IPsec VPN
Sections:
- IPsec Overview
- IPsec VPN Configuration
- IPsec Firewall Rules
- Device Access
- IPsec Routes for DHCP Relay
- IPsec VPN Testing
- IPsec Profiles
Resources:
- Sophos Site-to-Site VPN
- Sophos IPsec Connections
- Sophos Policy-based VPN
- Device Access (Local Service ACL)
- Send DHCP Traffic over Policy-based IPsec VPN to Servers
- Sophos Firewall Device Console Knowledge Base
- IPsec Profiles
- Add an IPsec Profile
- Best Practice for S2S Policy-based IPsec VPN
Overview:
- In this demonstration, I will be setting up policy-based IPsec VPNs on a pair of Sophos Firewalls
- Policy-based VPNs encrypts traffic passing through the listening interface based on the firewall rule and the local and remote subnets specified in the matching IPsec connection
- Policy-based VPNs gives administrators the option to use the default IPsec profiles or create custom profiles for the phase 1 and phase 2 IKE security settings
- In this lab demonstration, I will specify a default IPsec profile for the defined tunnel but later demonstrate configuring a custom profile for practice
IPsec VPN Fundamentals
Overview
- An IPsec VPN is a type of VPN that uses IPsec (a framework consisting of a suite of protocols) to secure communication over a potentially untrusted network, like the Internet
- IPsec is used to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity of the data being transmitted between two endpoints, such as two devices, routers, or networks
- Key features and components of IPsec VPN:
Key Features and Components
Encryption
- IPsec encrypts the data that is sent over the Internet, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it
- This ensures the confidentiality of sensitive data
Authentication
- IPsec uses various authentication methods (such as digital certificates or pre-shared keys) to verify that the devices involved in the VPN connection are who they claim to be
