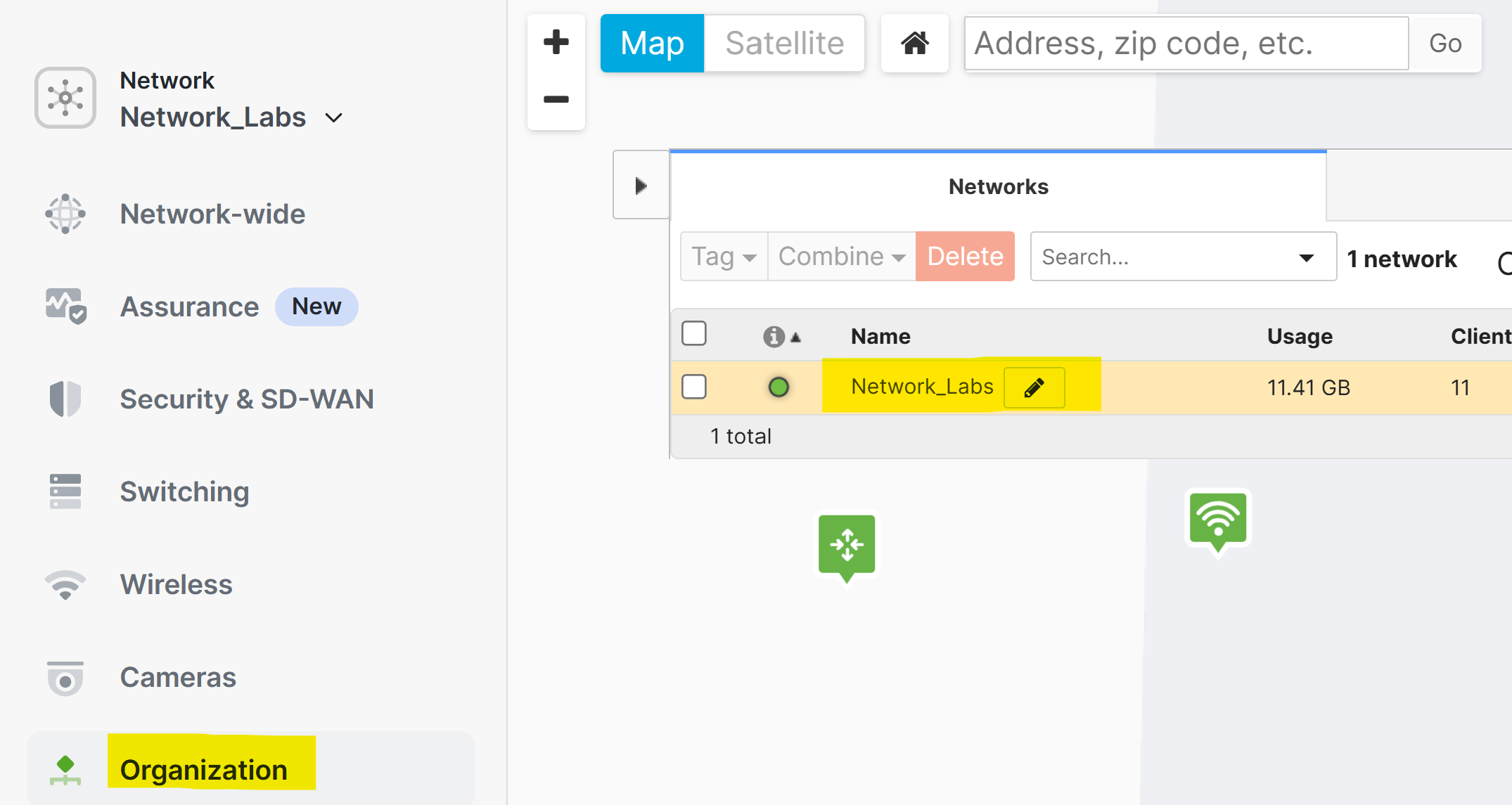
- Renaming a network or organization refers to changing the name used to identify a specific network or organization within the Meraki Dashboard
- This is useful for better organization, especially if you have multiple networks or organizations, or if the existing names no longer match the network's current purpose or location
- Methods to Update Network Name
- Network Wide General Settings Page
- Organization Wide Overview or Settings Page
- Additional Network Wide Network Settings
- Network Notes
- Country/Region
- Local Time Zone
General Network Specific Settings - Renaming Network
General Network Specific Settings - Renaming Network
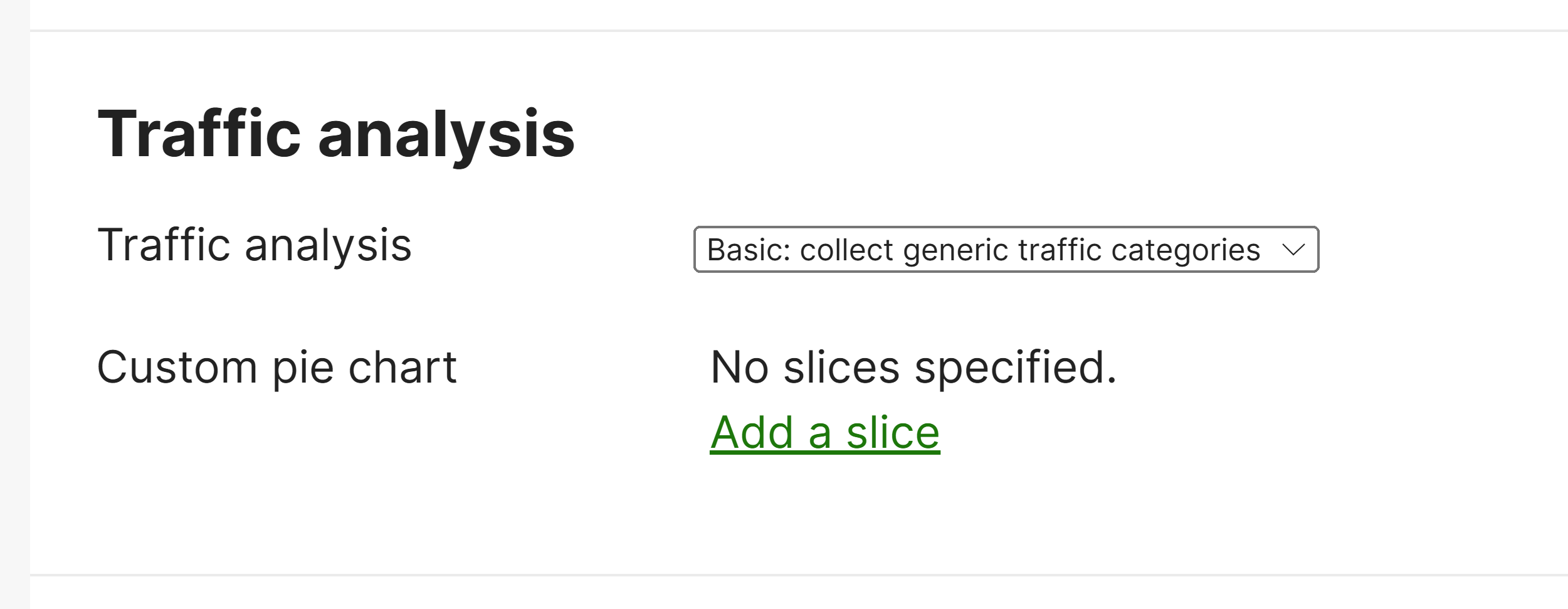
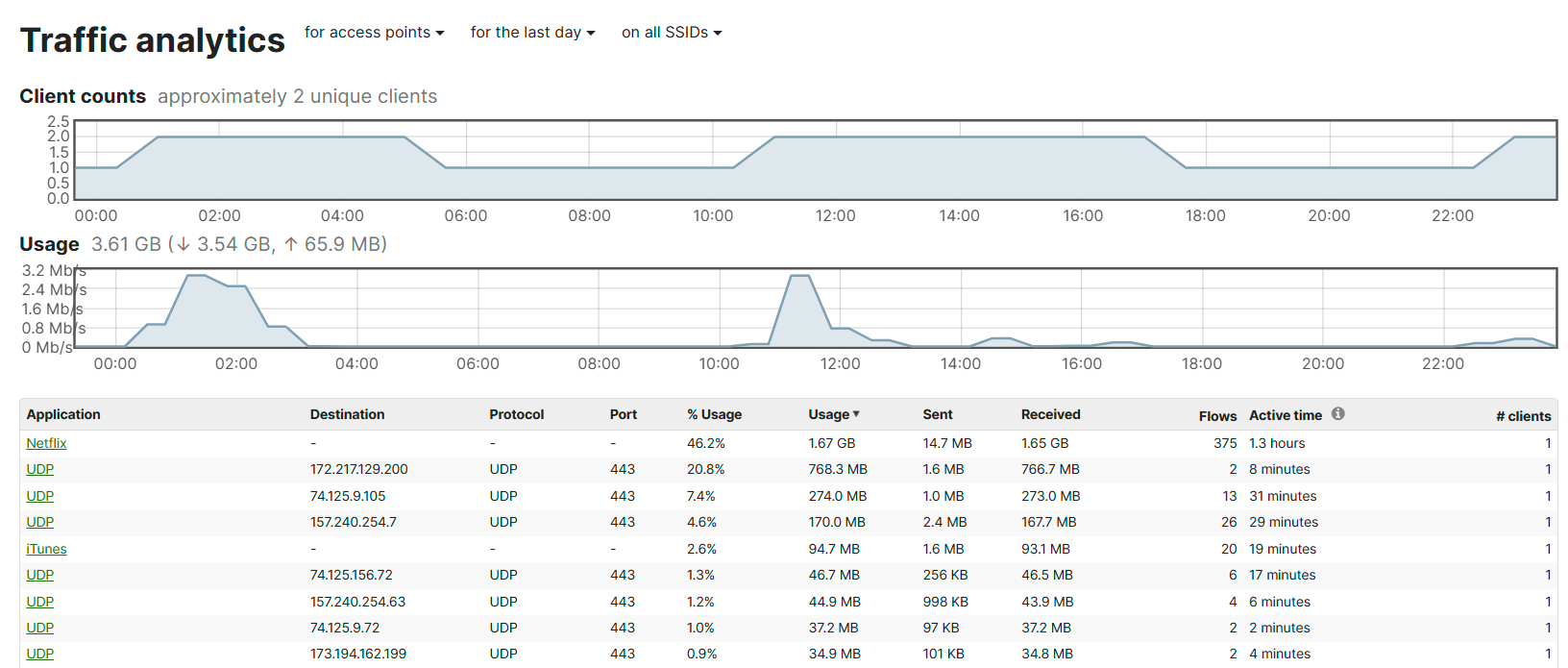
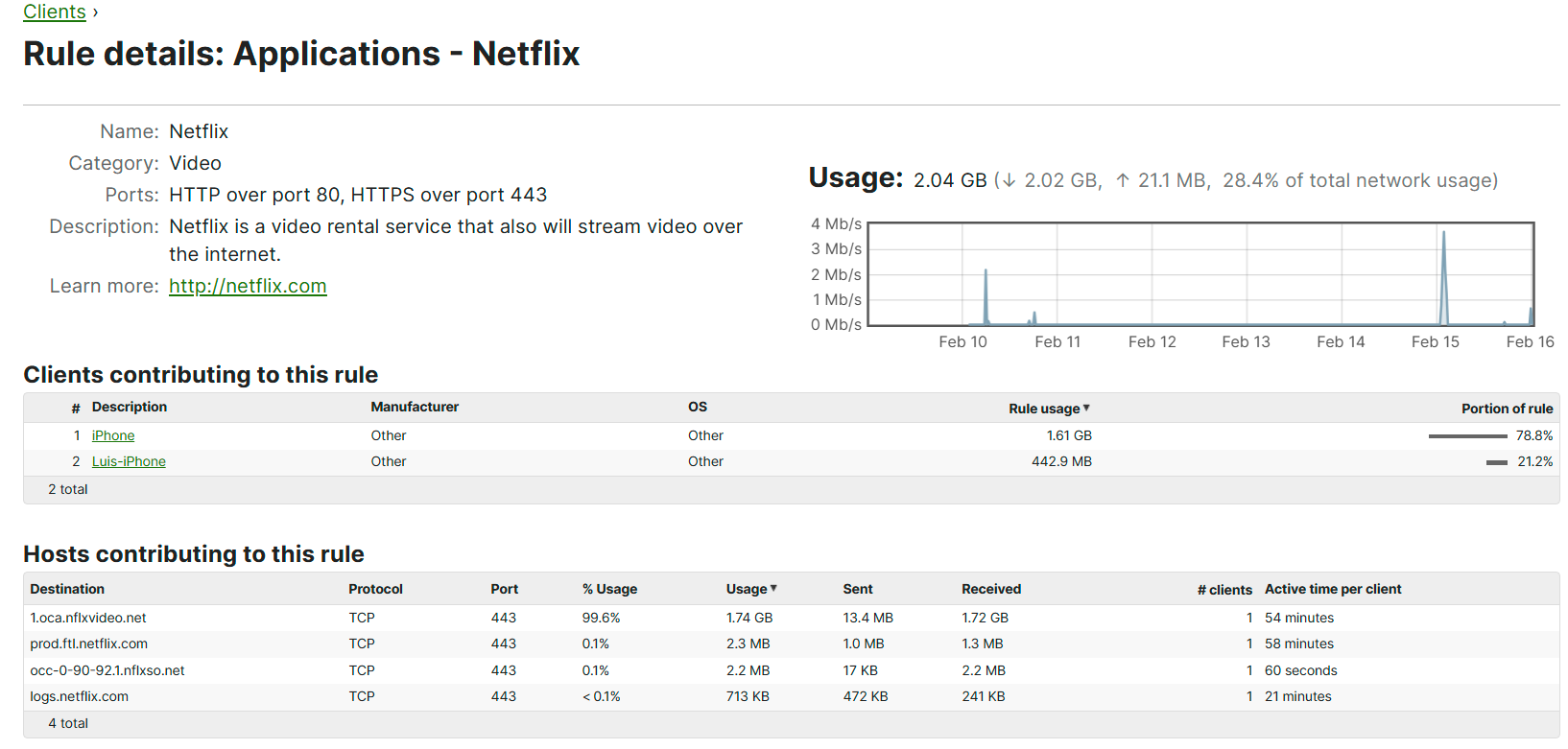
Traffic Analysis
- Per Cisco, traffic classification capabilities are useful as they seek insights into what hosts on the network are doing and for being able to prioritize or block specific applications
- These classifications are generally used by Layer 7 firewall and traffic shaping configurations
- Per Cisco, when enabling this feature in the Network-Wide General Settings page, the data displayed for traffic analytics is only collected after the enablement of this feature. Data prior to that point will not be available with the exception of pre-existing traffic flows. Once enabled, it may take up to 24 hours for information to fully propagate
- Meraki Traffic Classification Techniques
- HTTP traffic for hostnames
- SSL URL Inspection
- Traffic based on IP Address, Port, and Protocol Information
- IP Address to DNS hostname mapping
- Application Heuristic Information
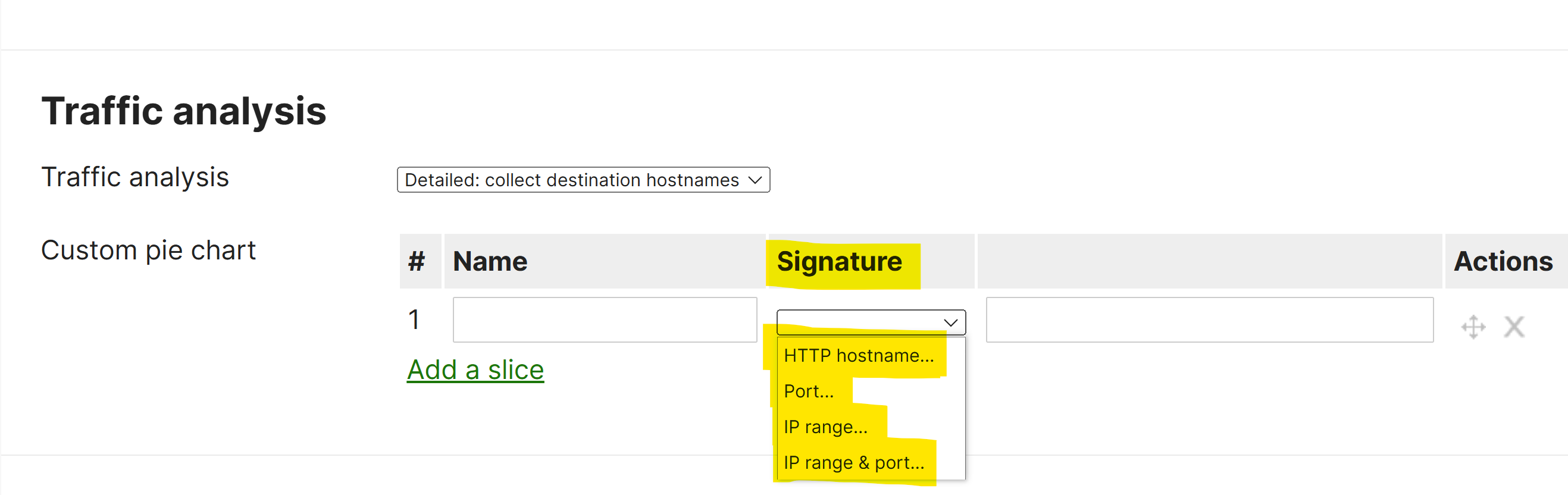