- This prevents unauthorized access to the network
Data Integrity
- IPsec provides mechanisms to ensure that data hasn't been altered during transmission
- This is done using cryptographic hash functions
Tunneling
- In an IPsec VPN, the data is encapsulated (or 'tunneled') within an encrypted IP packet
- This makes it appear as if the data is being sent to a different address, ensuring that even if it is intercepted, it cannot be easily traced to the original source
Security Associations (SA)
- An IPsec VPN relies on Security Associations, which are agreements between two endpoints on the encryption and authentication methods to use, as well as the keys to be shared
Protocols Used in IPsec
- AH (Authentication Header)
- IP Protocol 51
- Ensures data integrity and authentication of the IP packets
- However, it does not provide encryption
- ESP (Encapsulating Security Payload)
- IP Protocol 50
- Provides encryption, along with integrity and authentication
- This is the more commonly used protocol in an IPsec VPN
- ESP Modes of Operation
- Transport
- Payload is protected but the original IP header is not
- Packet Representation - [Original IP Header] [ESP Header] [Encrypted Payload]
- Tunnel
- Original IP and payload packet are protected
- Packet Representation - [New IP Header] [ESP Header] [Encrypted Original IP Header] [Encrypted Payload]
- Transport
How IPsec VPN Works Via IKE Phases
IKE (Internet Key Exchange) Overview
- IPsec leverages a suite of protocols
- Transform sets consist of these security protocols and algorithms that are shared between two endpoints to encrypt and authenticate data transmitted over the VPN
- IKE is therefore utilized for the negotiation of transform set parameters to establish a secure tunnel
- IKE and ISAKMP are often used interchangeably
- Types of IKE
- IKEv1
- IKEv1 uses two phases for negotiation
- Phase 1 and Phase 2 as mentioned below
- IKEv2
- IKEv2 simplifies the process by combining both Phase 1 and Phase 2 into a single phase, making it more efficient
- IKEv2 uses a single exchange to handle both the security association and the key exchange, which reduces latency and speeds up overall setup process
- IKEv2 is not compatible with IKEv1
- IKEv2 supports better encryption algorithms
- IKEv1
Phase 1 (IKE - Internet Key Exchange)
- This phase establishes a secure control plane communication channel between the two devices (the client and the VPN gateway or two routers)
- It negotiates the encryption methods and the keys to use
- The result is a secure, authenticated channel (often referred to as the 'IKE SA' or IKE Security Association)
- Phase 1 HAGLE Parameters
- Hash
- Authentication
- Diffie-Hellman group
- Lifetime (24 hour by default)
- Encryption
Phase 2 (IPsec)
- Once the secure channel is established in Phase 1, Phase 2 sets up the actual data plane IPsec tunnel for transmitting encrypted data
- It uses the parameters established in Phase 1 to negotiate encryption keys for the data packets
- The IPsec VPN can now securely transmit data between the two endpoints, ensuring confidentiality, integrity, and authenticity
- Perfect Forward Secrecy (PFS) is supported and can be used to acquire new session keys for Phase 2
- Lifetime of a Phase 2 tunnel is 12 hours by default in most vendors
Types of IPsec VPN Configurations
Site-to-Site VPN
- This type of VPN connects two networks over the Internet securely
- For example, it could be used to connect the headquarters of a company to a remote branch office
- Both sites use IPsec to encrypt and authenticate all communication between them
Remote Access VPN
- In this setup, individual users (often employees working remotely) connect to a central network (like a company's internal network) using an IPsec VPN client