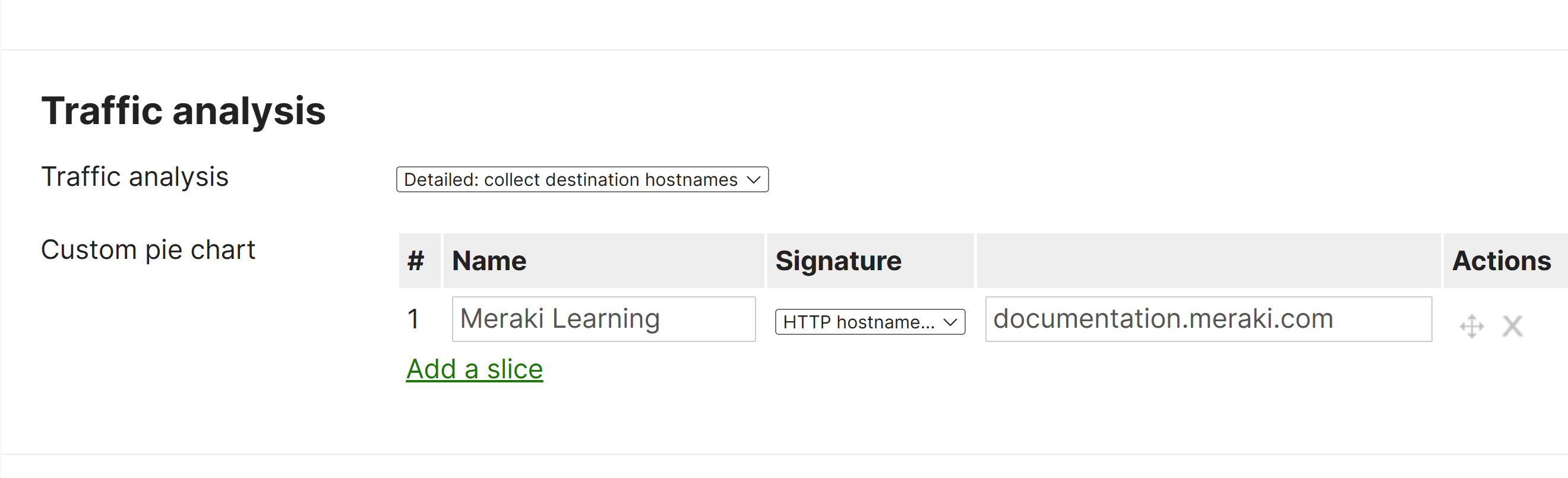
Custom Pie Charts
- The Traffic Analysis page includes a Custom Pie Chart feature that allows admins to create and display custom visual representations of network data categories in the form of pie charts
- The custom pie charts feature allows you to tailor the data visualization to meet the specific needs of your organization, enabling you to track, analyze, and interpret the performance and health of your network more easily
Traffic Analysis Feature
Traffic Analysis Feature

Traffic Analysis - Custom Pie Chart Feature
Traffic Analysis - Custom Pie Chart Feature
Traffic Analytics Menu
Traffic Analytics - Detailed Traffic Analysis
Traffic Analytics - Export Feature
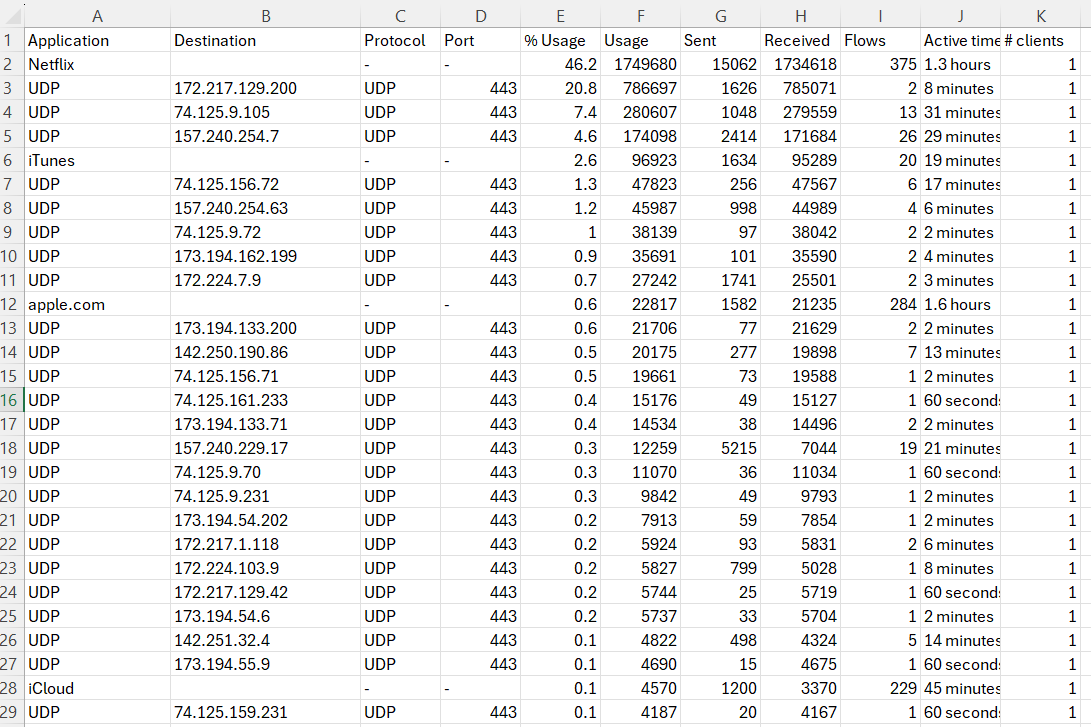
Traffic Analytics - Detailed Traffic Analysis
Device Configuration
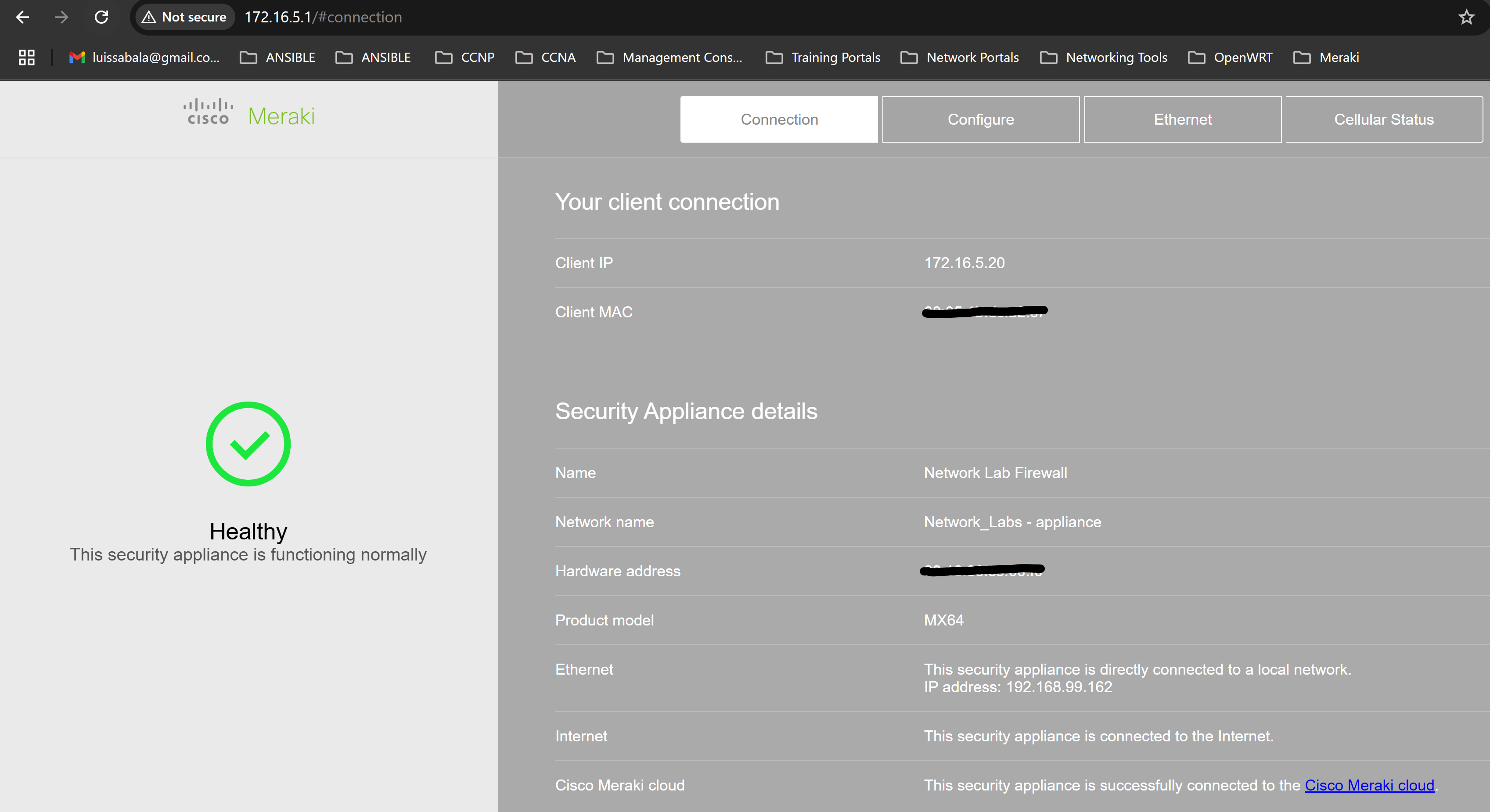