- Their data is encrypted and securely transmitted over the Internet to the company's VPN gateway
DMVPN
- Referred to as Dynamic Multipoint VPN
- This Cisco VPN deployment is for Hub and Spoke topologies
- The NHRP protocol is used to dynamically form tunnels with spokes
- Routing protocols can be run and utilizes either IKEv1 or IKEv2
FlexVPN
- An enhanced version of Cisco's DMVPN
- Solution for Hub and Spoke topologies
- This VPN technology relies on IKEv2 only
GetVPN
- Referred to as Group Encrypted Transport
- This Cisco VPN technology is commonly used for Service Provider MPLS networks interconnecting branch sites
- An encrypted tunnel builds over the MPLS network preserving the original IP Header and QoS tags
Benefits of IPsec VPN
Security
- IPsec VPN provides robust encryption, ensuring that sensitive information is protected while being transmitted over the Internet
- By using cryptographic hashes and authentication protocols, IPsec ensures that the data has not been tampered with and that both parties are who they claim to be
Scalability
- IPsec VPNs can scale to support large networks, whether it's connecting multiple offices in a business or supporting hundreds of remote workers
Support for Multiple Platforms
- IPsec VPN is supported by a wide variety of devices and platforms, including routers, firewalls, operating systems, and mobile devices, making it a versatile solution for different environments
Compatibility with IPv6
- IPsec supports both IPv4 and IPv6, allowing it to work in modern networking environments
Potential Drawbacks
Complexity
- Configuring an IPsec VPN can be complex, especially when dealing with advanced features like multi-site connections or remote access configurations
NAT Traversal
- IPsec can have issues when passing through NAT (Network Address Translation) devices, as the IP addresses may get altered