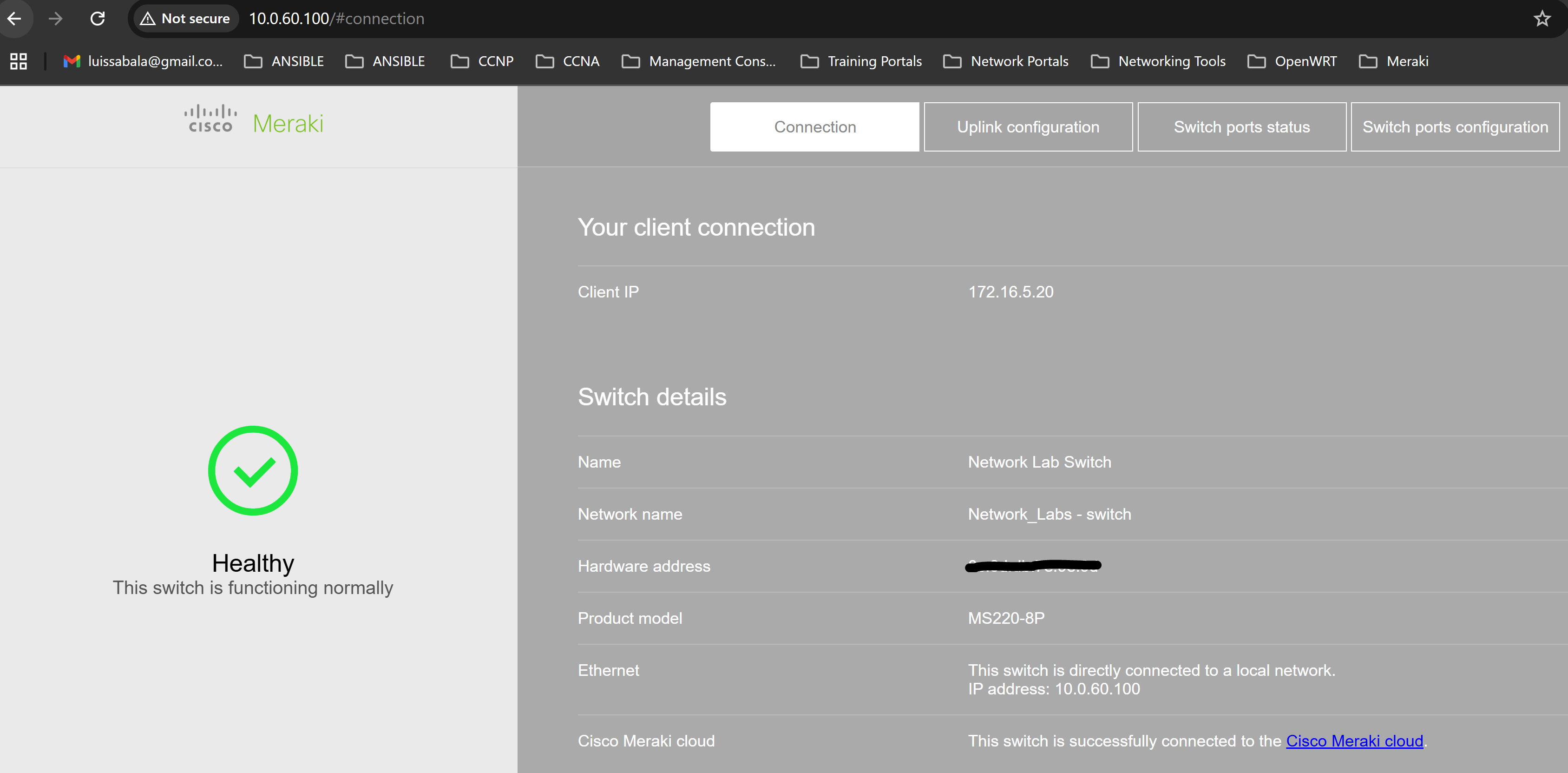
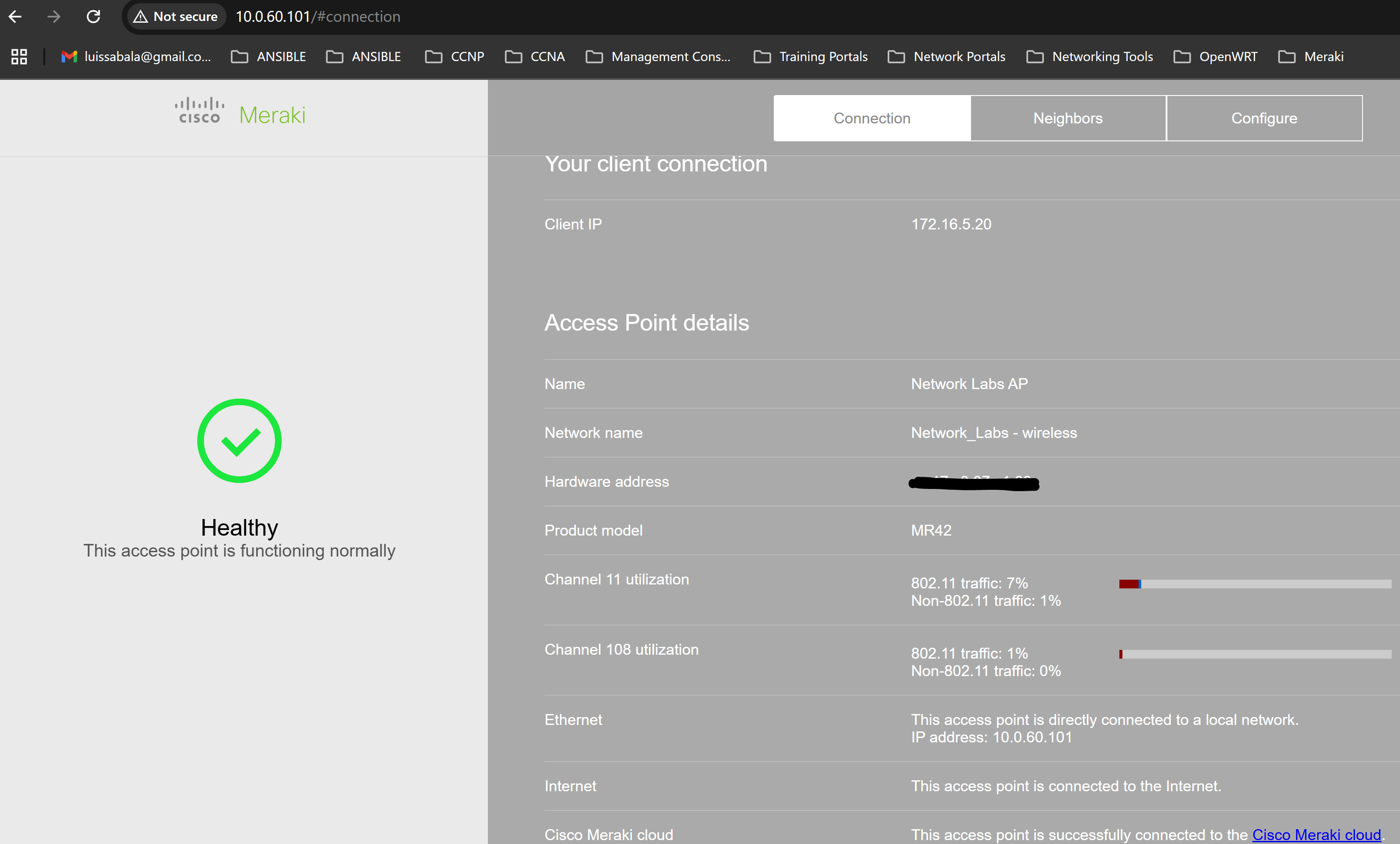
- Per Cisco, most Cisco Meraki devices have a local status page that can be accessed to make local configuration changes, monitor device status and channel utilization, and perform local troubleshooting
- A use case for accessing the local status page of Meraki devices is when Meraki cloud access is unavailable or when you need to view device specific details quickly
- Additional Device Configuration Settings
- Default Block Message
- Secure Port
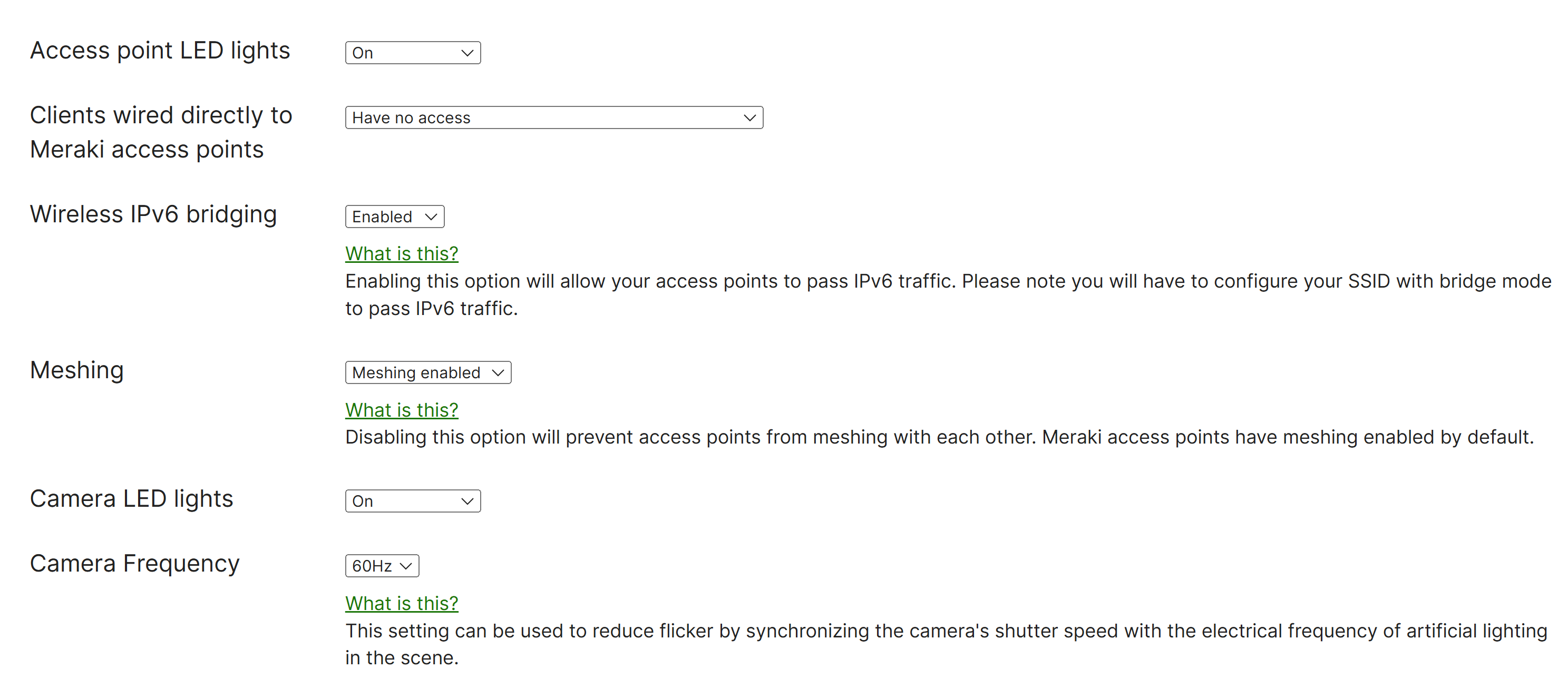
- Access Point LED Lights
- Wireless IPv6 Bridging
- Meshing
- Camera LED Lights
- Camera Frequency
Device Configuration Settings
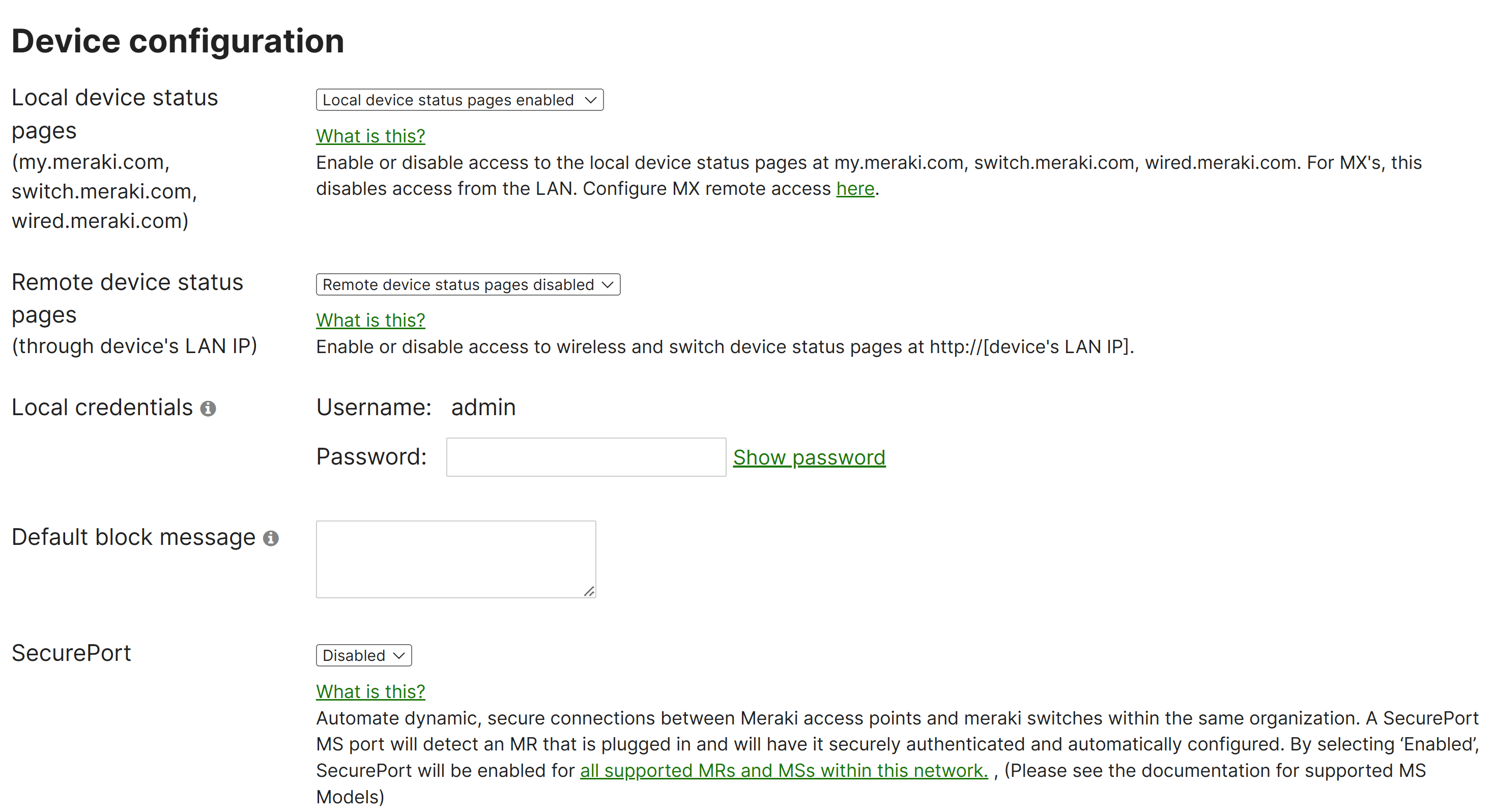
Device Configuration Settings
Local Status Page Login Credentials
Local Status Page of MX Security Appliance
Local Status Page of MS Switch