- However, this can be resolved using features like NAT-T (NAT Traversal), which allows IPsec to work with NAT devices
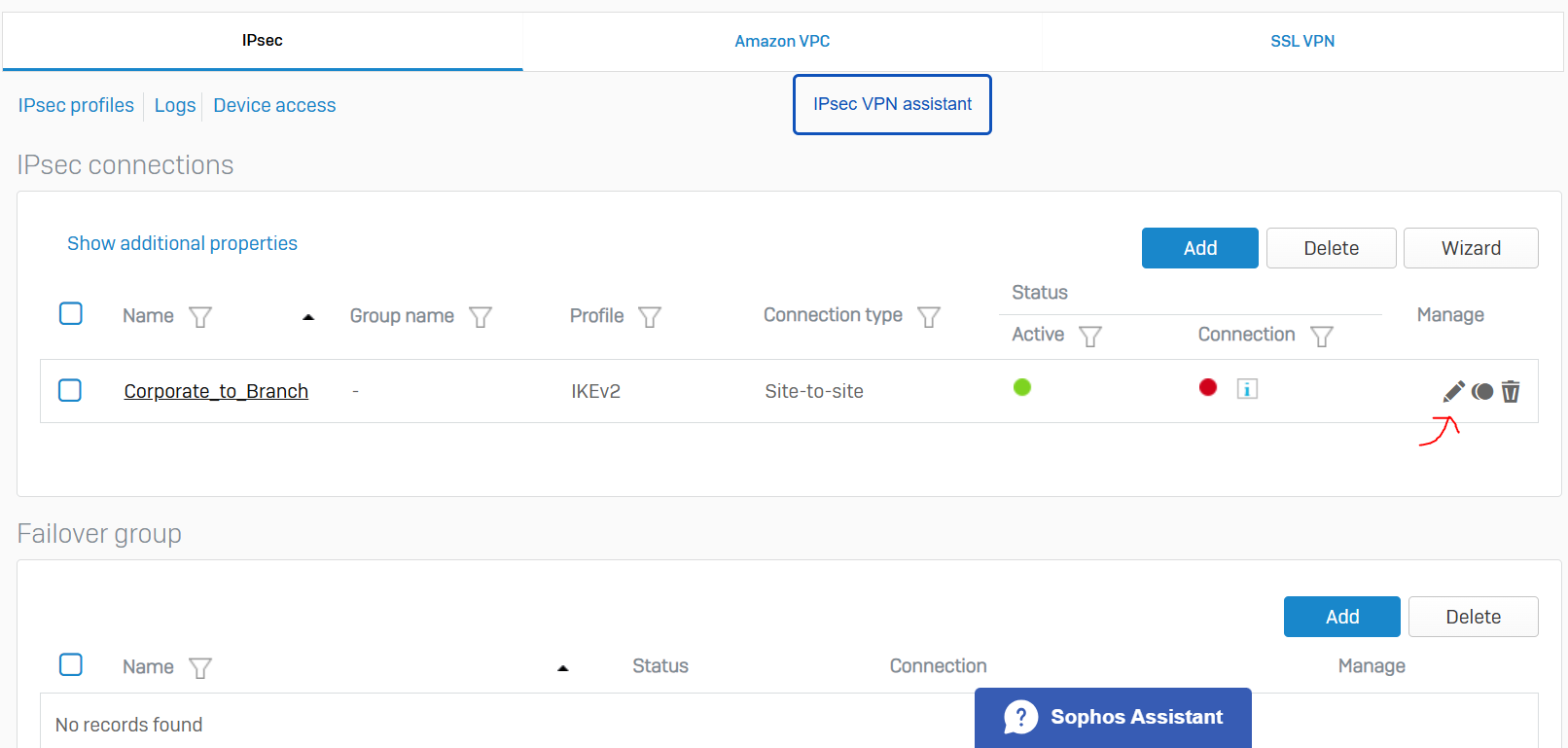
IPsec VPN Configuration
Overview
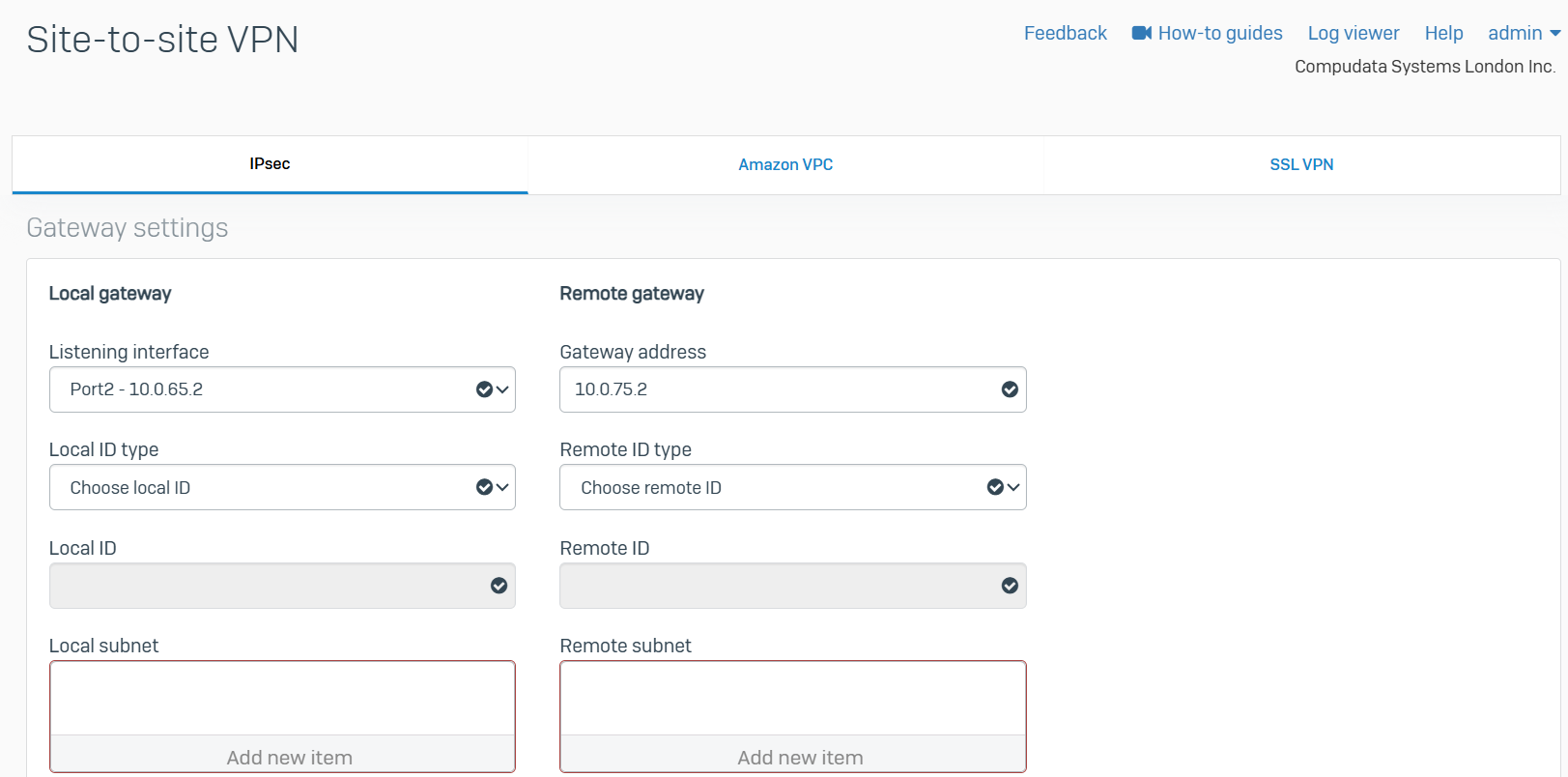
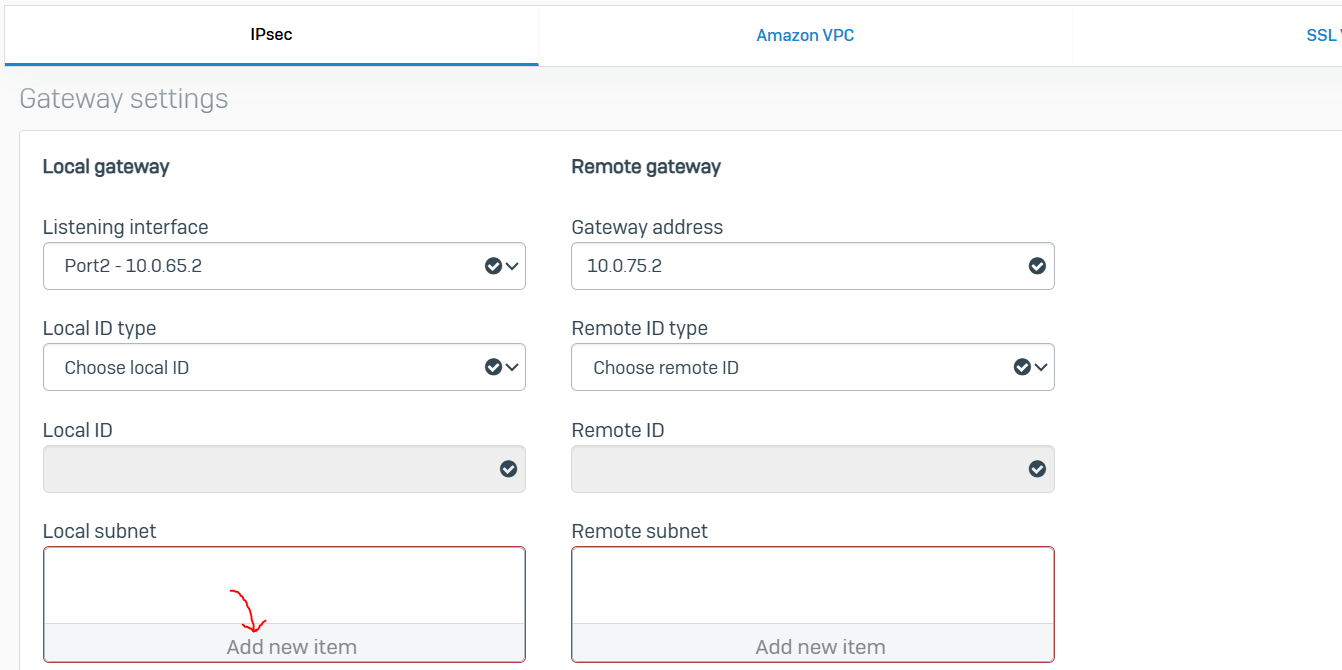
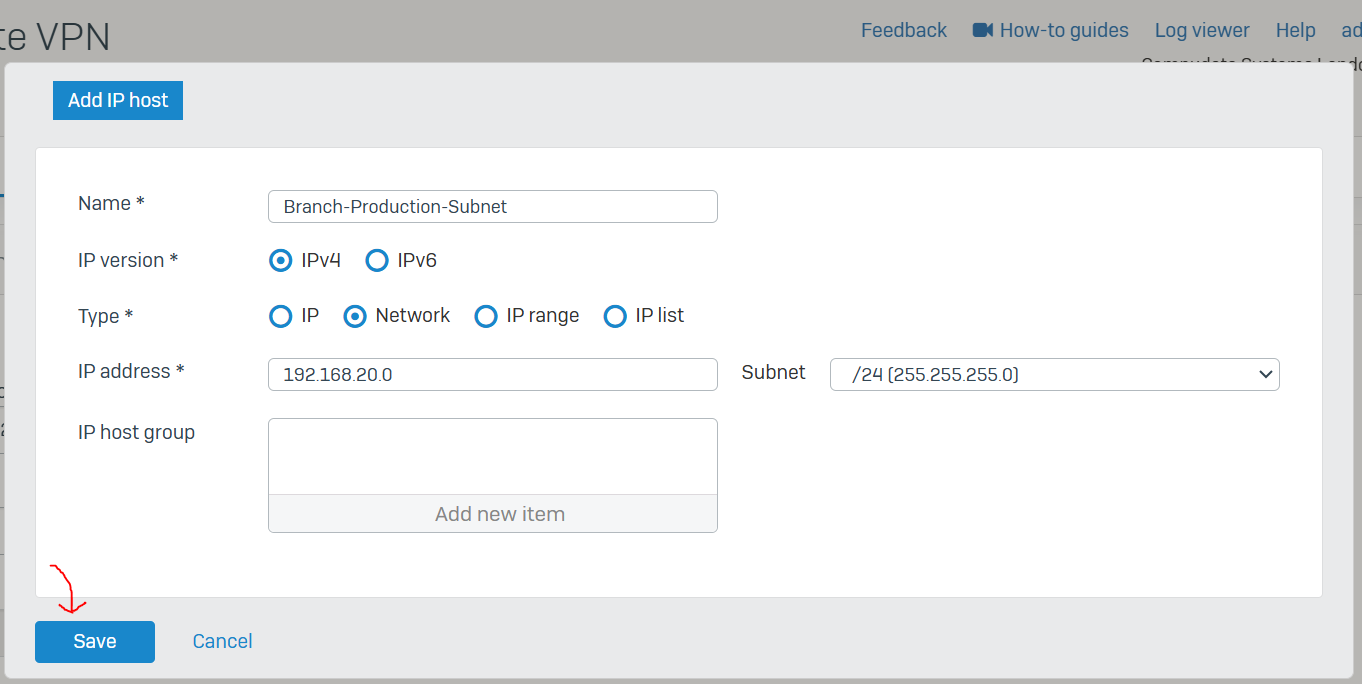
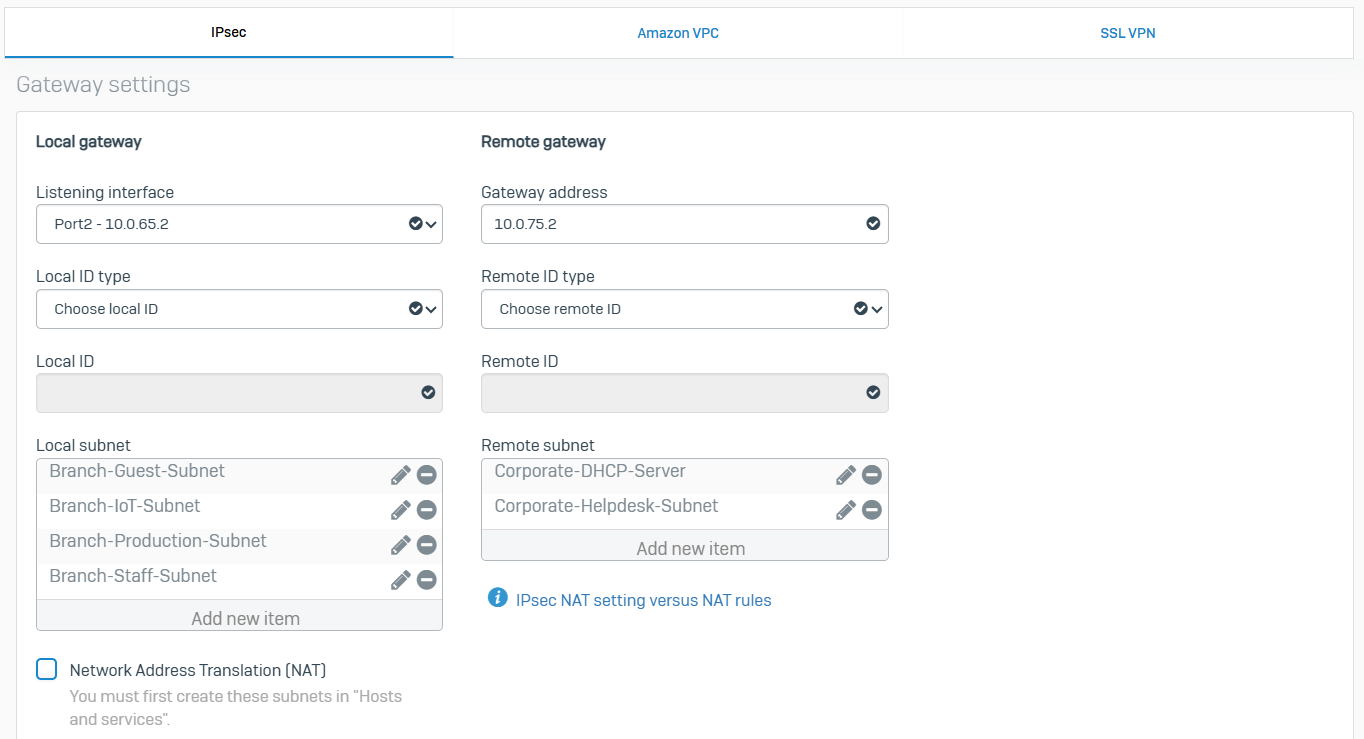
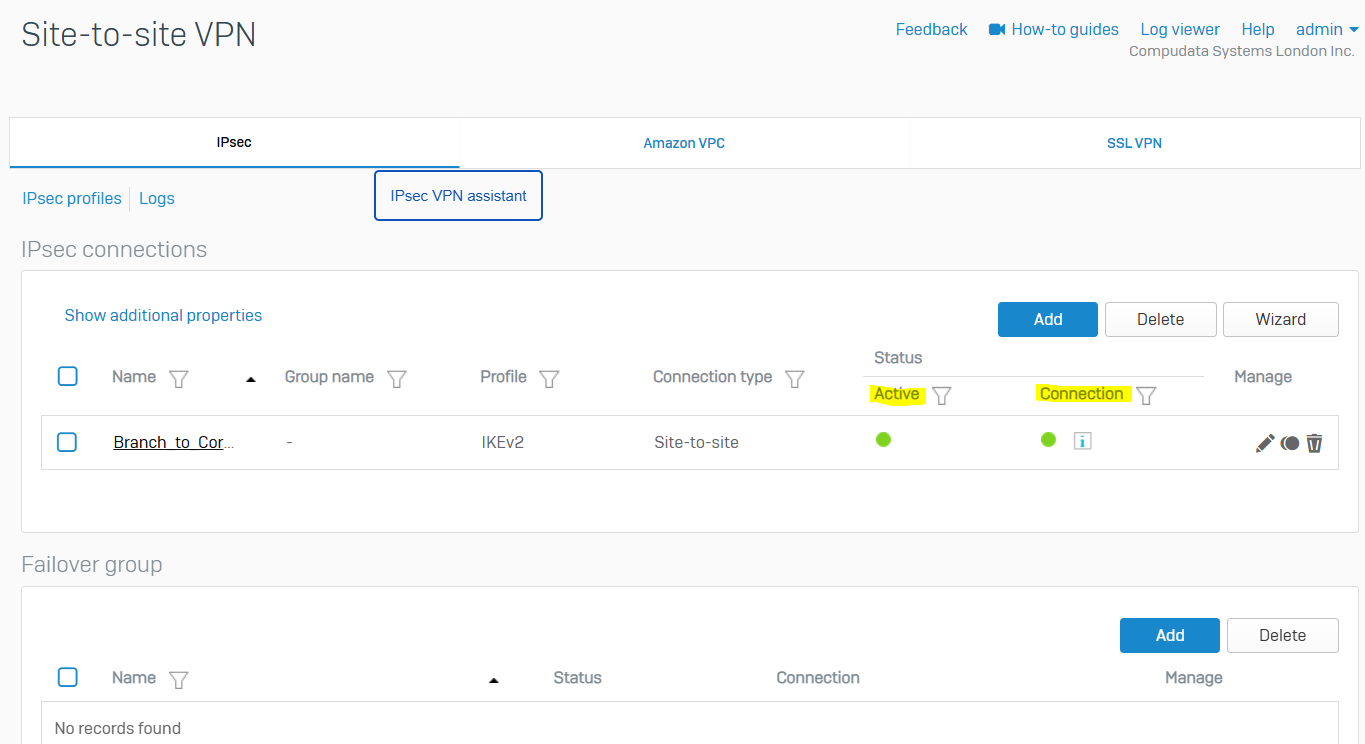
- For both the Corporate and Branch site LANs, I will demonstrate configuring a policy-based IPsec VPN tunnel between both Sophos Firewalls for confidentiality, authentication, and integrity
- When configuring an IPsec tunnel on a Sophos Firewall, it is important to understand the concepts and fundamentals of IPsec VPNs in addition to the firewall rules that impacts which subnets are reachable via the IPsec tunnel
- Upon successfully configuring an IPsec tunnel between both LANs, I will test and verify the reachability between internal networks located in their respective LAN
IPsec VPN Topology
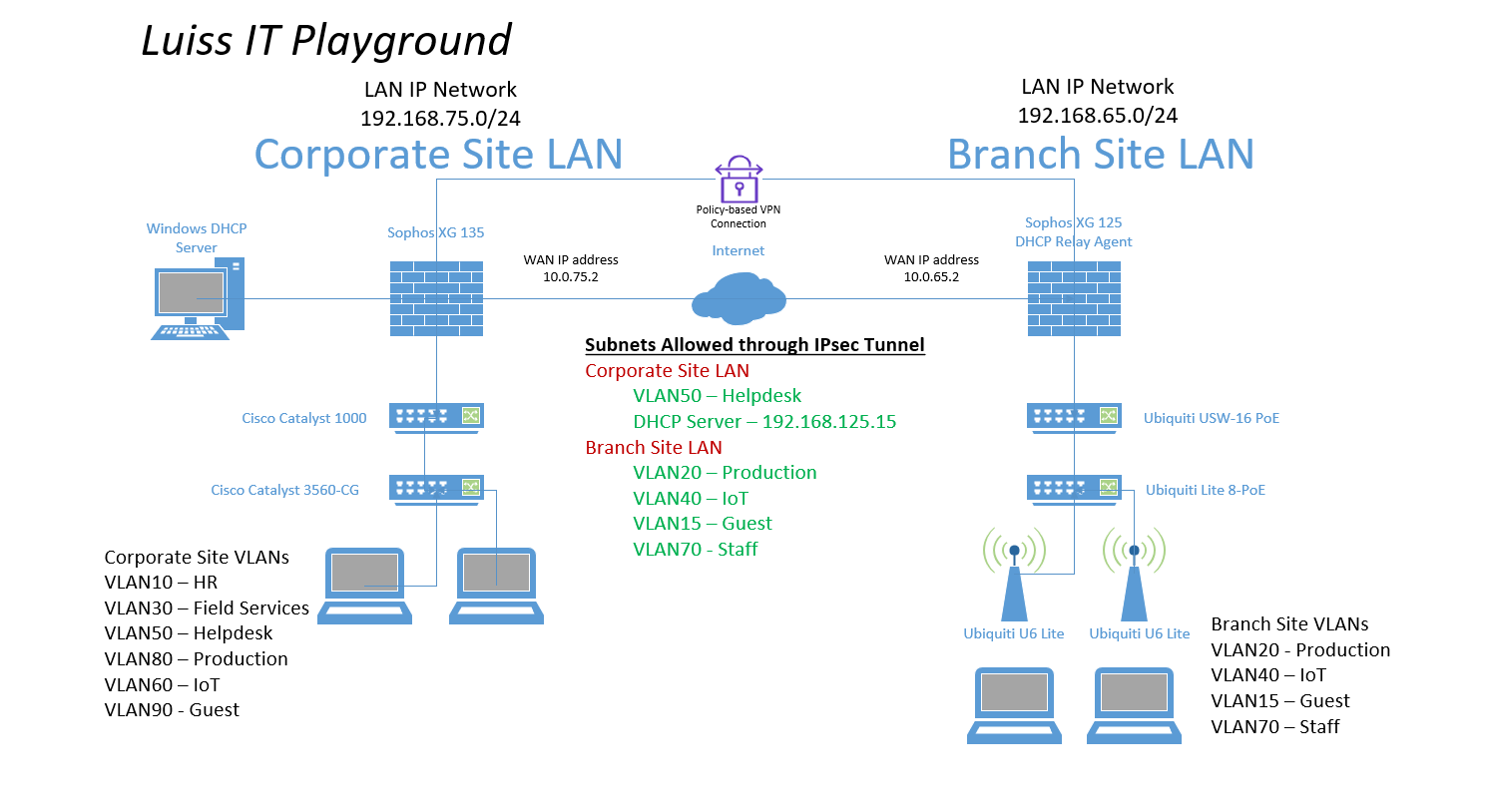
IPsec Configuration - Corporate Site LAN
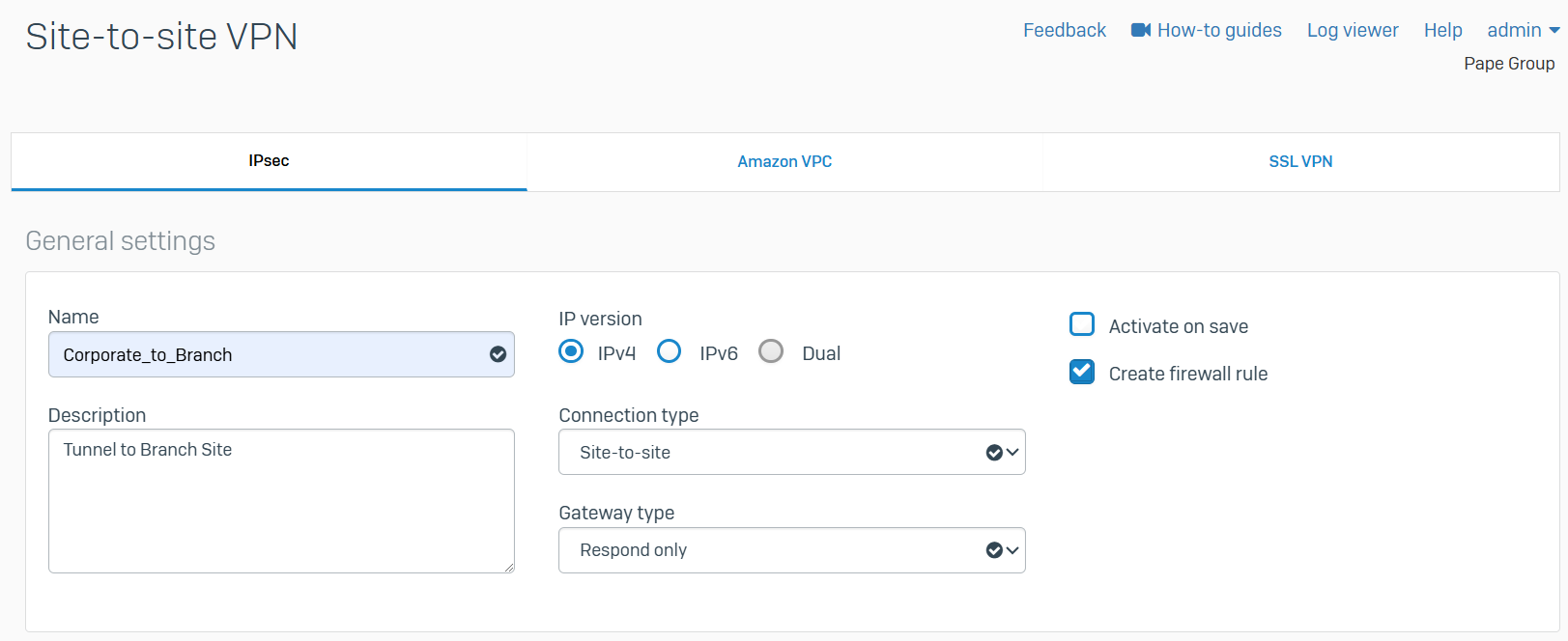
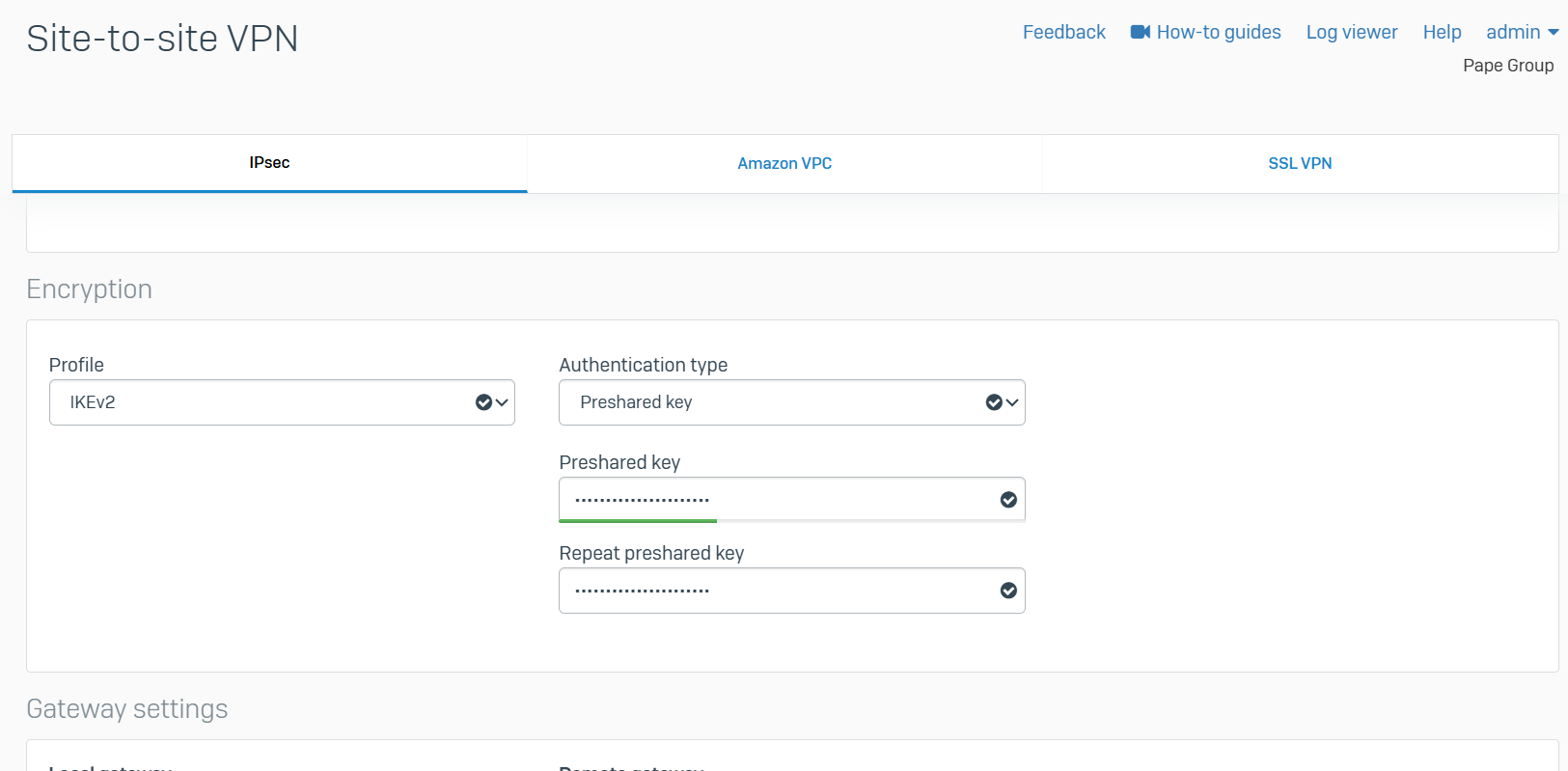
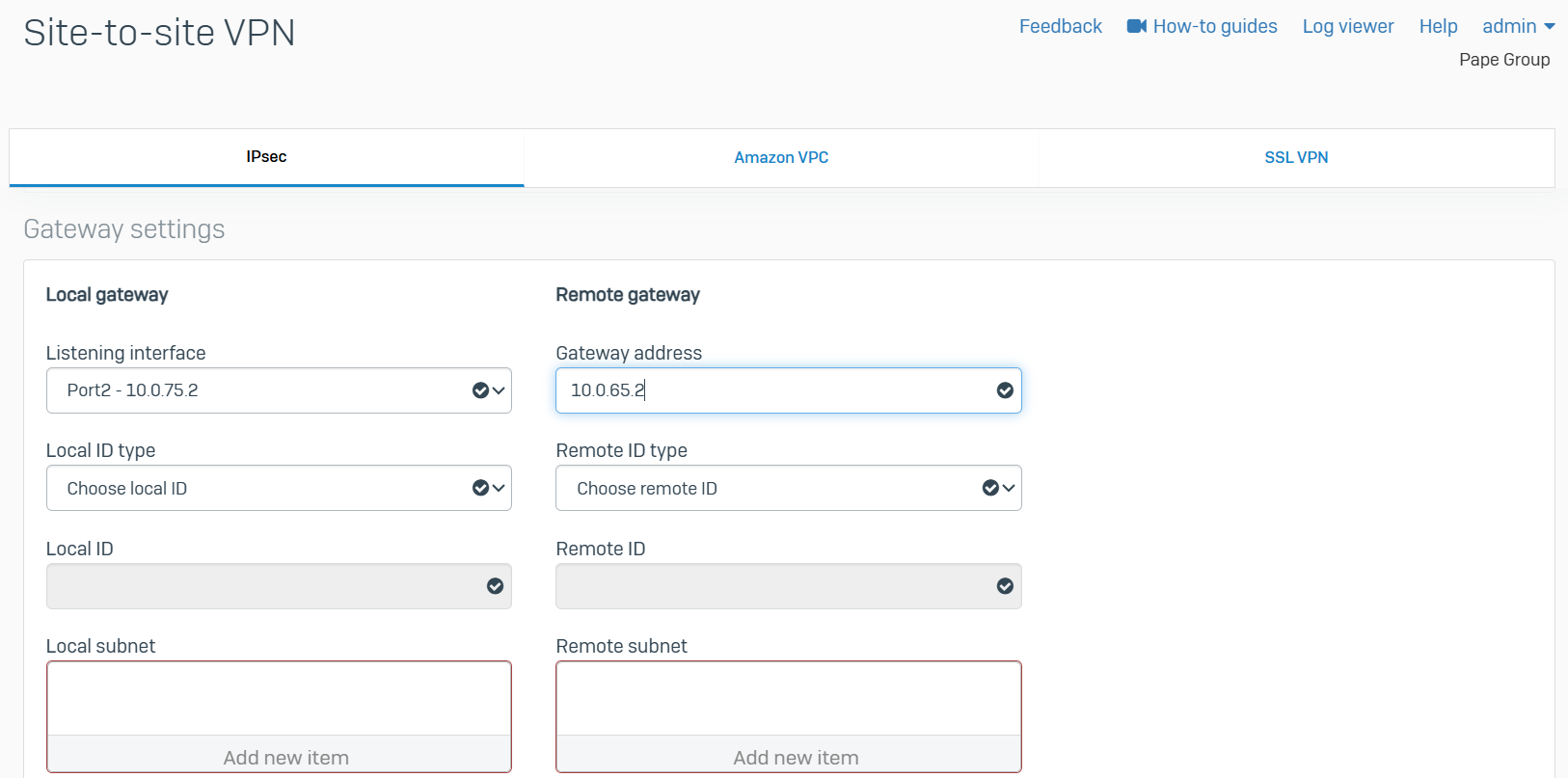
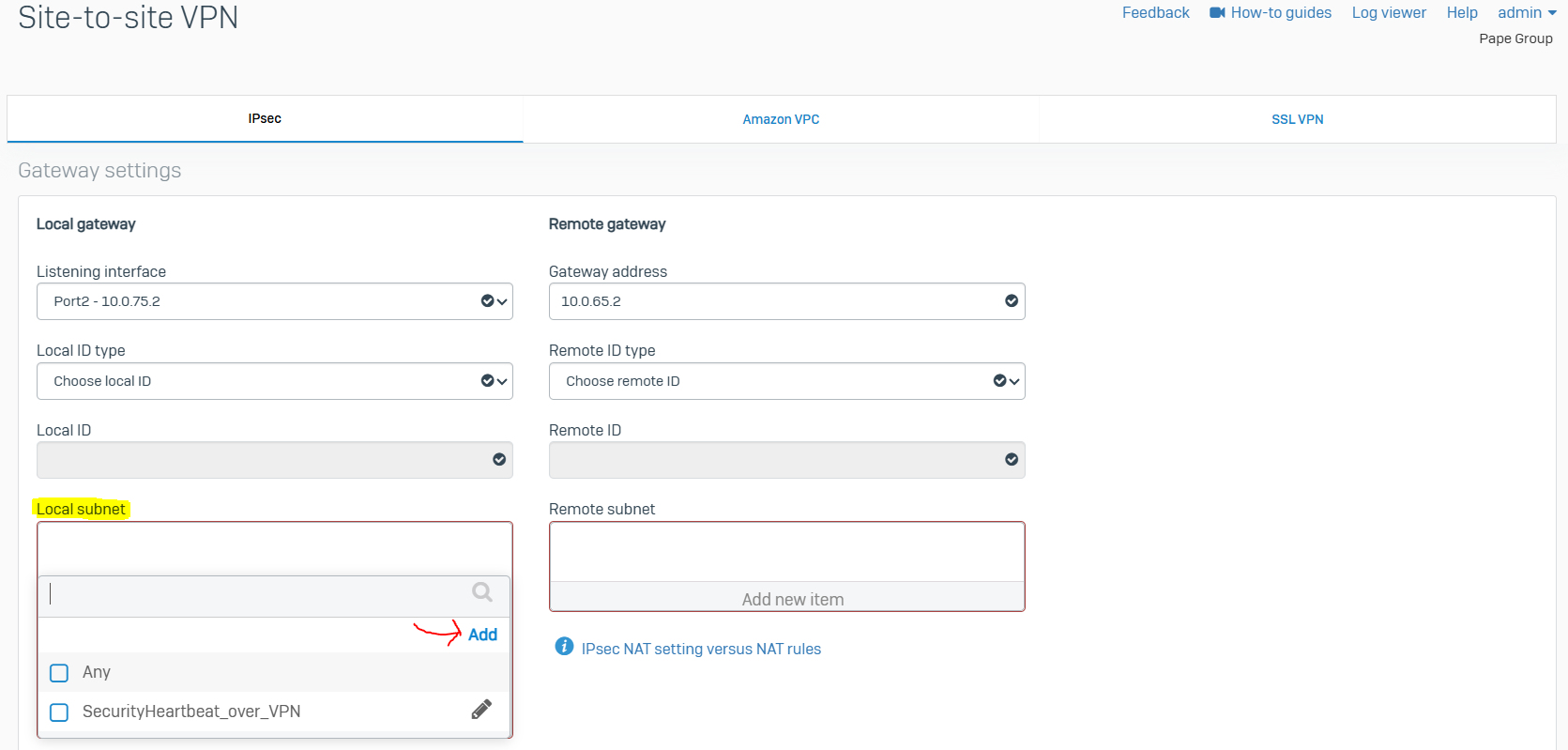
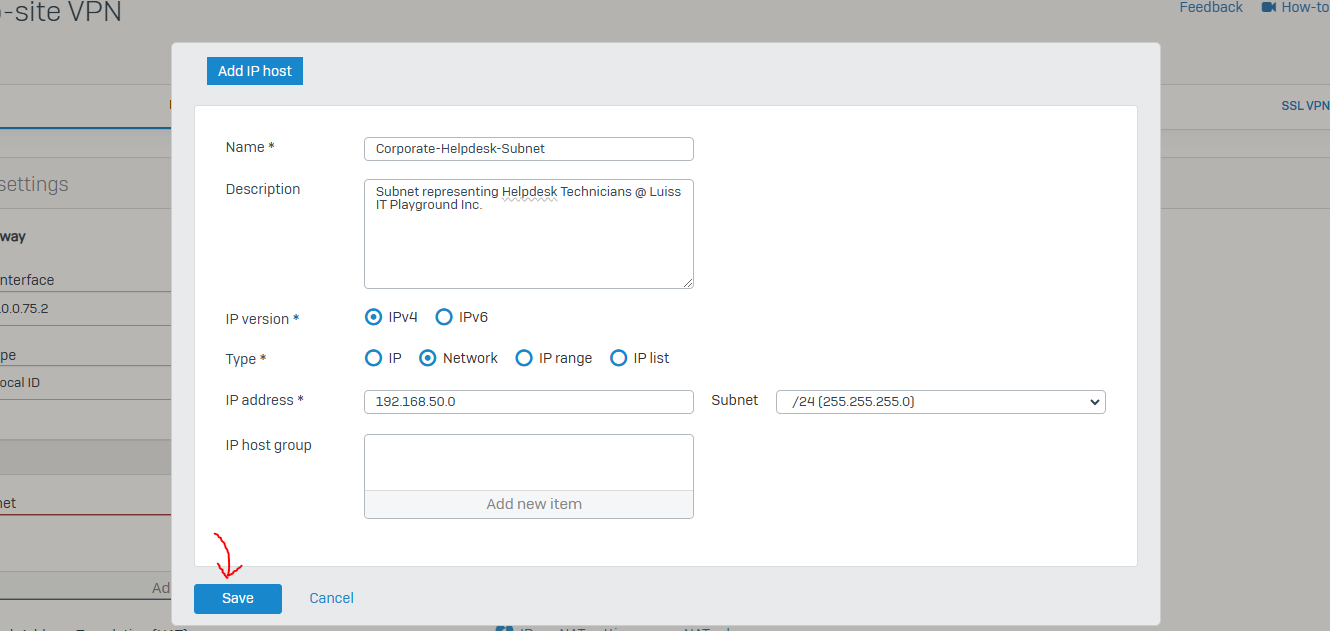

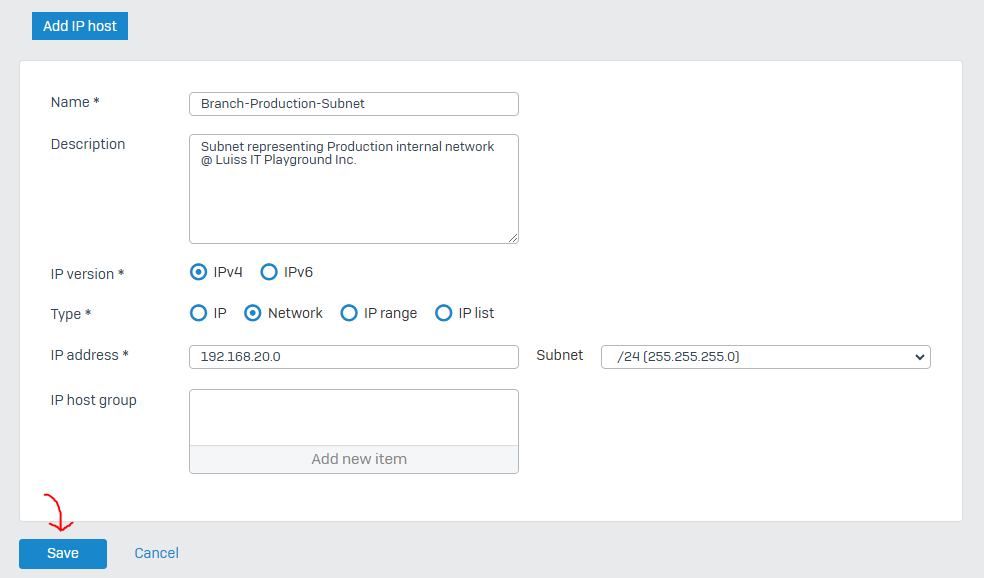


IPsec Configuration - Branch Site LAN
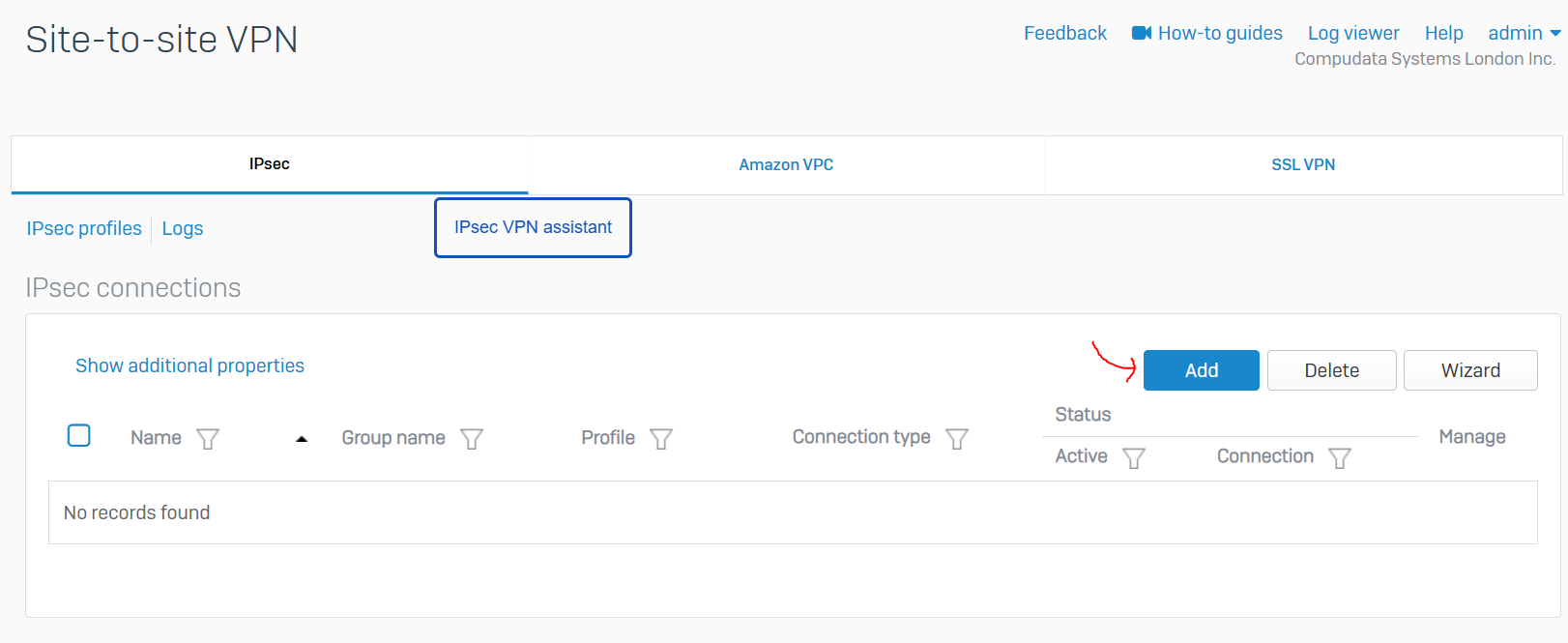
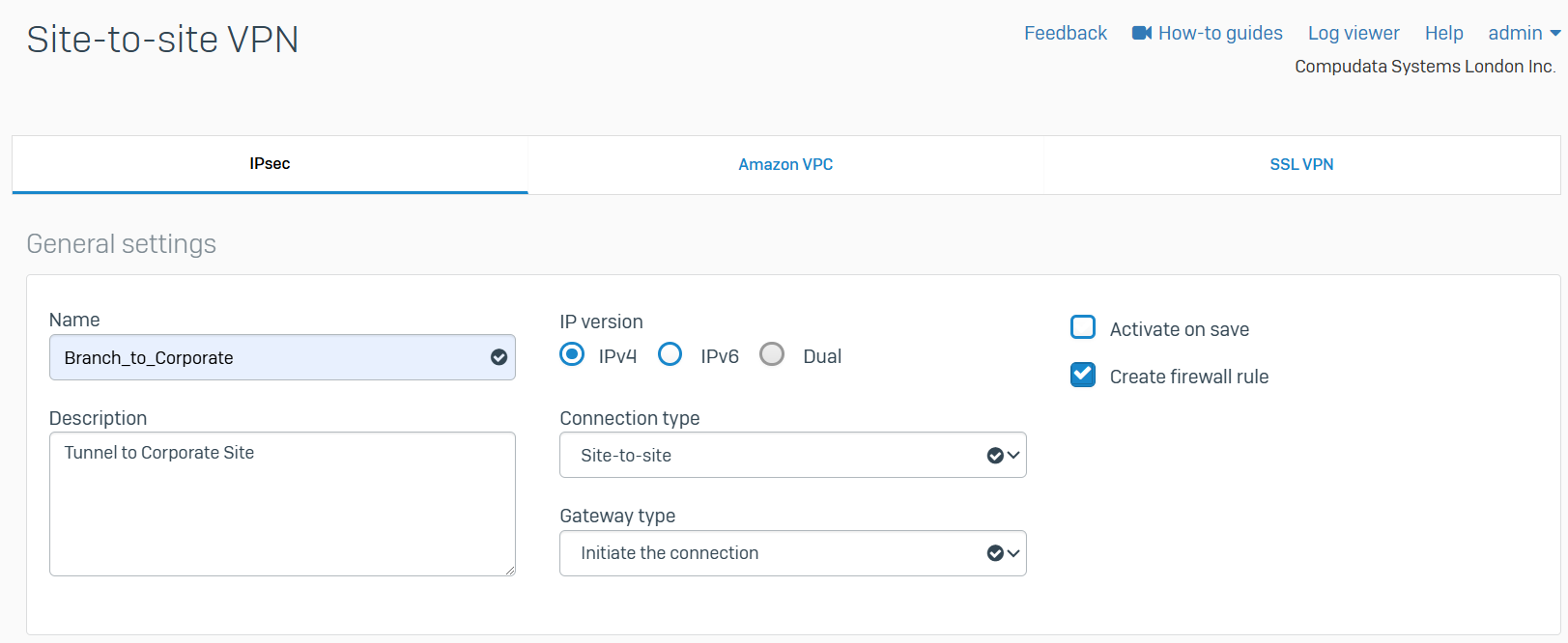
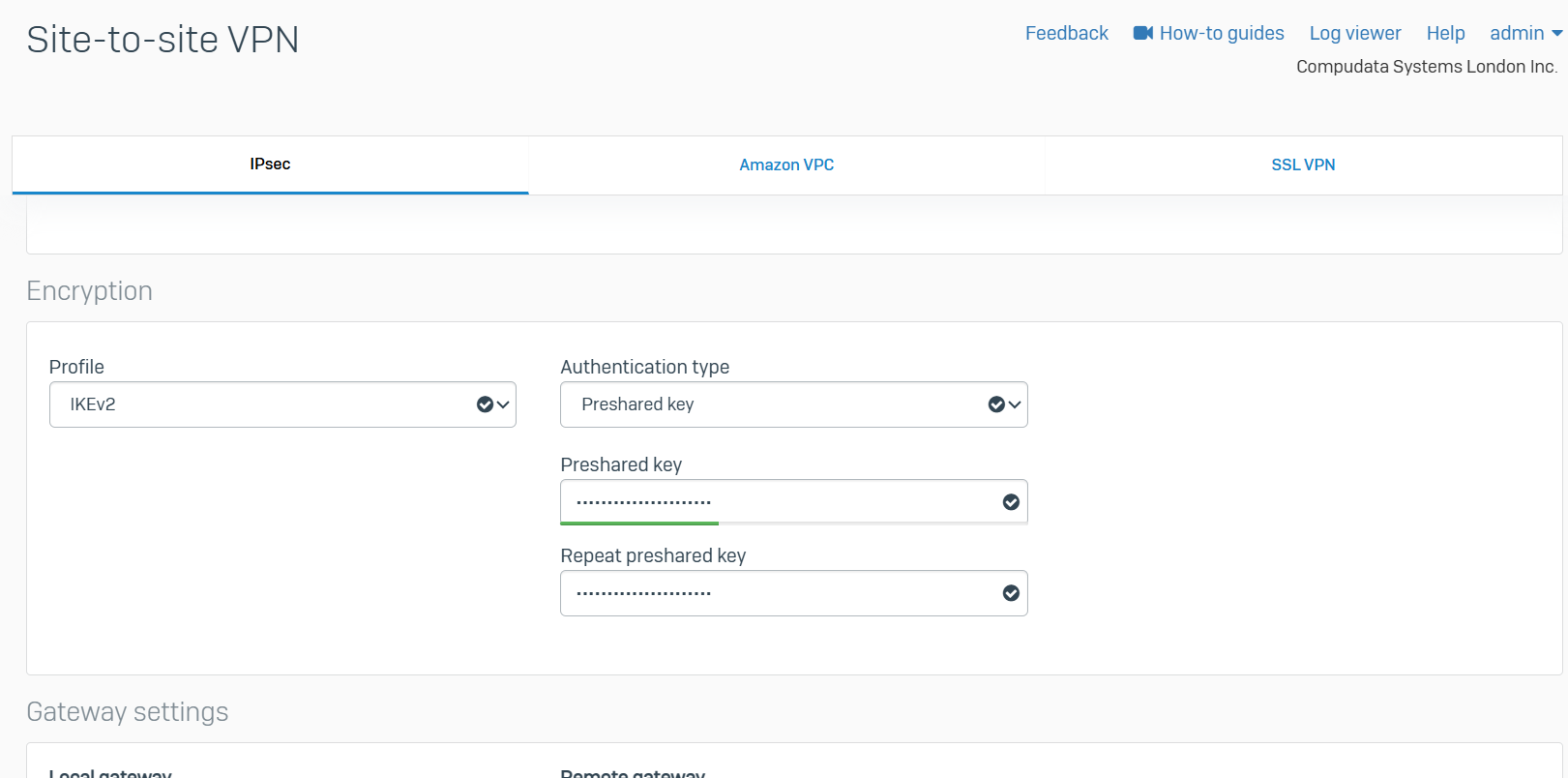


IPsec VPN Firewall Rules
Overview
- Sophos gives us the option to configure a firewall rule automatically when defining a new IPsec site-to-site VPN
- With firewall rules, you can allow or disallow traffic flow between zones and networks. You can implement policies and actions to enforce security controls and traffic prioritization
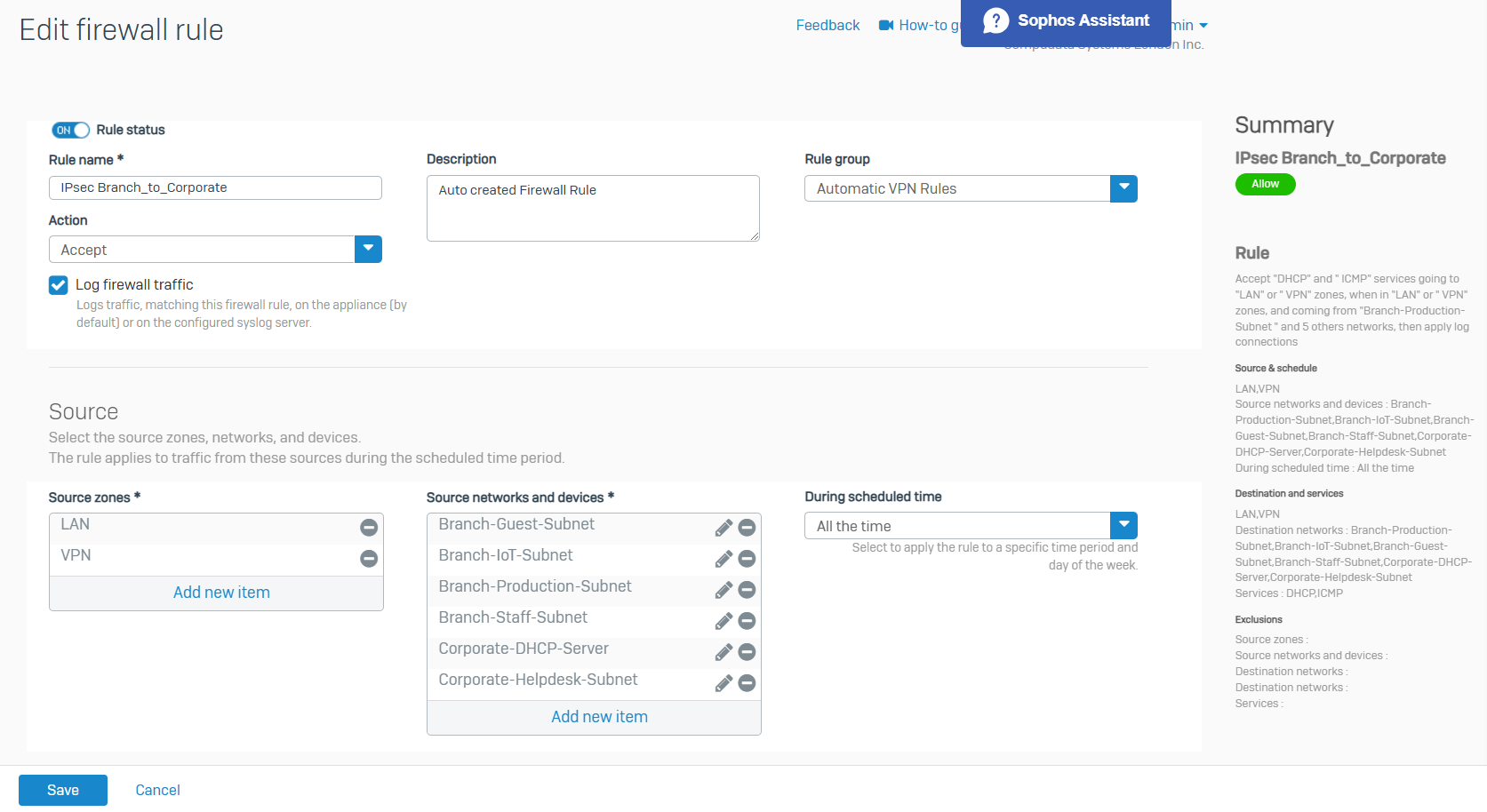
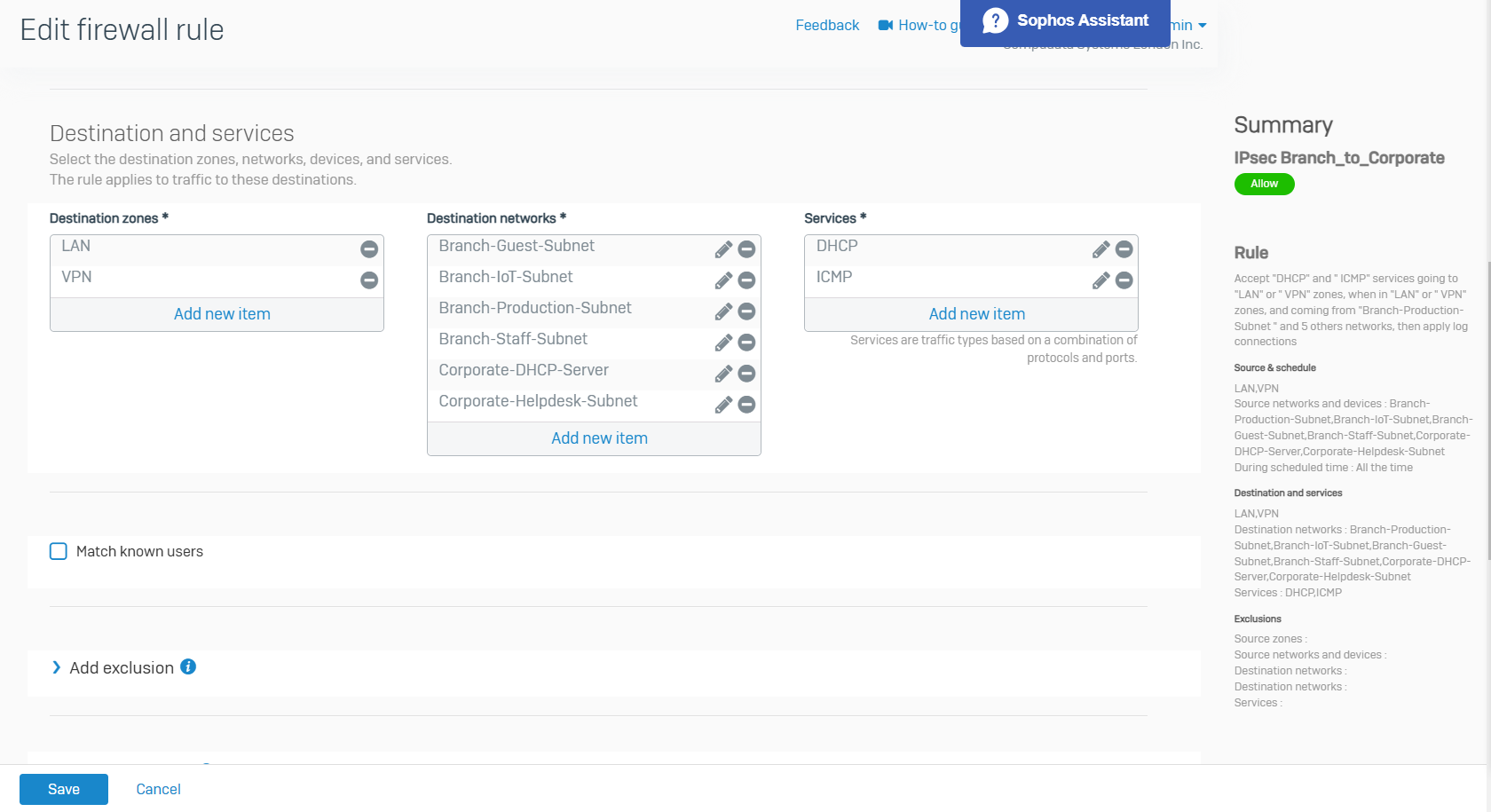
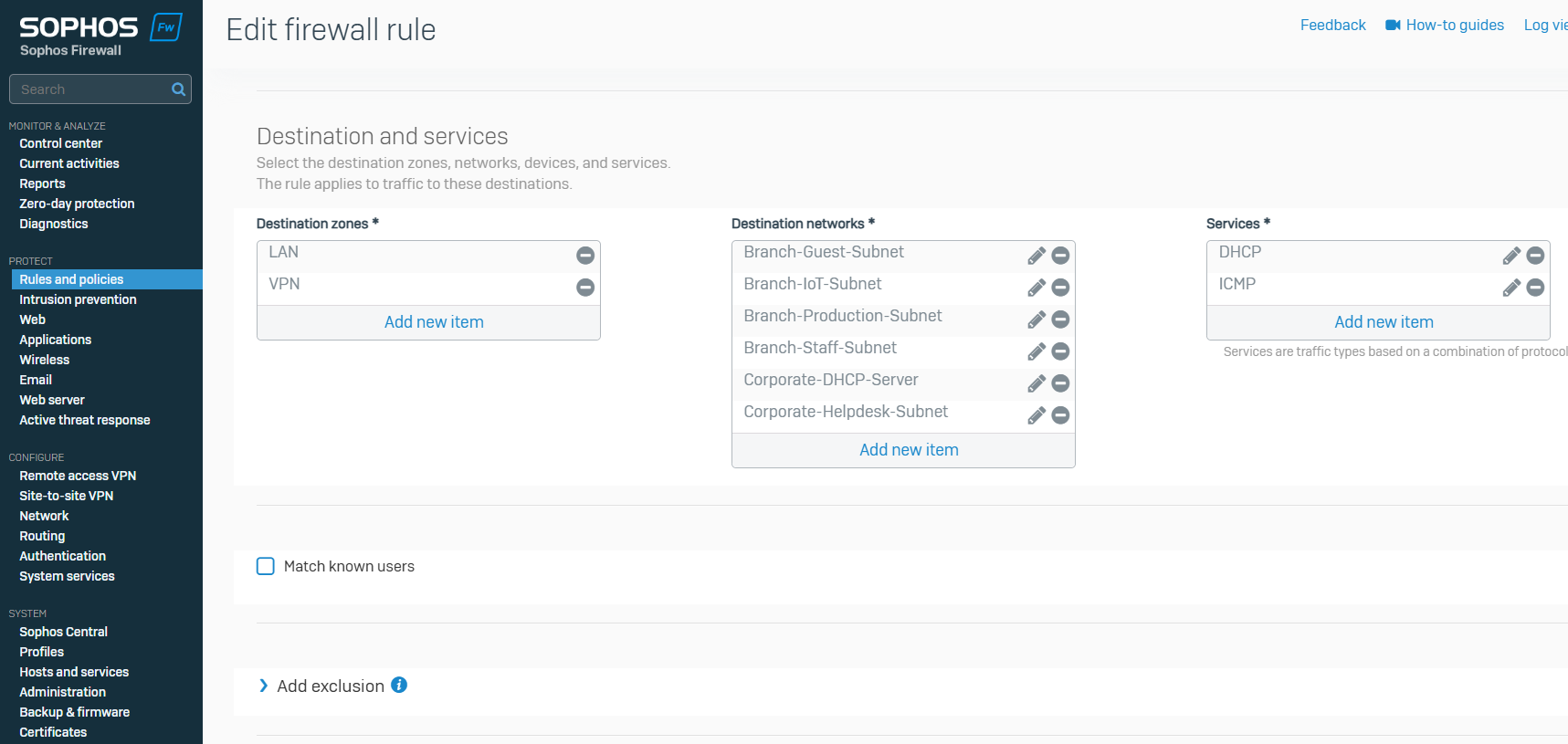
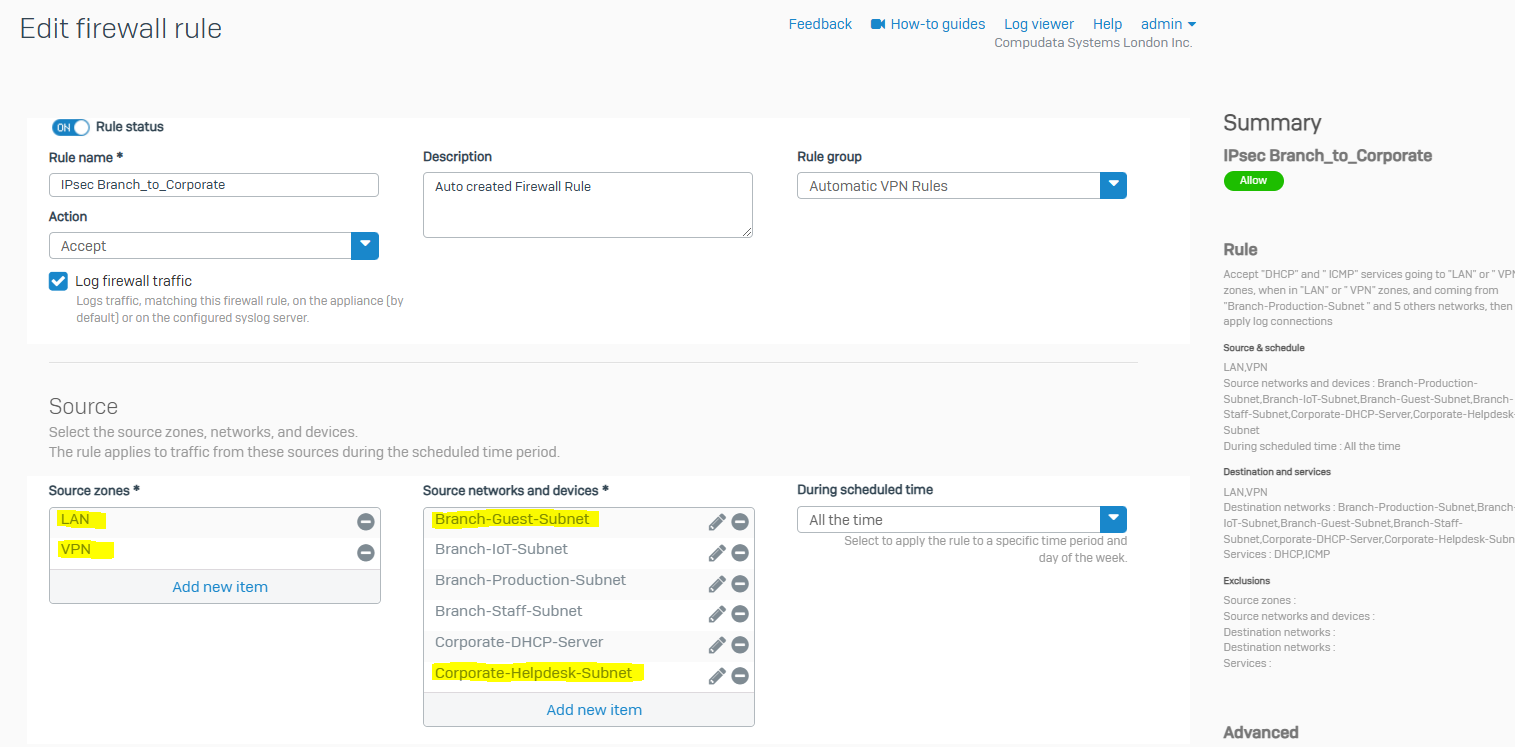
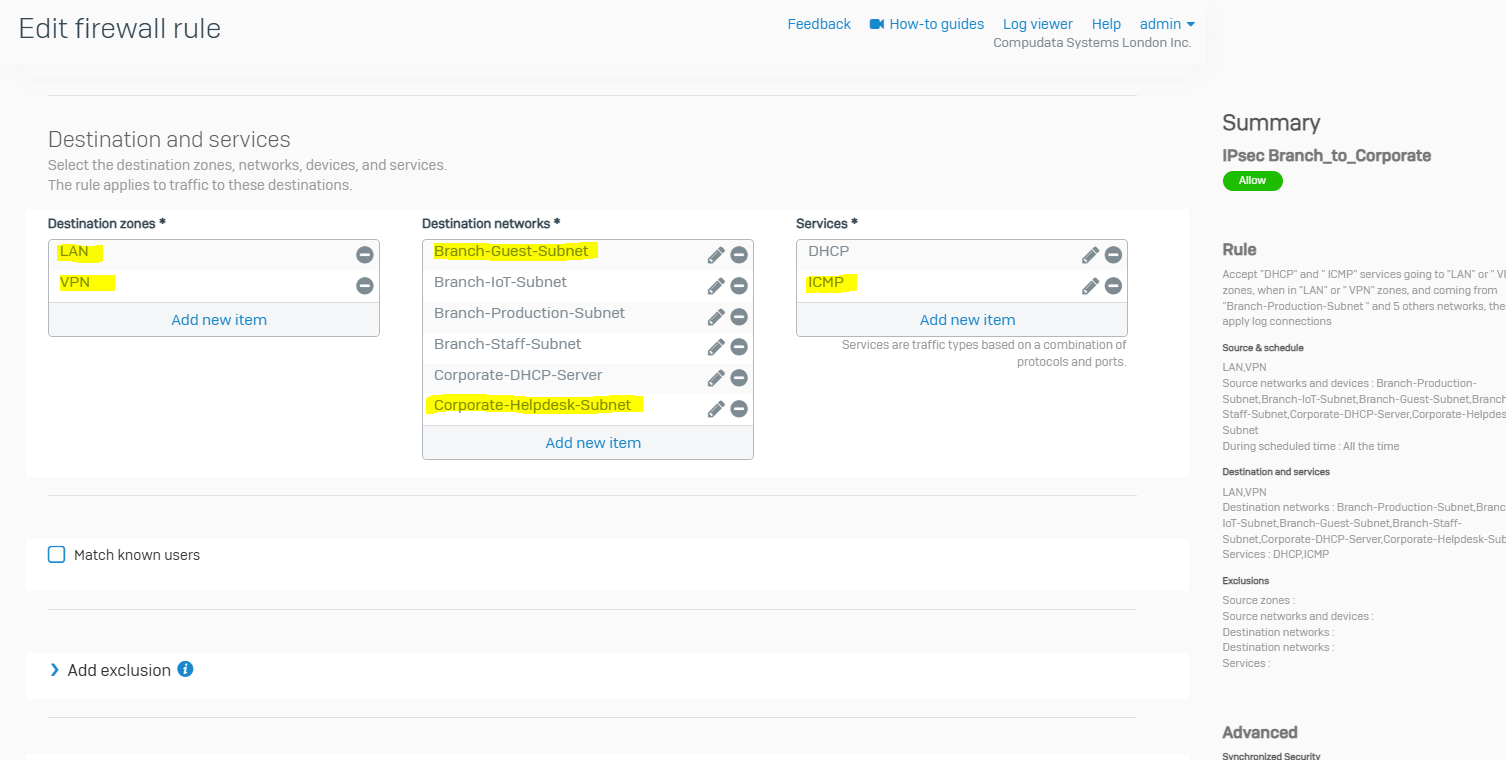
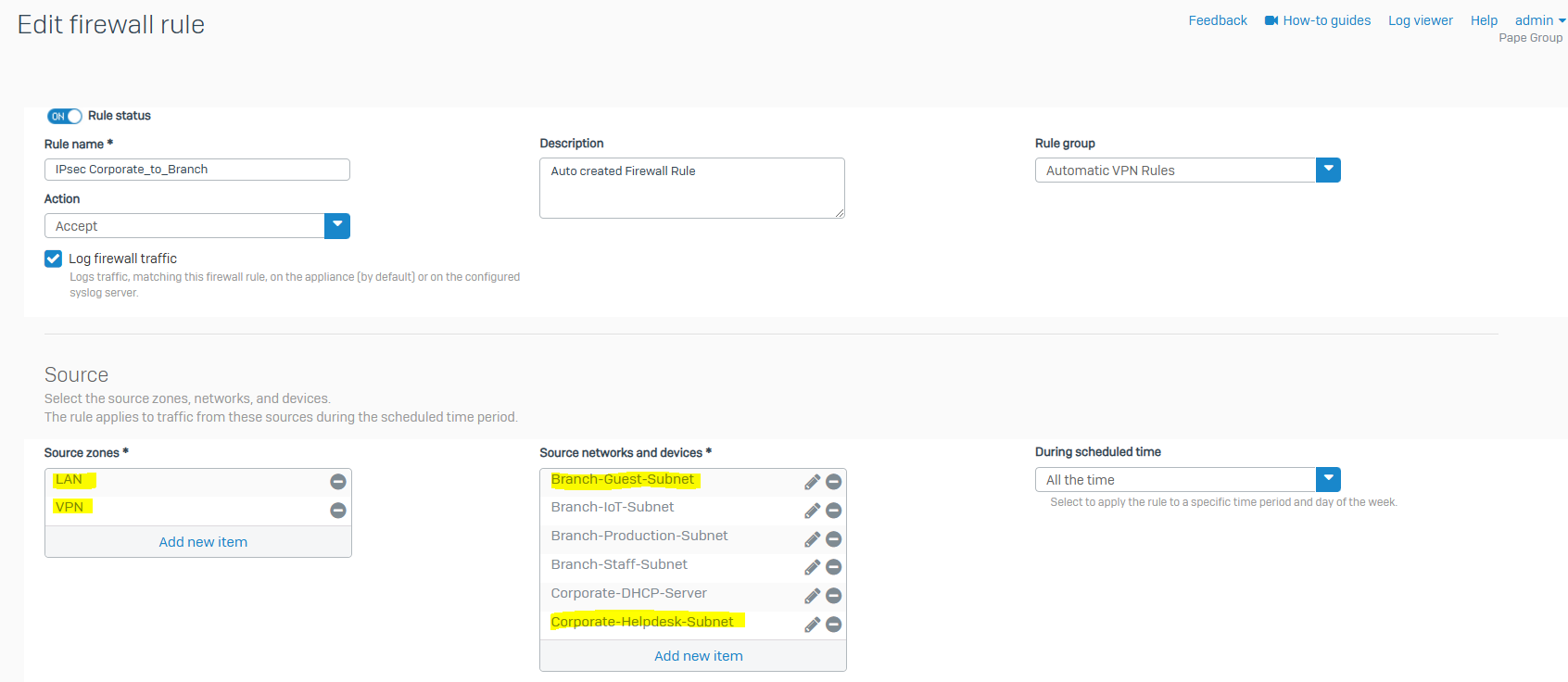
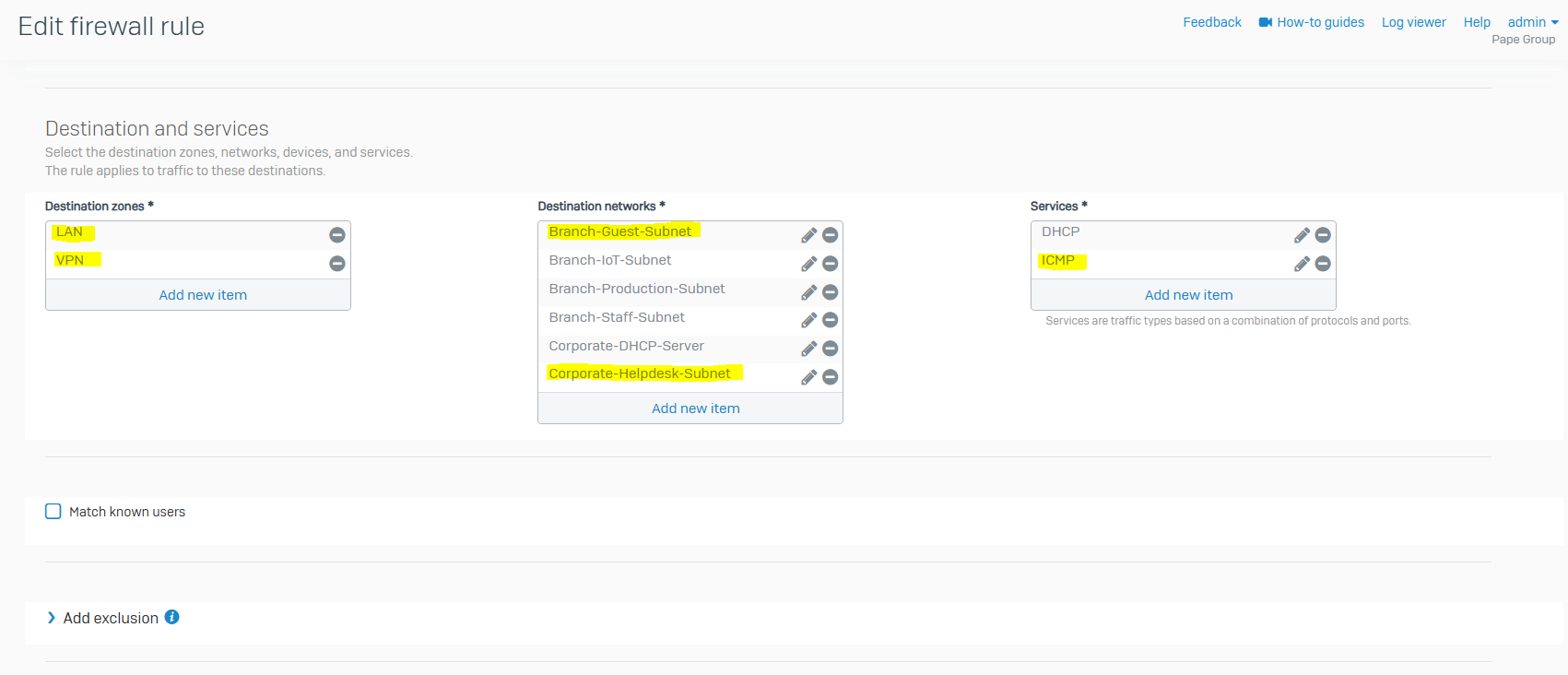
- In this demonstration, I will be tightening up the automatically created firewall rule by specifying the specific source and destination zones with the subnets that are allowed to traverse through the IPsec tunnel
- In a future lesson, I will go in depth with defining and explaining different types of firewall rules to improve the security skills
IPsec VPN Topology

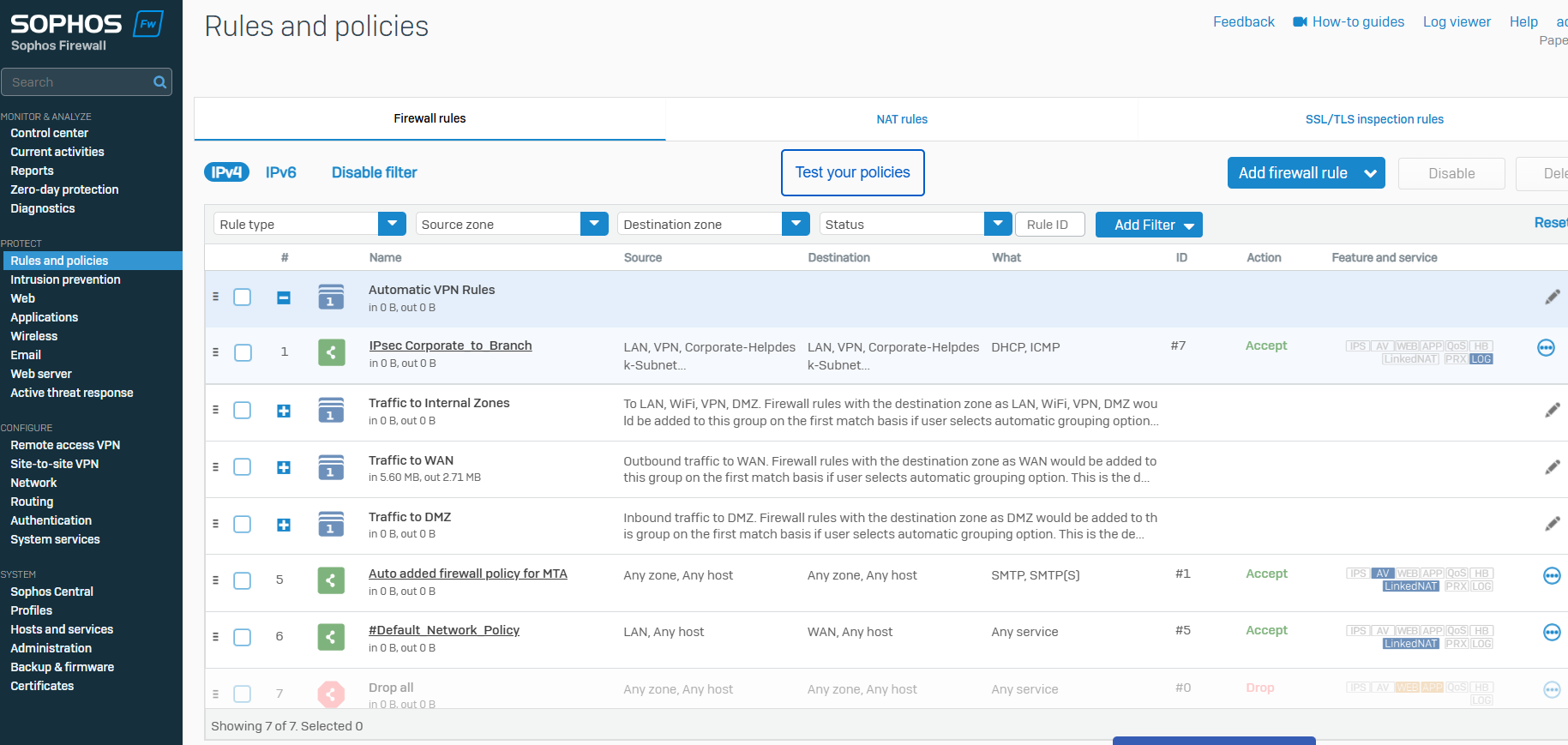
Branch IPsec VPN Firewall Rule
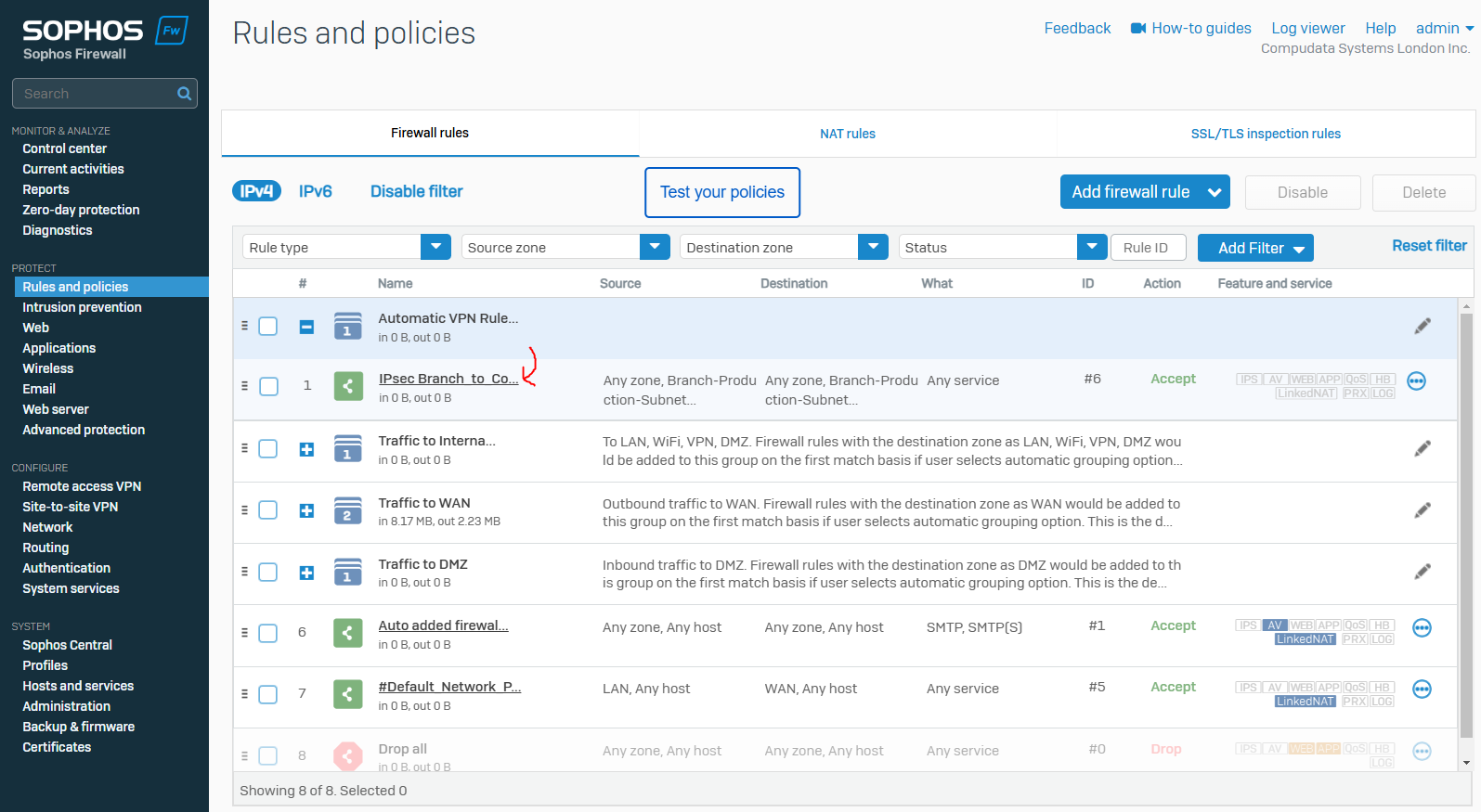
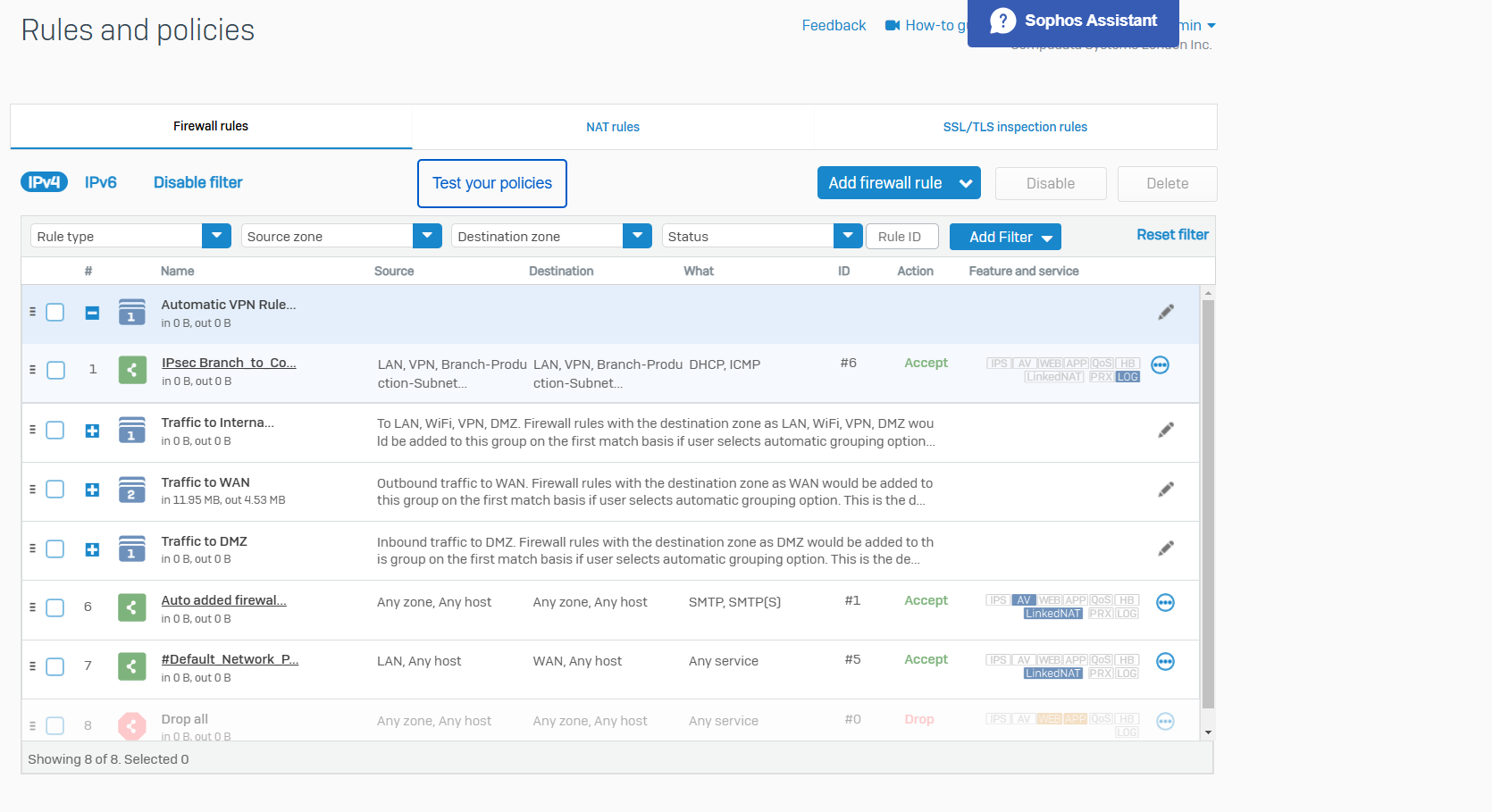
Corporate IPsec VPN Firewall Rule
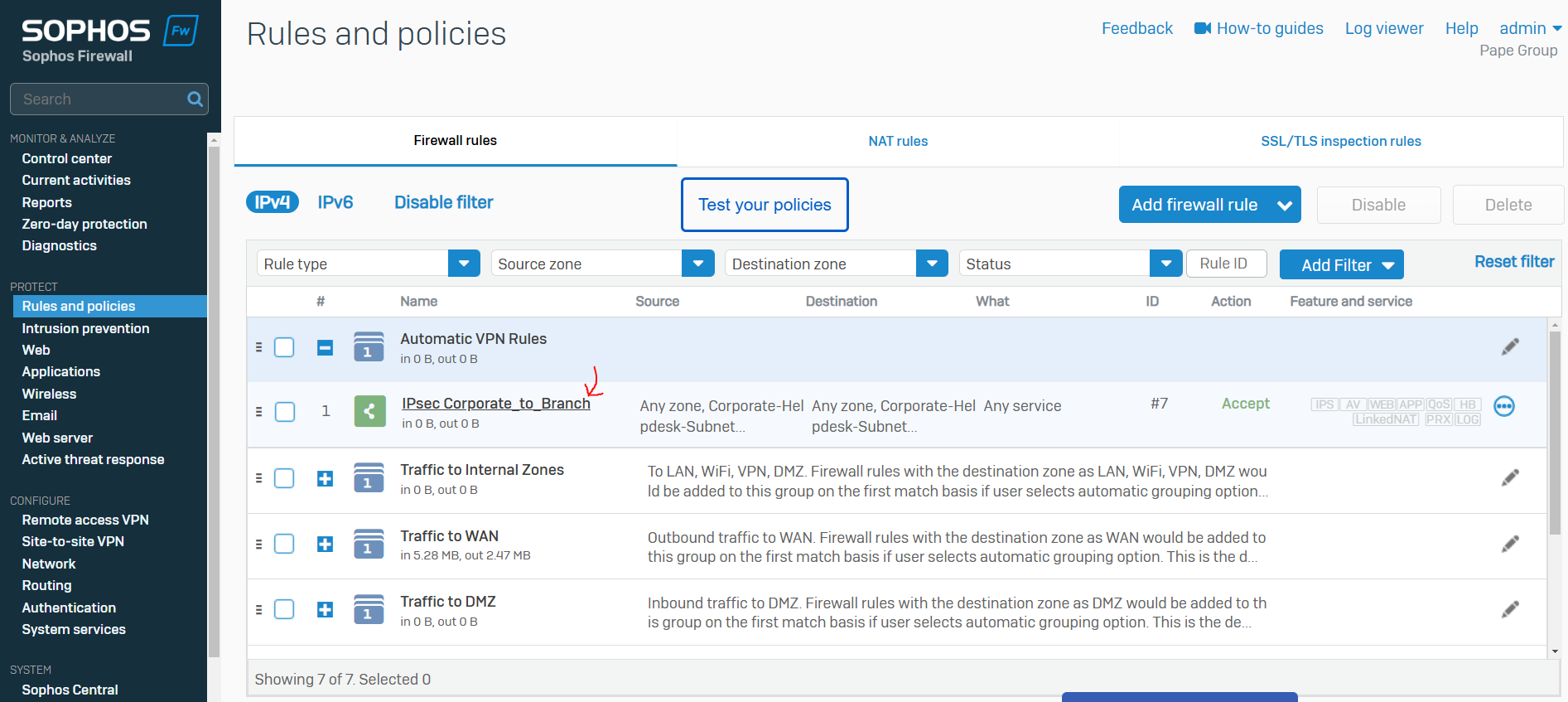

Device Access Administration
Overview
- You can control access to the management services of Sophos Firewall from custom and default zones using the local service ACL (Access Control List)
- Local services are management services specific to the internal functioning of Sophos Firewall, such as web admin and CLI consoles, and authentication services
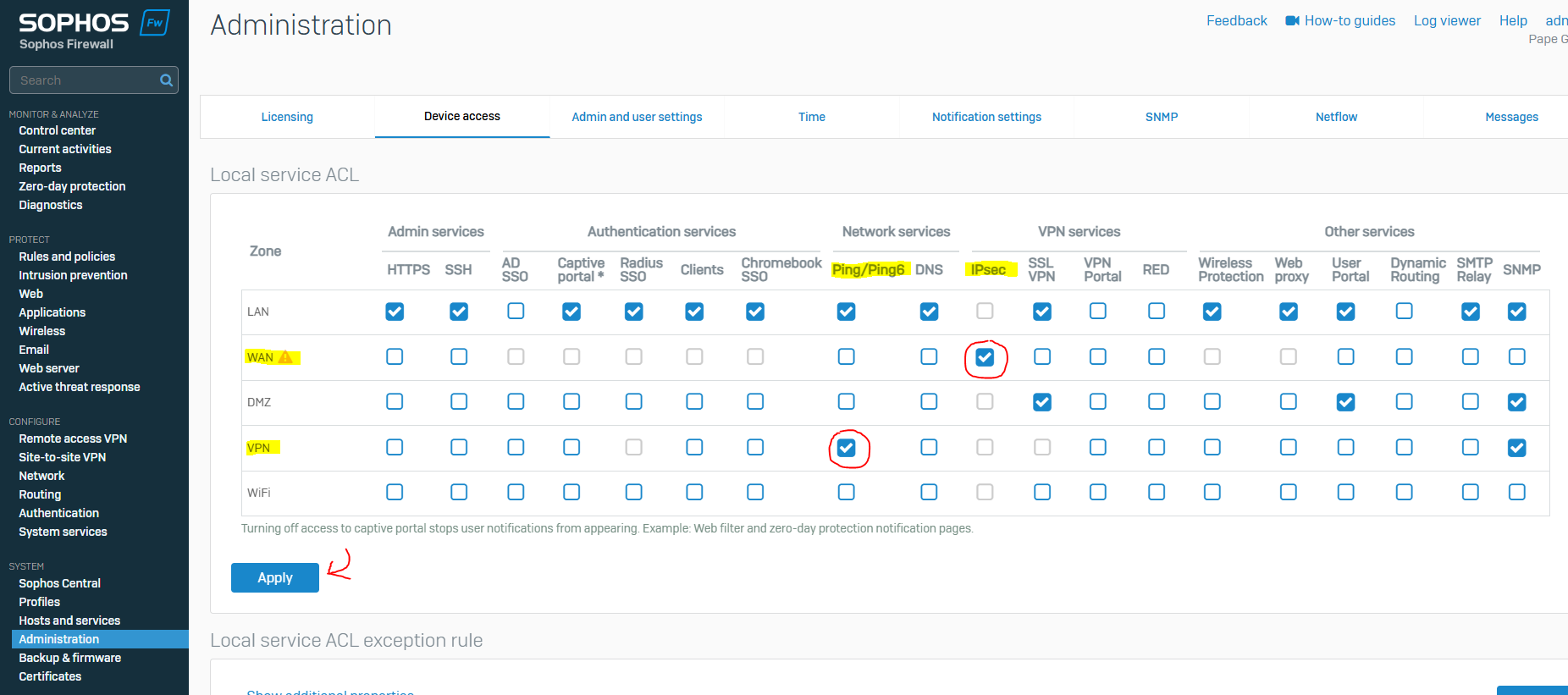
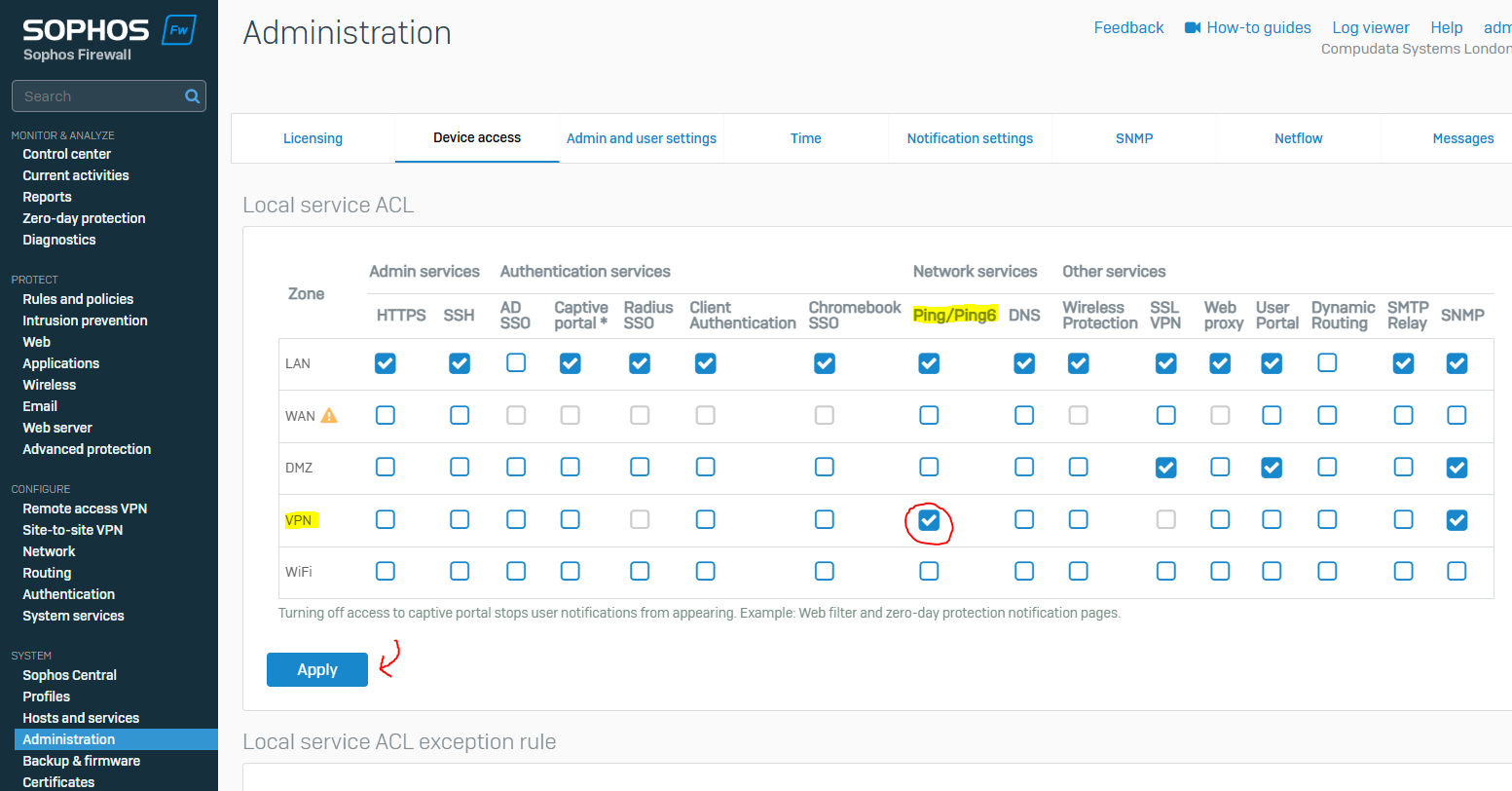
- In this demonstration, I will be allowing the 'IPsec' service to run in the WAN zone as IPsec traffic will have to be routed through the WAN infrastructure (overlay) in order for Site-to-Site VPNs to work
- In this demonstration, I will also be enabling the 'ping' service from the VPN zone to test ping reachability between internal subnets via the IPsec tunnel
- It's important to note that some models of Sophos firewalls do not have a 'IPsec' service listed within the local service ACL. In these situations, you would only need to configure a dedicated VPN policy, whether it be policy-based or route-based VPN