Local Status Page of MR Access Point
Reporting
- Per Cisco, aside from the Event Log that is available within the Meraki Dashboard, there are several methods for device reporting and information gathering
- Meraki can be integrated with either Syslog, API, or SNMP tools for device reporting
- Syslog Integration
- With the Syslog deployment method, MX appliances support sending four categories of messages/roles: Event Log, IDS Alerts, URLs, and Flows
- MR access points can send the same roles with the exception of IDS Alerts
- MS switches currently only support Event Log messages
- Per Cisco, if the Syslog server is across a VPN tunnel, the Syslog traffic source will be a 6.x.x.x address. This is true in VPN Concentrator mode or in Routed/NAT mode in Single LAN configuration
- API Reporting
- Meraki supports the capability of API calls to gather statistics and other information from Meraki networks
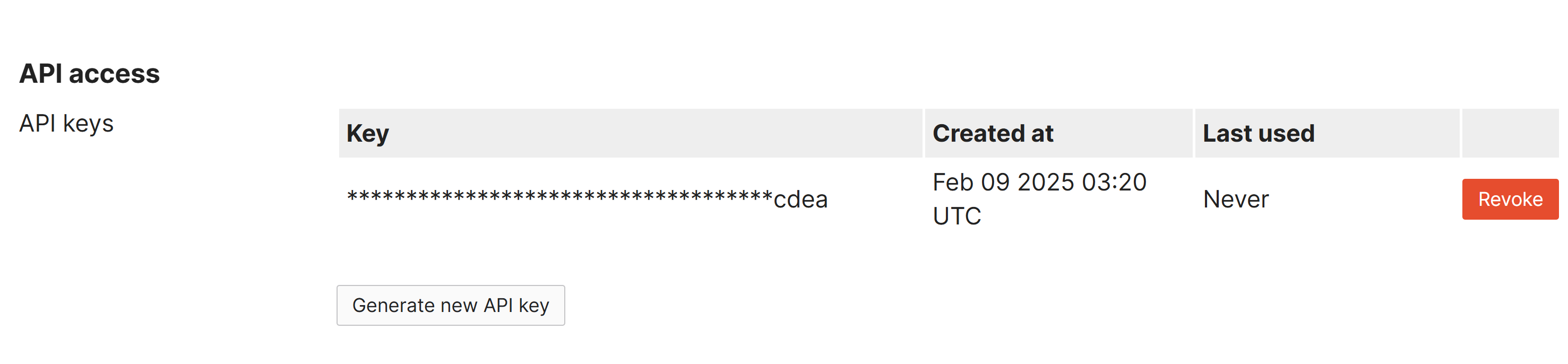
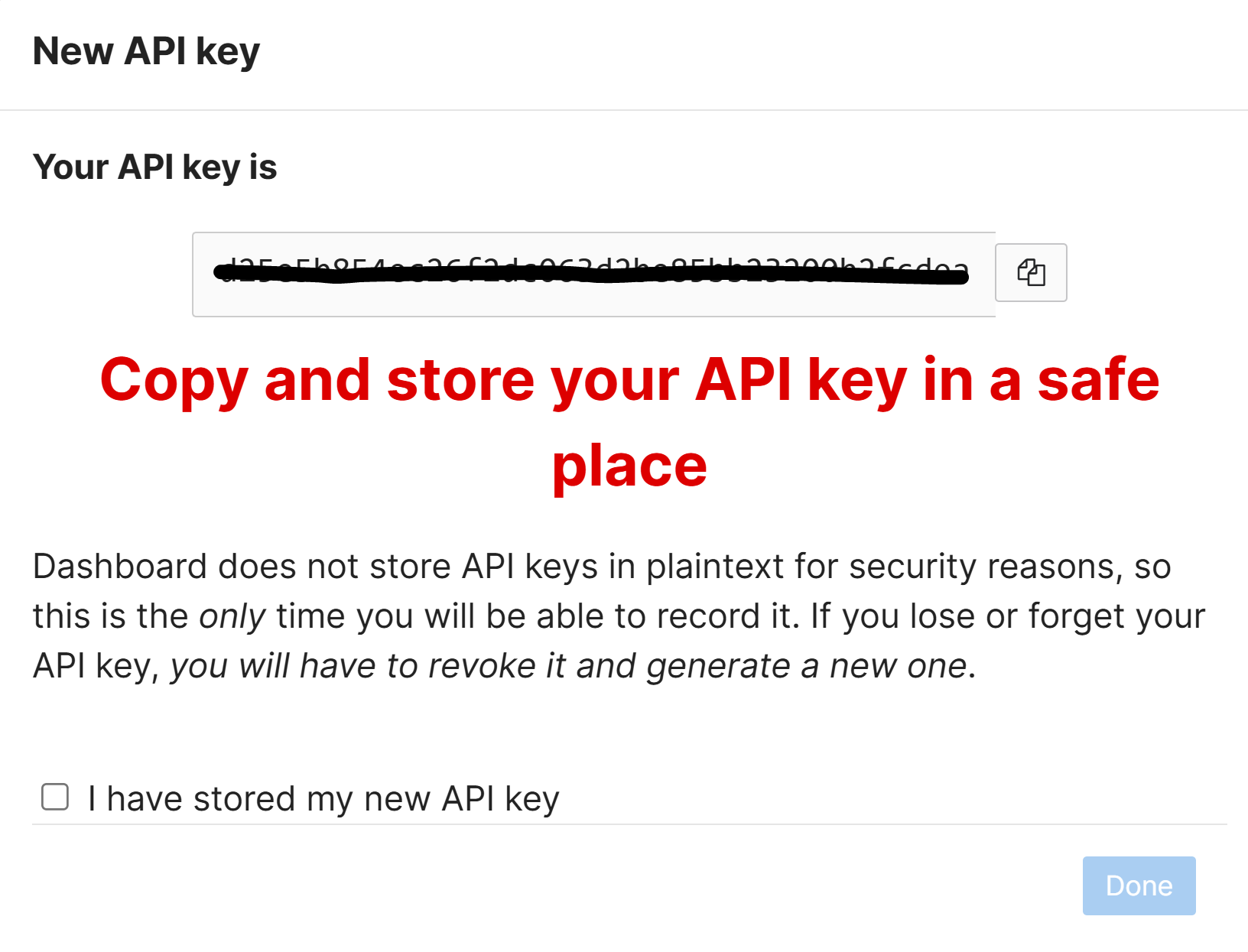
- The API is enabled by default on all organizations and can be accessed in the 'My Profile' page at the top right corner of the Meraki Dashboard
- The API key is associated with the admin account which generates it and will inherit the same permissions as the account with the ability to generate, revoke, and regenerate the API key on the profile
- Per Cisco, only you will be able to view your unique API key. No one else that has access to the Meraki Dashboard, including Meraki Support, is able to view your API key
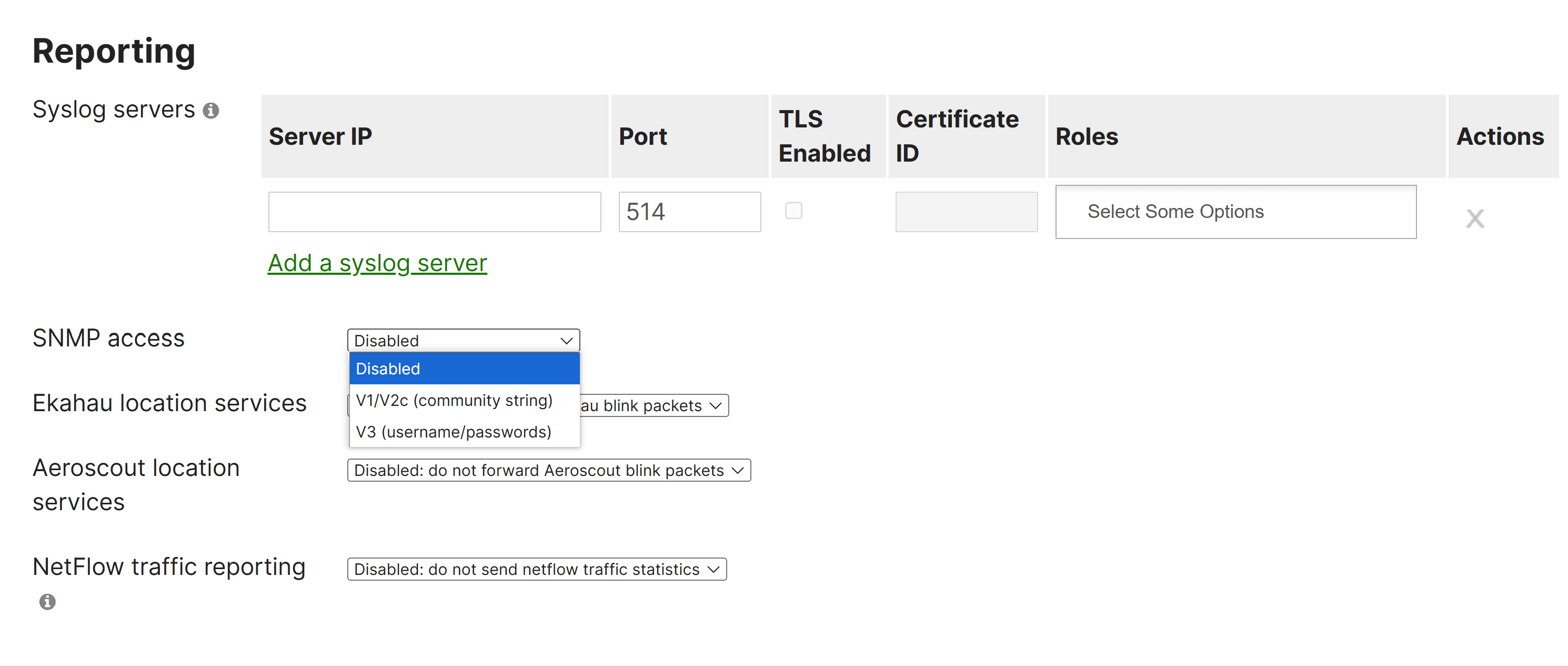
- SNMP Integration
- SNMP allows network admins to query devices for various types of information with Meraki allowing SNMP polling to gather info either from the dashboard or directly from Meraki devices themselves