IPsec VPN Topology

Corporate Site - Device Access Administration
Branch Site - Device Access Administration
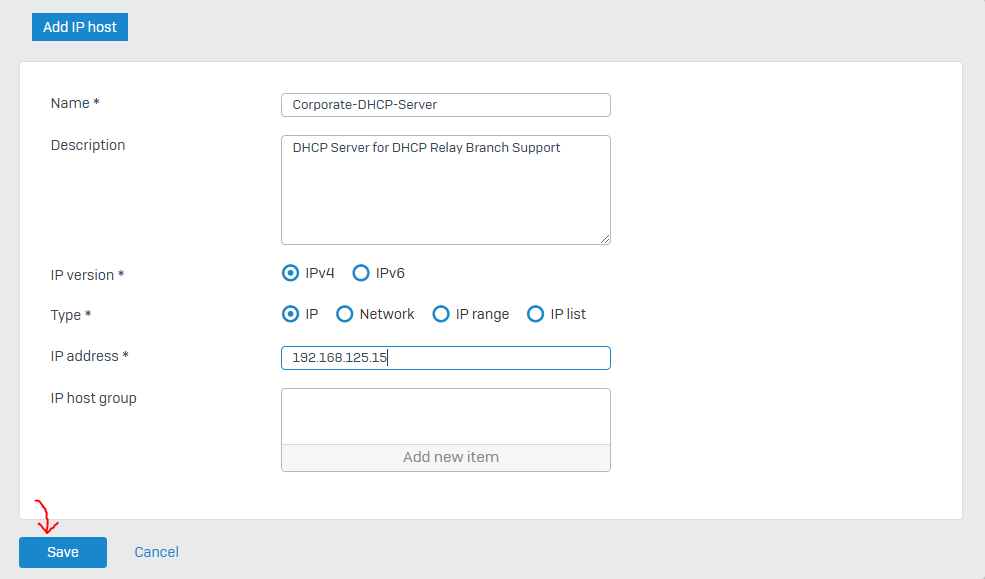
IPsec Routes for DHCP Relay Traffic (via Policy-based IPsec VPN)
Overview
- Sophos Firewall creates IPsec routes automatically when policy-based IPsec tunnels are established
- However, you must add IPsec routes for some traffic (such as DHCP relay) manually
- DHCP relay has already been defined on the branch Sophos Firewall previously for all VLANs: DHCP Relay
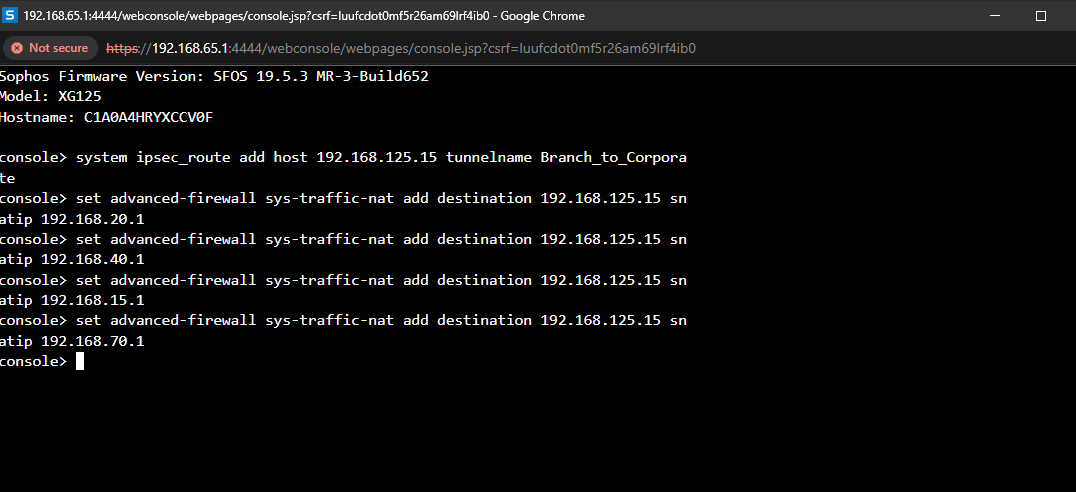
- In this demonstration from the device console, I will define manual IPsec routes on the branch Sophos Firewall for system-generated traffic to the DHCP Windows Server at the Corporate site office. I will then apply source NAT on the system generated traffic to translate the internal source IP address (DHCP Relay interface) at the branch site to the destination IP address (DHCP server at the Corporate site)
IPsec Route Use Cases (via Policy-based IPsec Tunnels)
- You want to route system generated traffic, such as authentication requests or DHCP relay, from a remote office to the head office through an IPsec connection
- You can't add some subnets to the IPsec connection for internal reasons, however you want their traffic to flow through the connection
IPsec VPN Topology

Branch Site - IPsec Routes



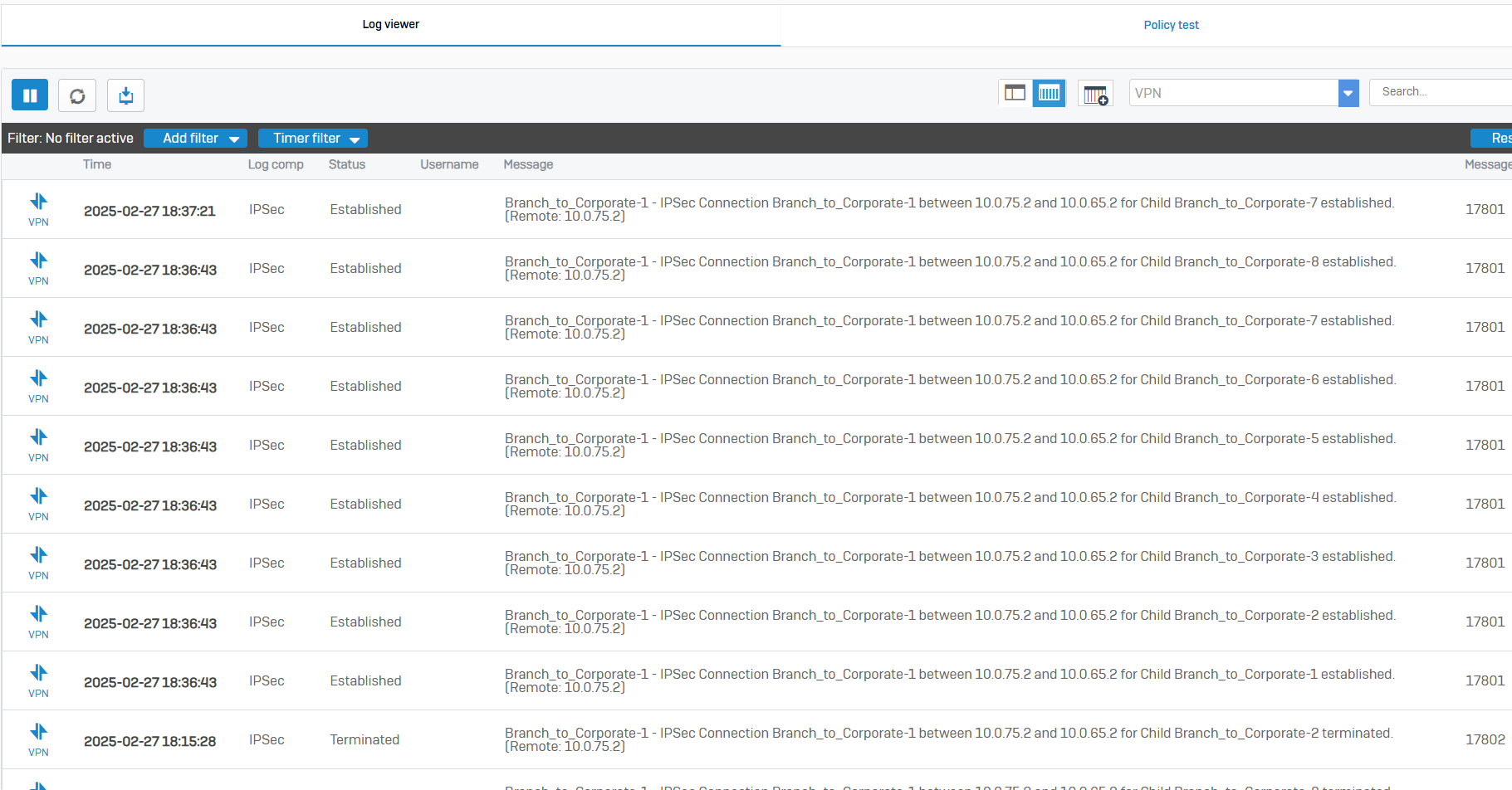
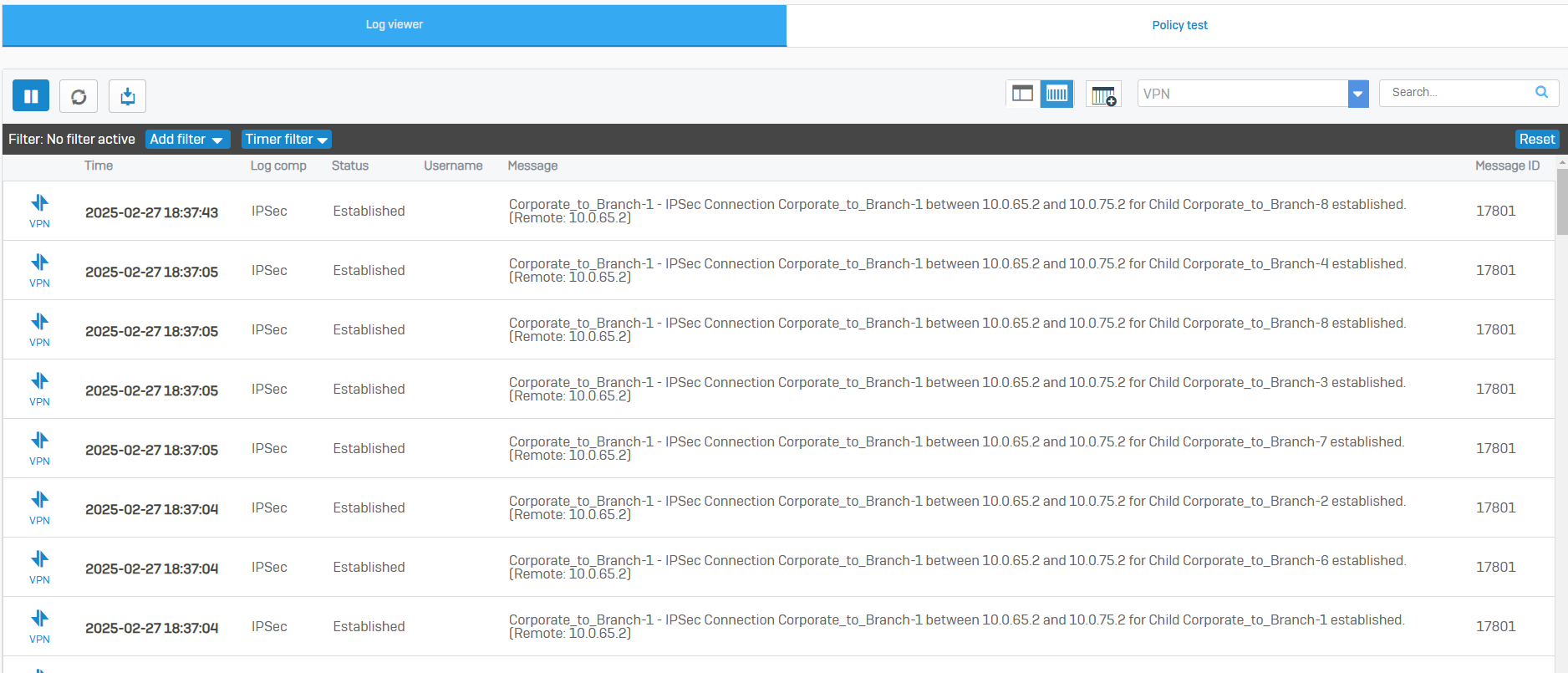
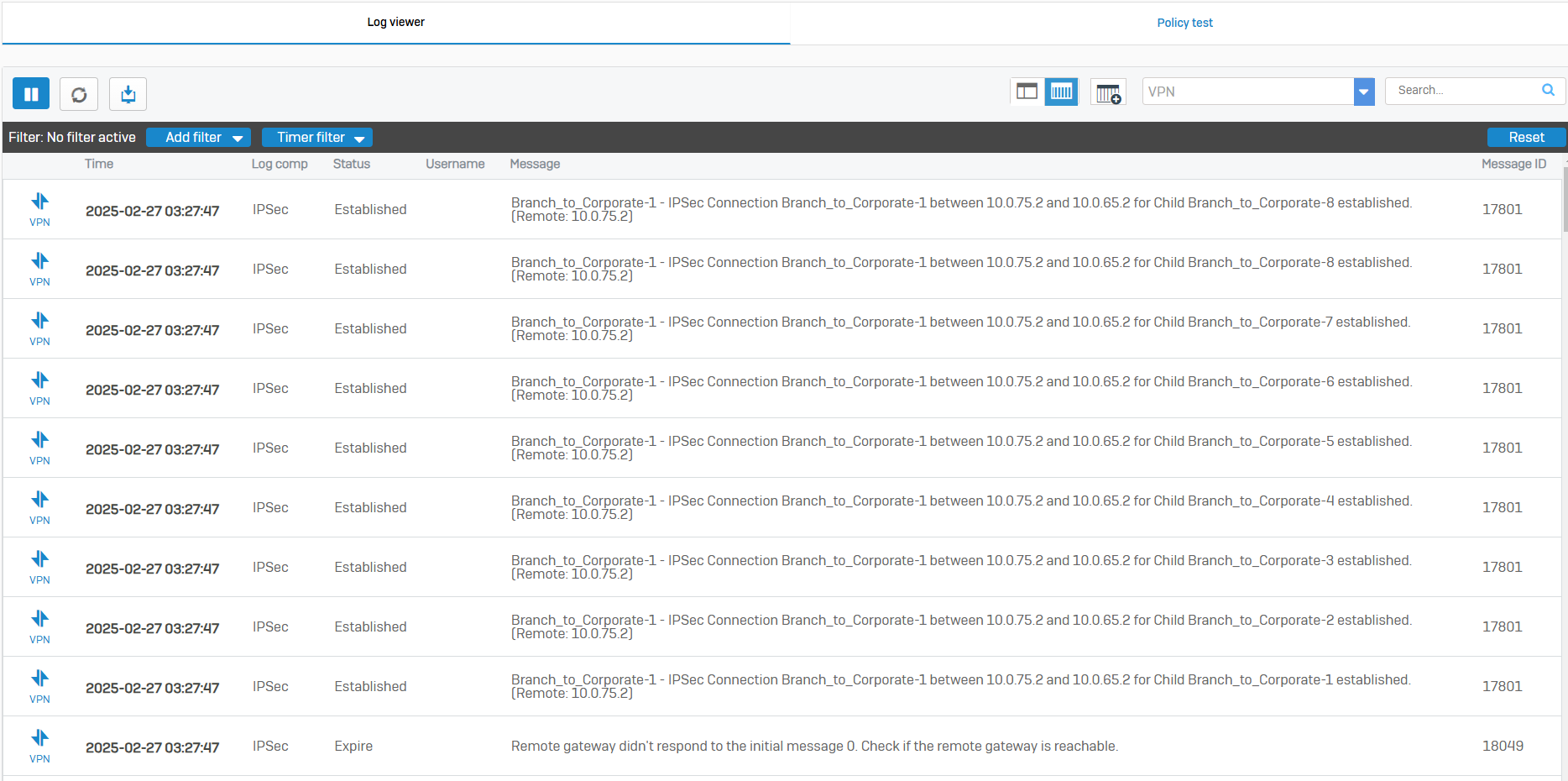
IPsec VPN Verification & Testing
Overview
- At this point, firewall rules, IPsec tunnels, and IPsec routes have already been configured thus far
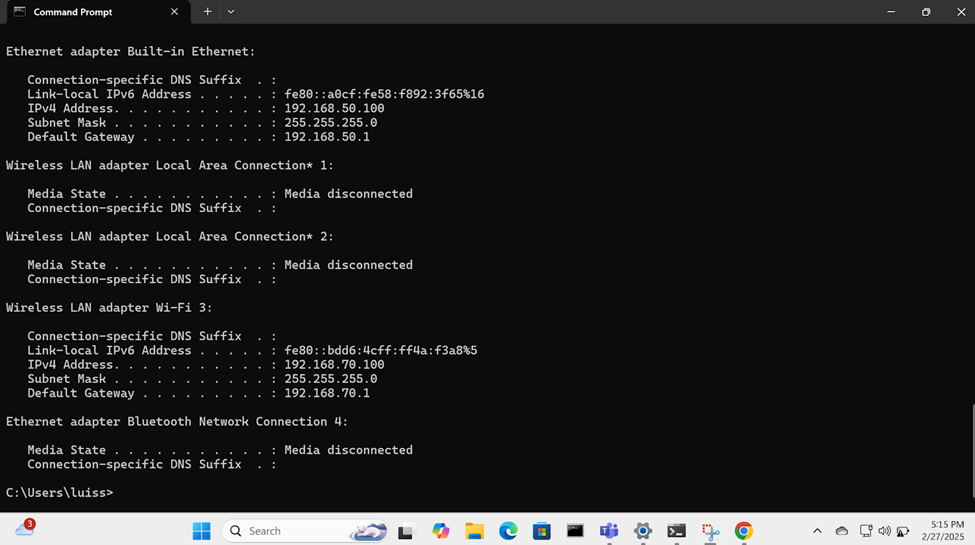
- In this demonstration, I will verify that DHCP relay is working as intended so DHCP clients at the Branch site can acquire an IP address from the DHCP server located at the Corporate site via the IPsec tunnel
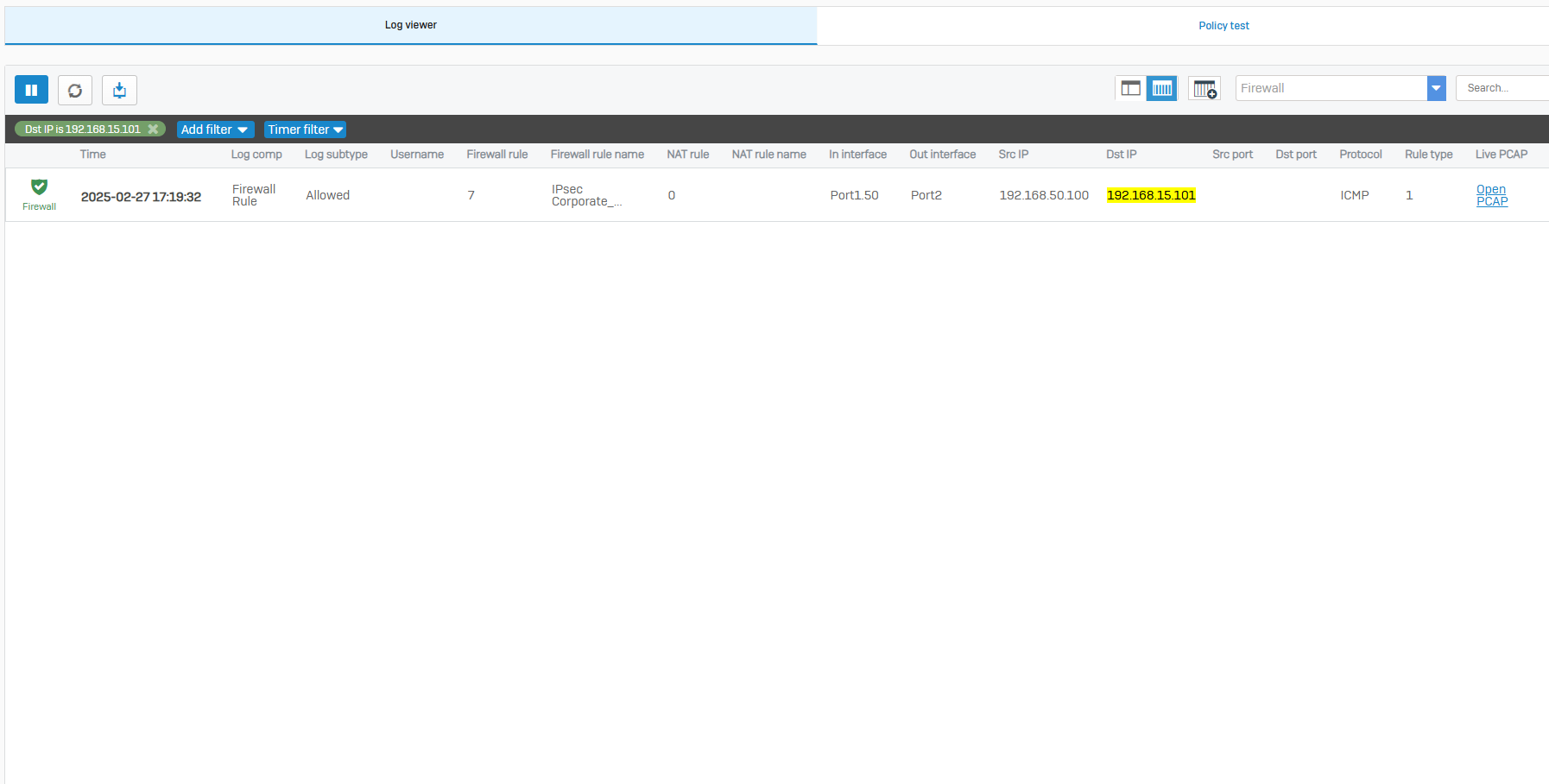
- In this demonstration, I will ensure the Helpdesk technicians on the VLAN50 network at the Corporate site are able to ping the DHCP client devices located at the Branch site via the IPsec tunnel
IPsec VPN Topology

DHCP Relay to Windows Server
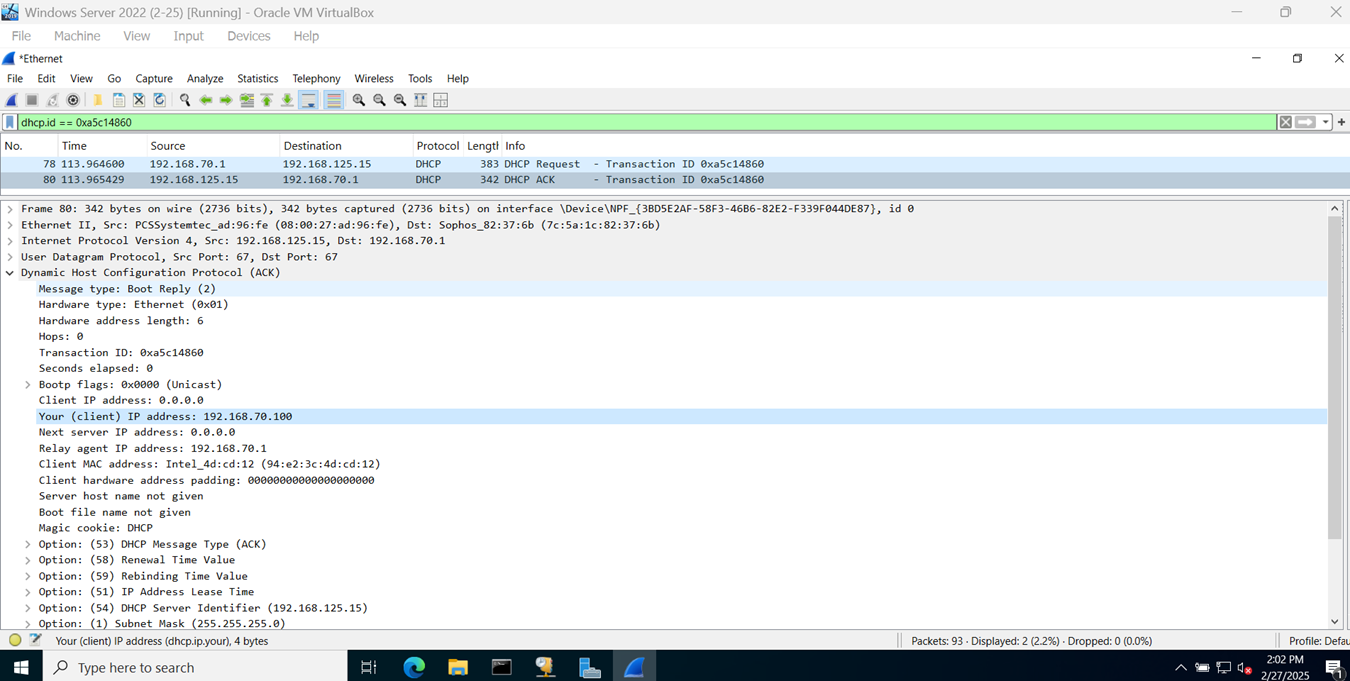





Helpdesk VLAN 50 ICMP


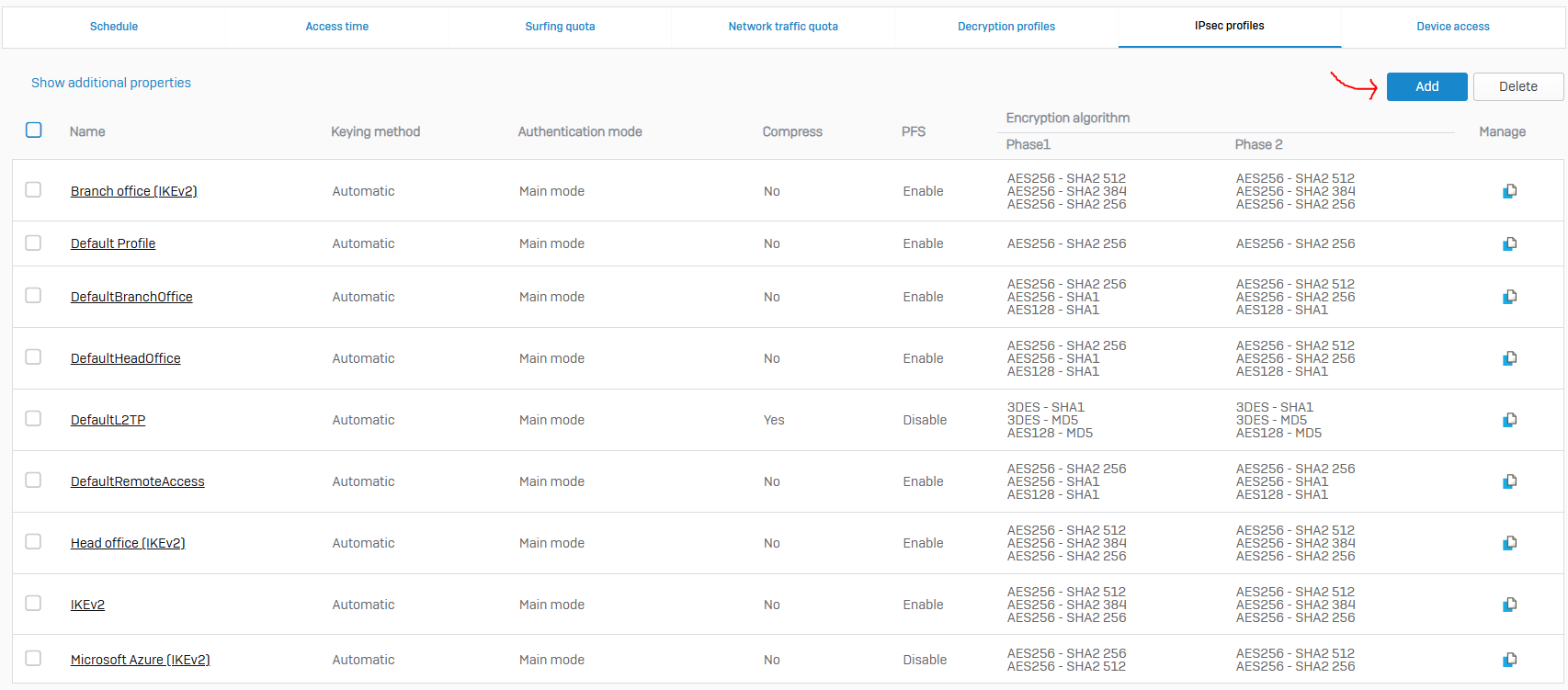
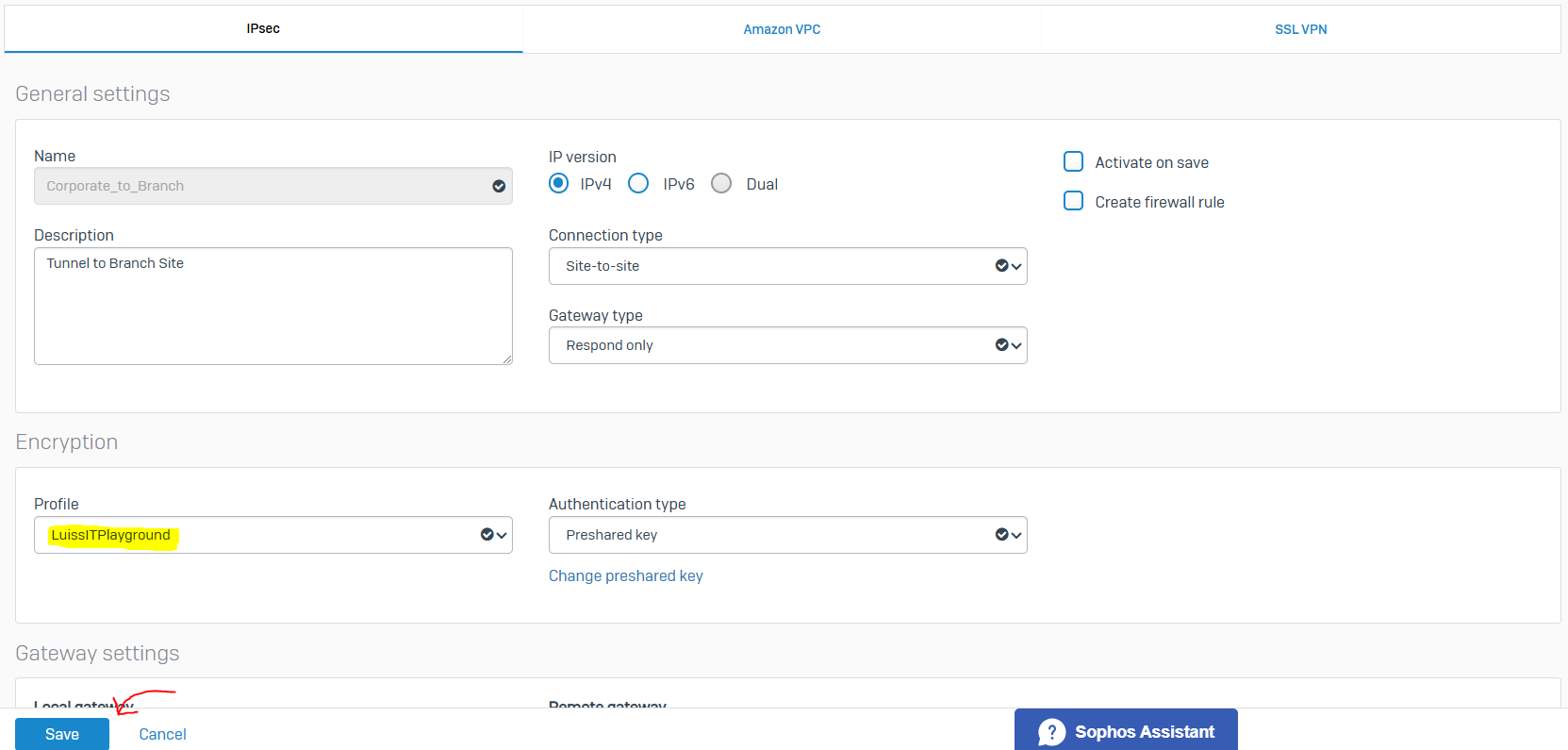
IPsec VPN Custom Profiles
Overview
- IPsec profiles specify the encryption and authentication algorithms and key exchange mechanisms for policy-based and route-based IPsec connections
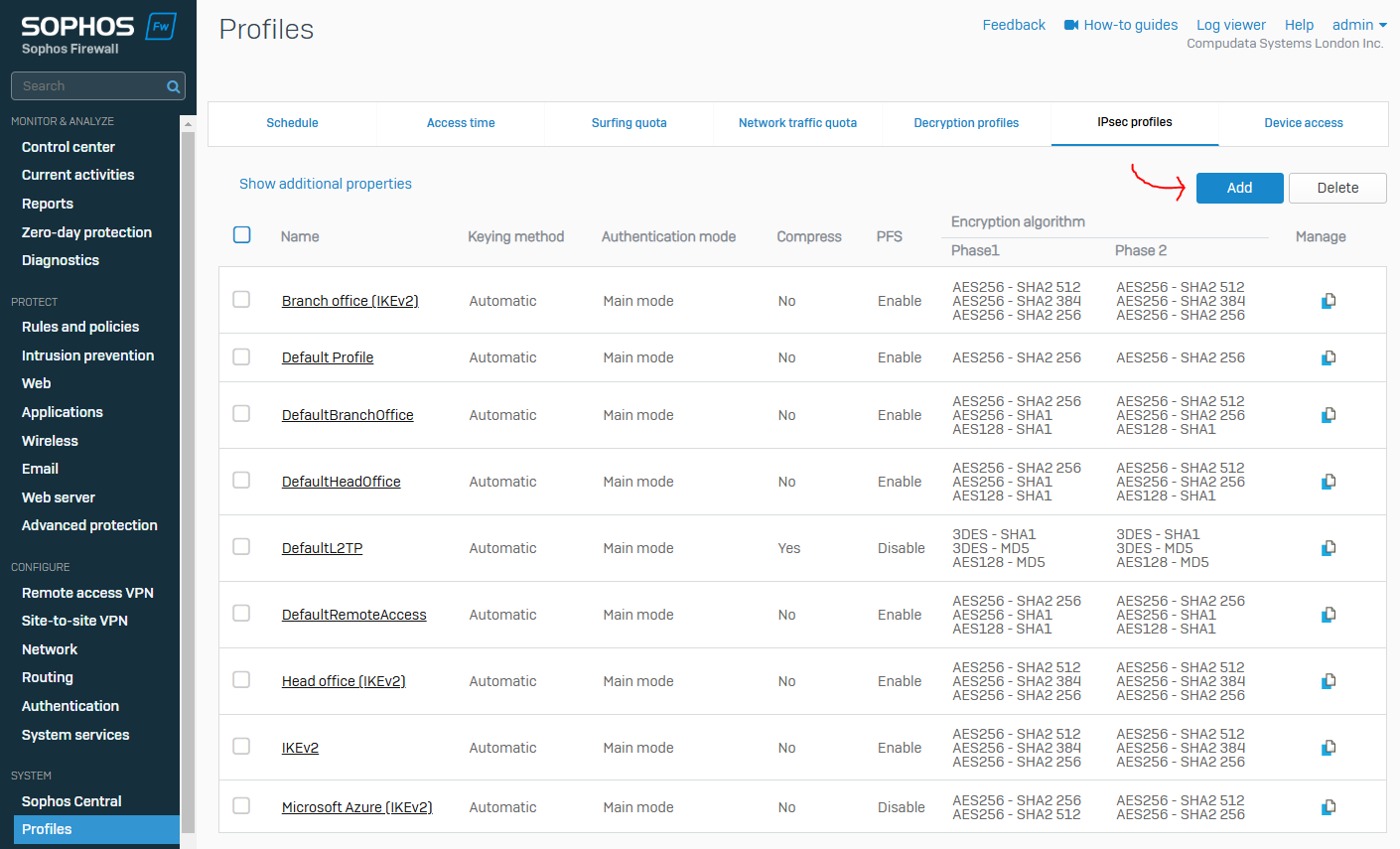
- Sophos defines several default profiles to support common VPN deployment scenarios and the ability to clone profiles if needed
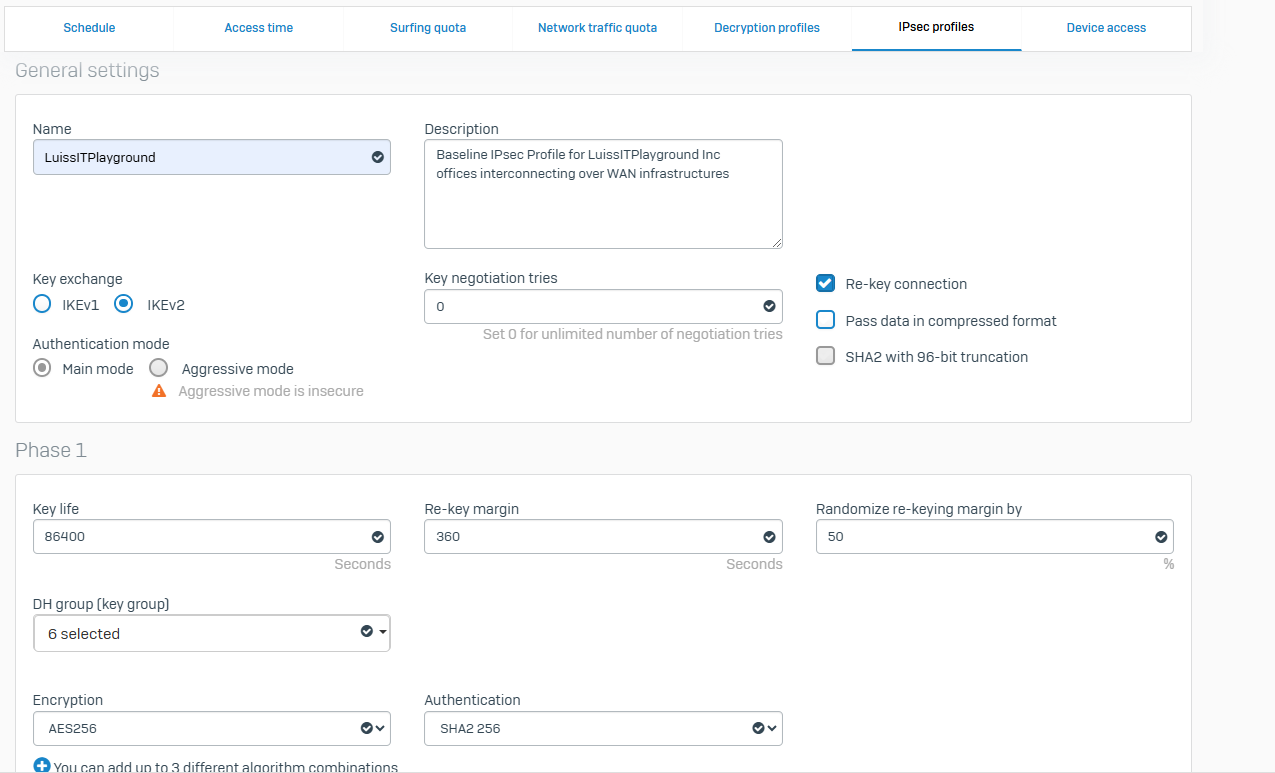
- With IPsec custom profiles, you define the phase 1 and phase 2 security parameters, and assign a profile to IPsec connections
- To configure IPsec profiles, go to 'Profiles >> IPsec profiles' from the web admin GUI
- Sophos Firewall establishes IPsec connections based on matching IPsec profiles configured at the connection's local and remote ends
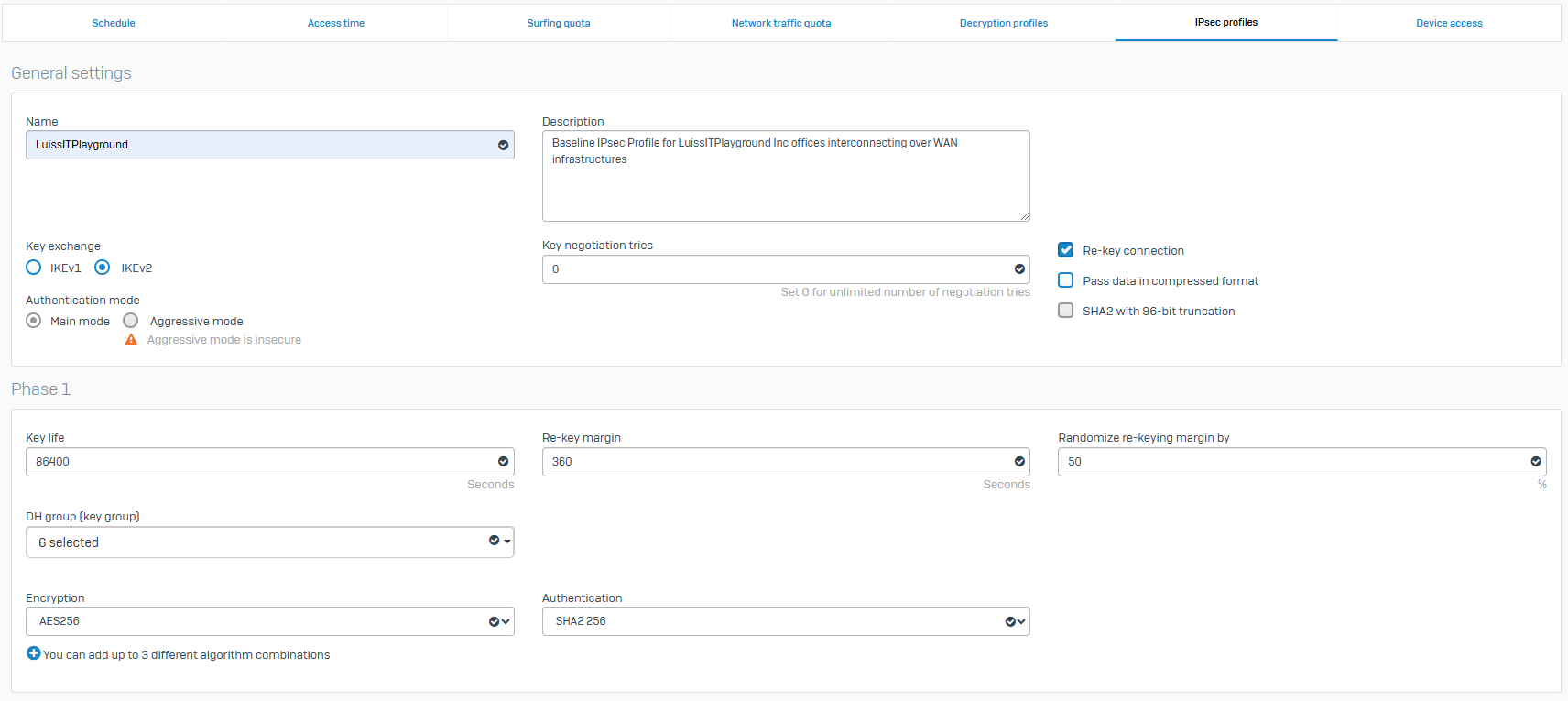
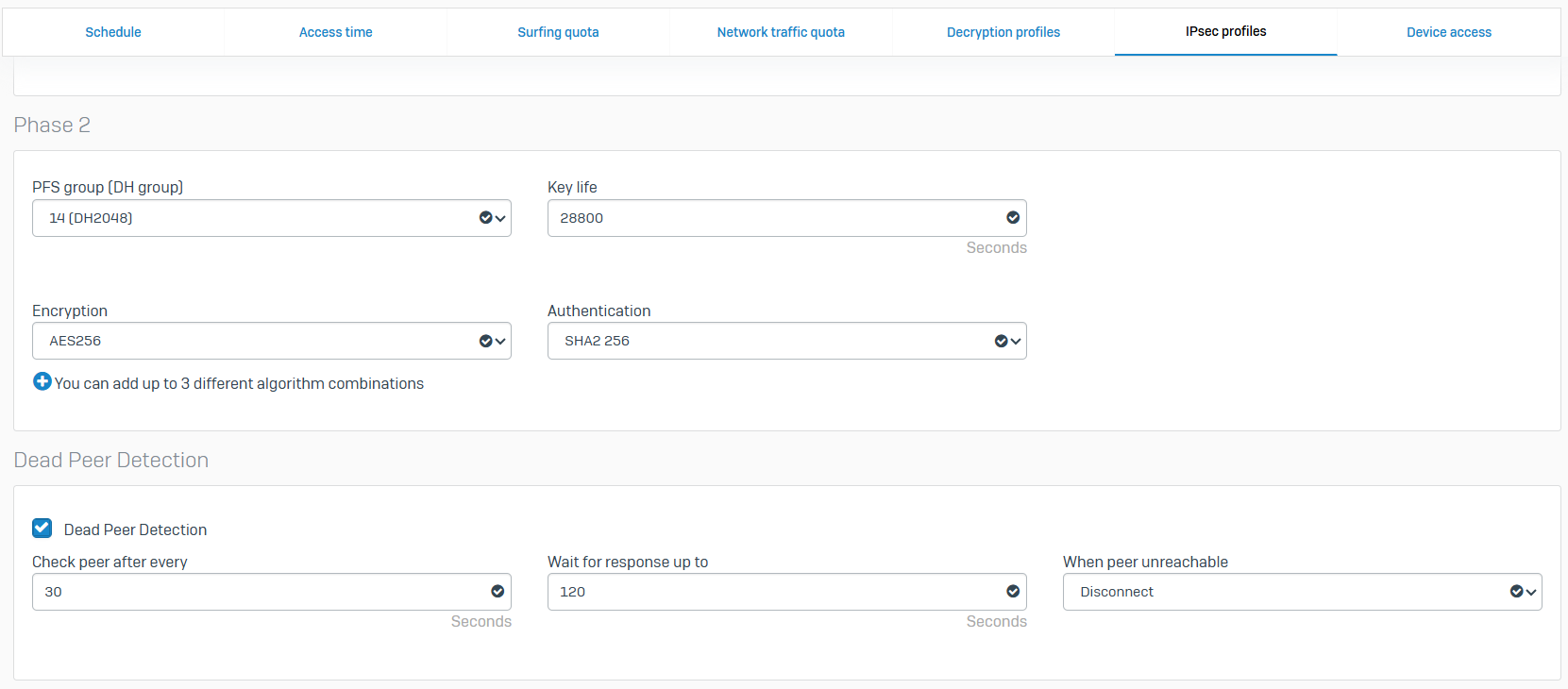
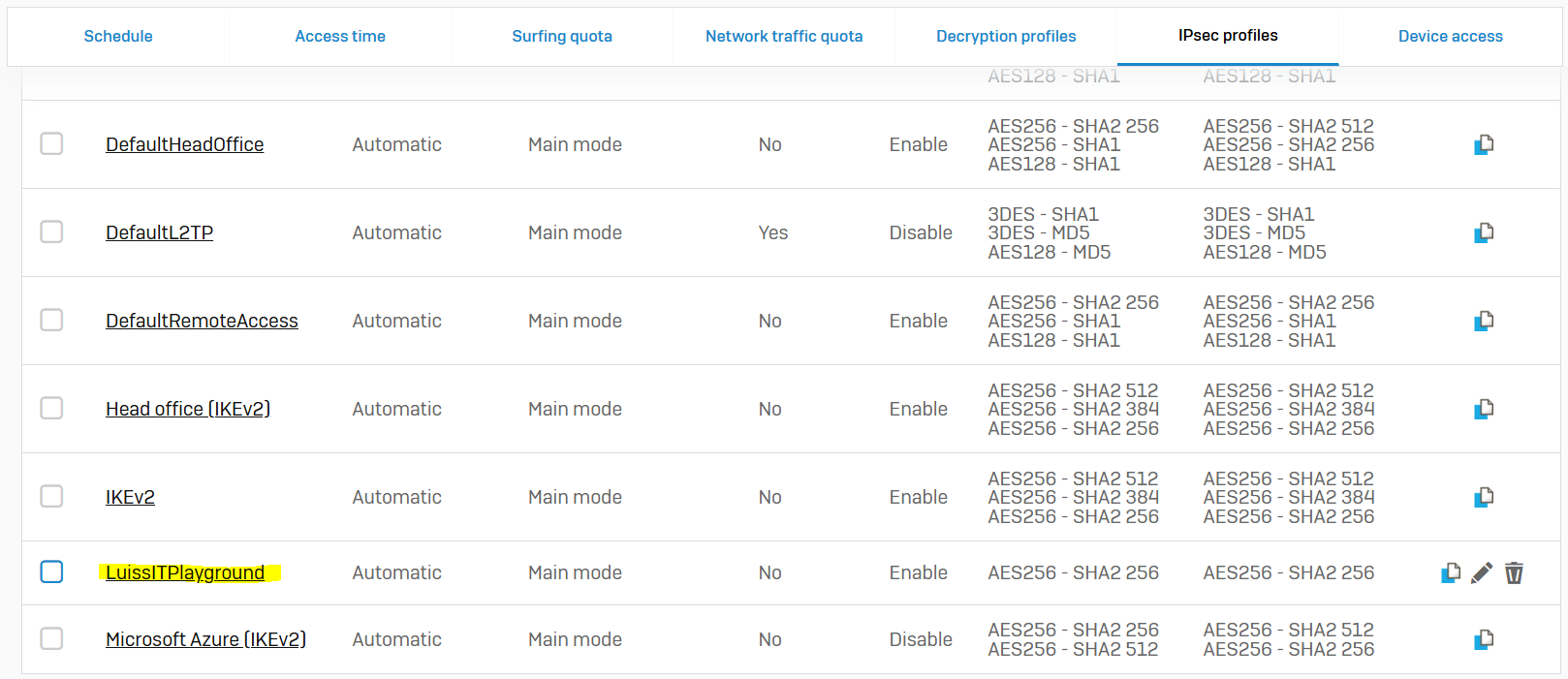
- In this demonstration, I will define a custom IPsec profile by specifying the phase 1 and phase 2 IKE parameters to establish an IPsec tunnel between the firewalls located in the Corporate and Branch LANs referenced in my Lab Topology
IPsec VPN Topology

Branch Site Custom IPsec Profile
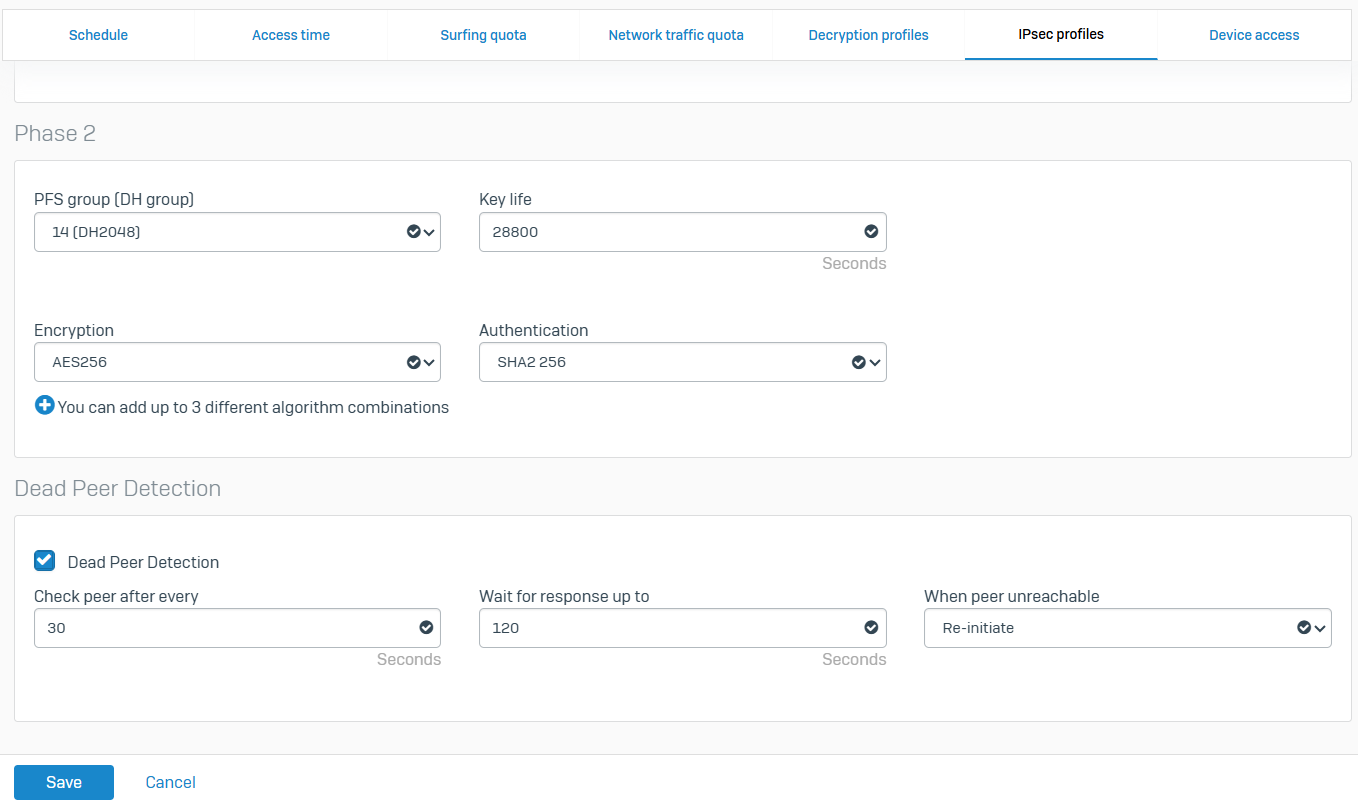
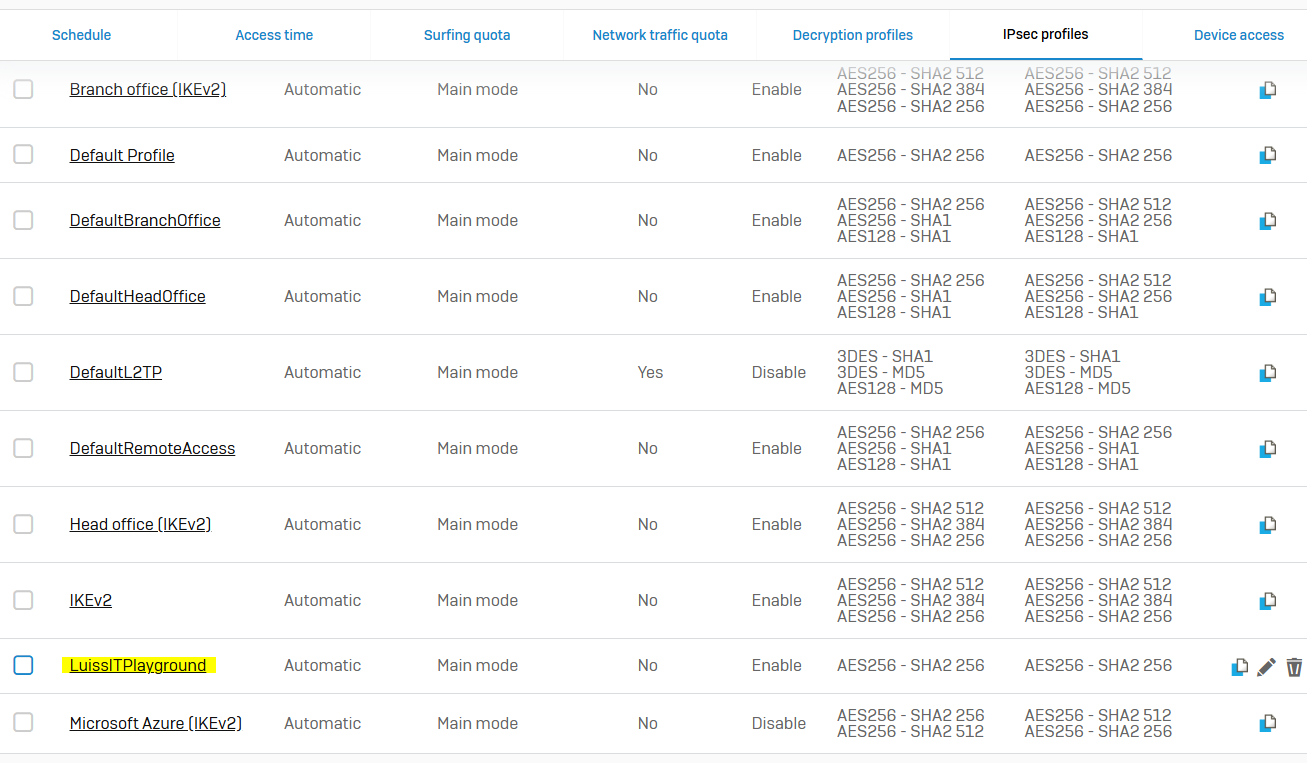
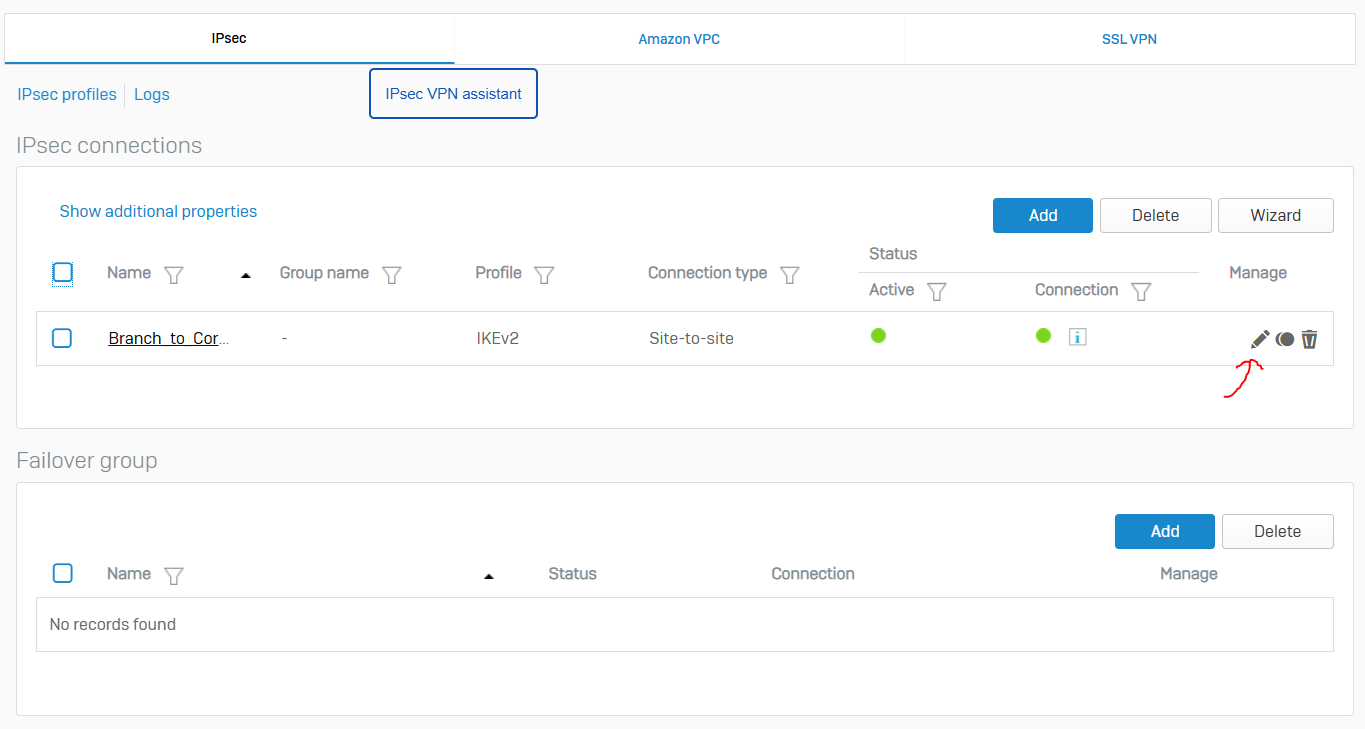
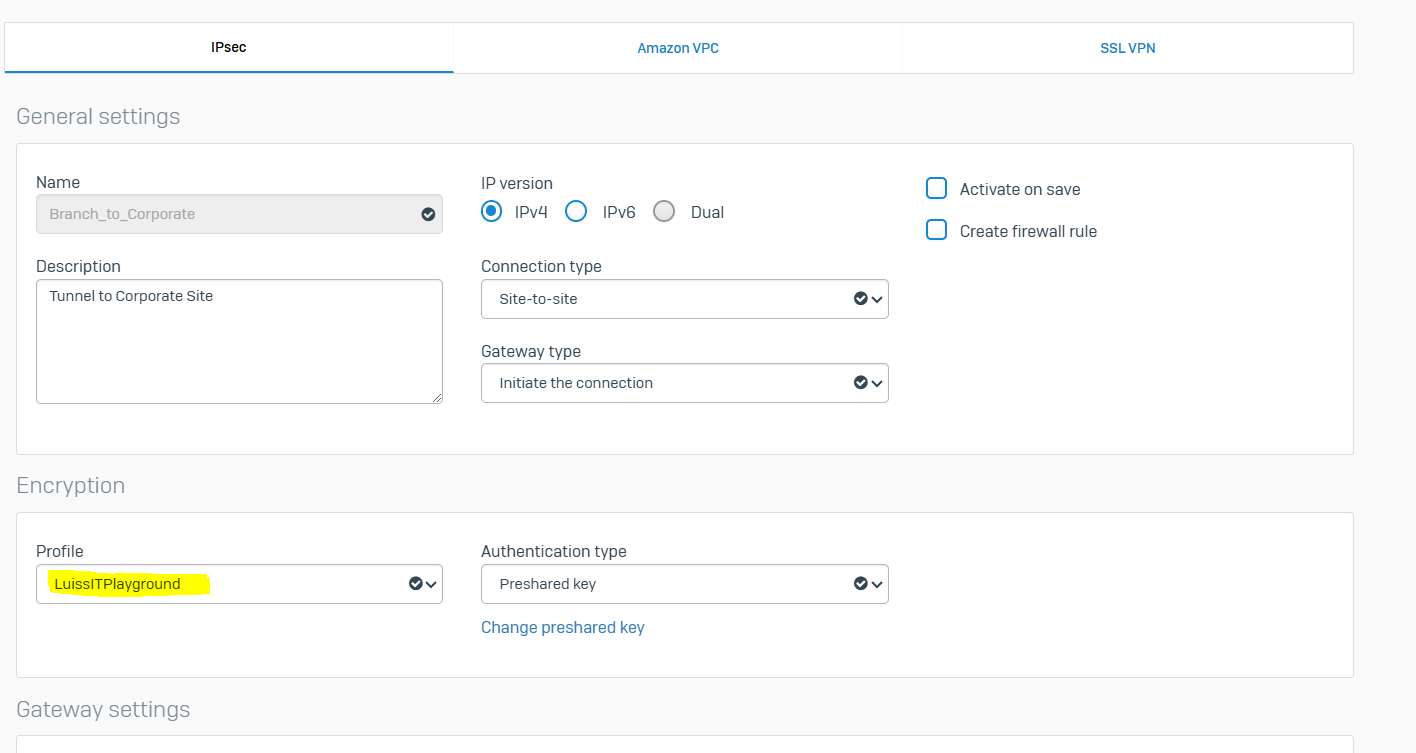
Corporate Site Custom IPsec Profile