- Third party network monitoring tools can use SNMP to monitor certain parameters on Meraki devices
- Meraki supports standard and Meraki proprietary MIBs which are essentially databases of SNMP object identifiers or OIDs. OIDs identify the managed objects that inform the SNMP server on what values to poll from the device
- Meraki supports SNMPv2c and SNMPv3 and can be defined and enabled under 'Organization >> Configure >> Settings >> SNMP' from the Meraki Dashboard
Reporting Overview Settings
API Feature
API Feature
Organization Wide SNMP Settings

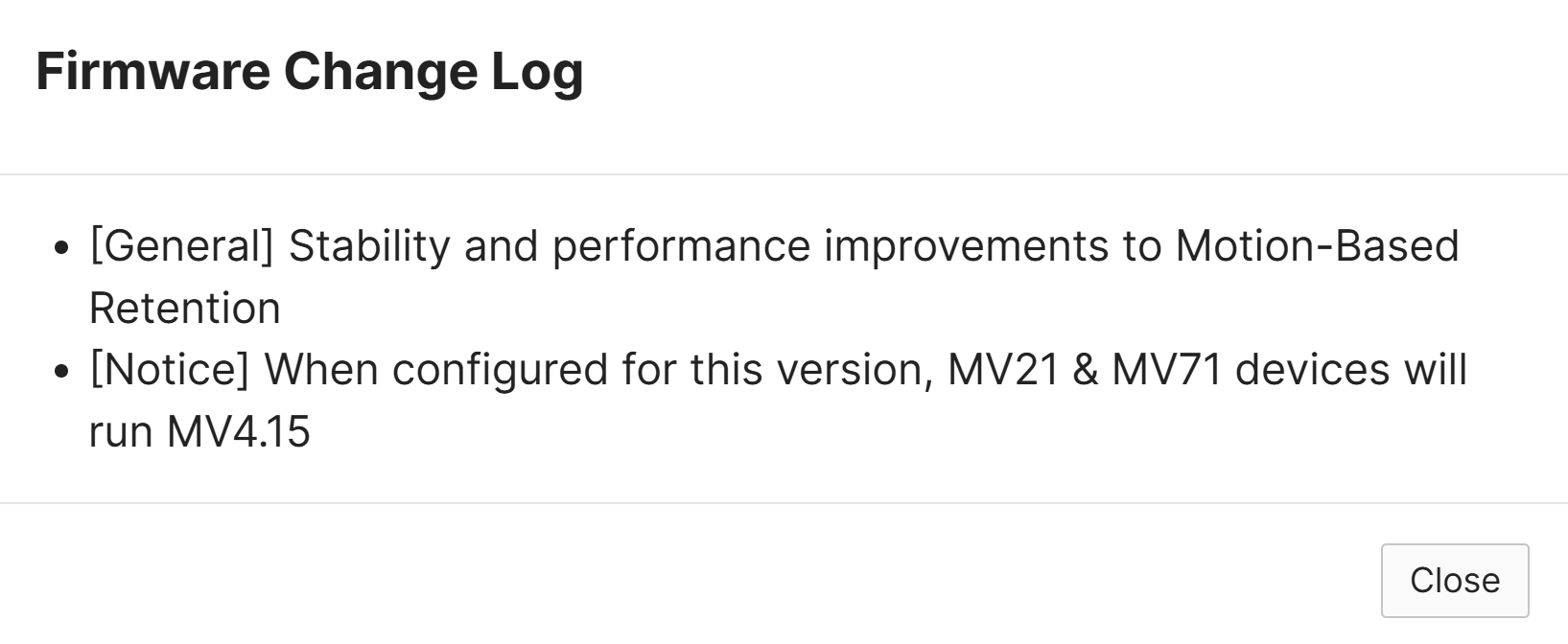
Firmware Upgrades
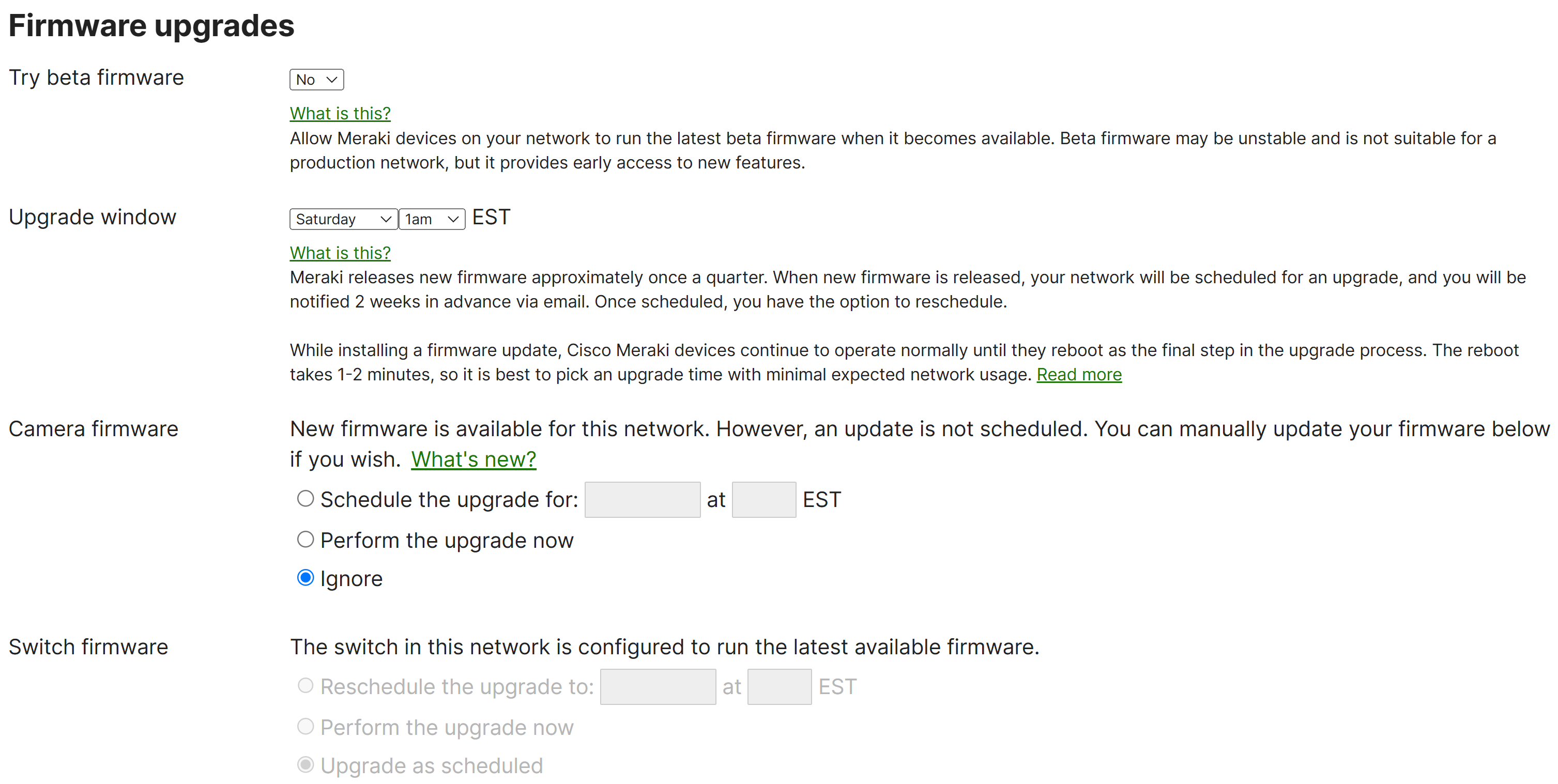
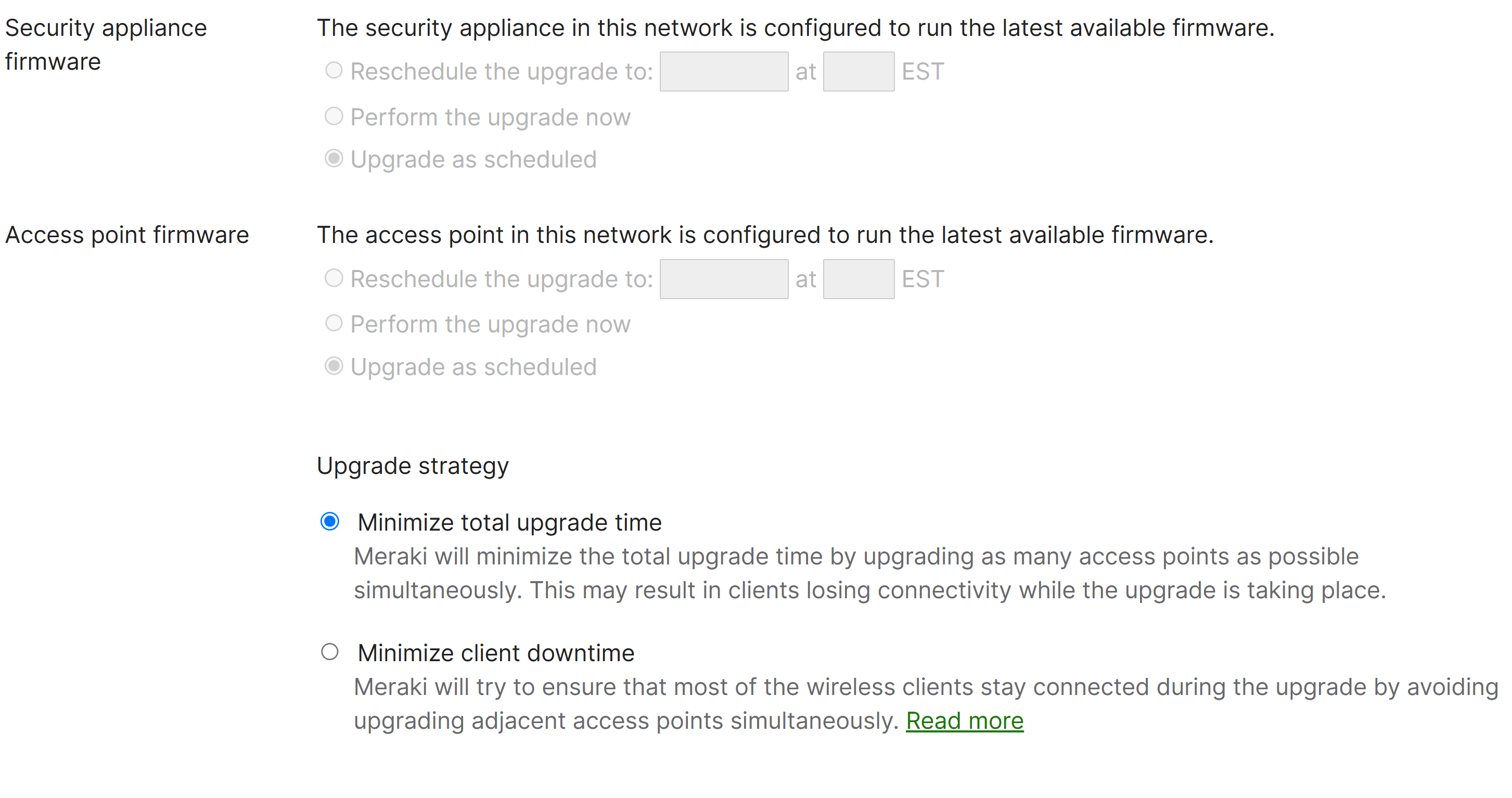
- Per Cisco, Firmware upgrades can be scheduled on a per-device type basis for each dashboard network
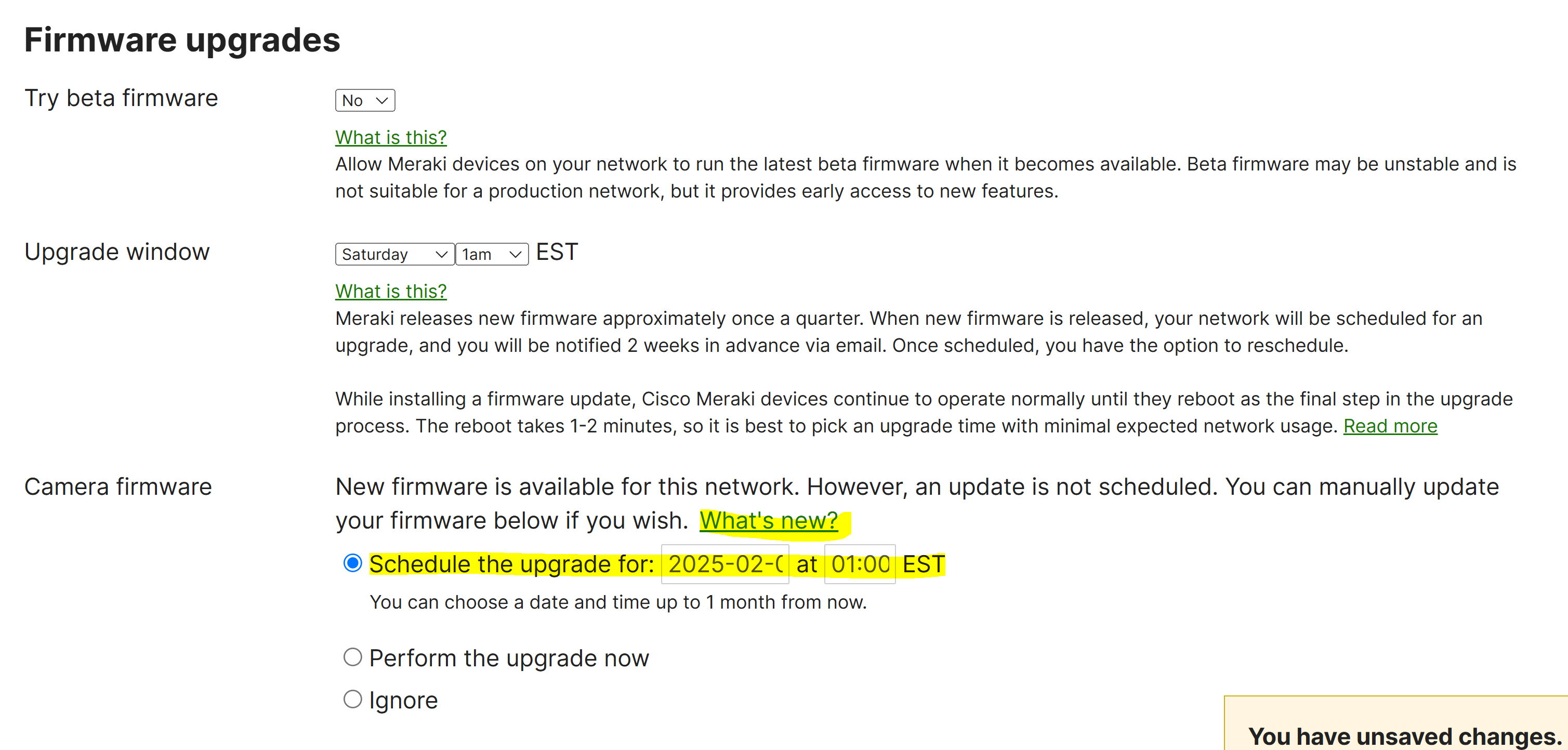
- Meraki allows admins to manually schedule, reschedule, and ignore firmware upgrades for a particular device type as they become available
- When new firmware upgrades become available for a type of Meraki device, firmware change logs notes become available to view and includes information about new features, bug fixes, and known issues that are associated with a particular firmware version
- Meraki has precautions set in place when it comes to devices running older firmware trying to upgrade to a build that could cause compatibility issues. Cisco's use of Firmware Upgrade Barriers solves this issue by having devices upgrade firmware in several stages prior to reaching the latest batch on a major firmware version
Firmware Upgrade Settings
Firmware Upgrade Settings
Scheduling Available Upgrade for MV Camera
Firmware Upgrade Change Log